One of the most popular modern building materials - light blocks (picked ceramic, foam concrete, gas-silicate). The walls of them are built with a ventilated air layer or without it. We tell what option is correct.
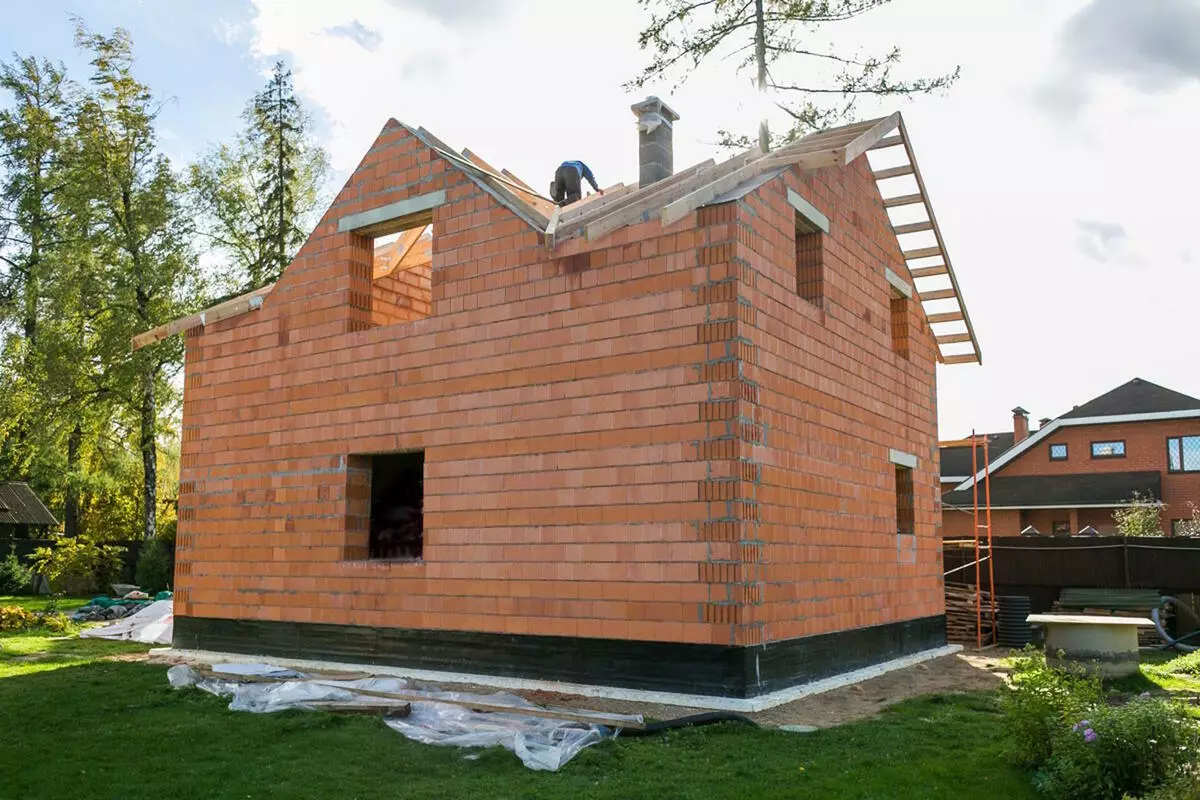


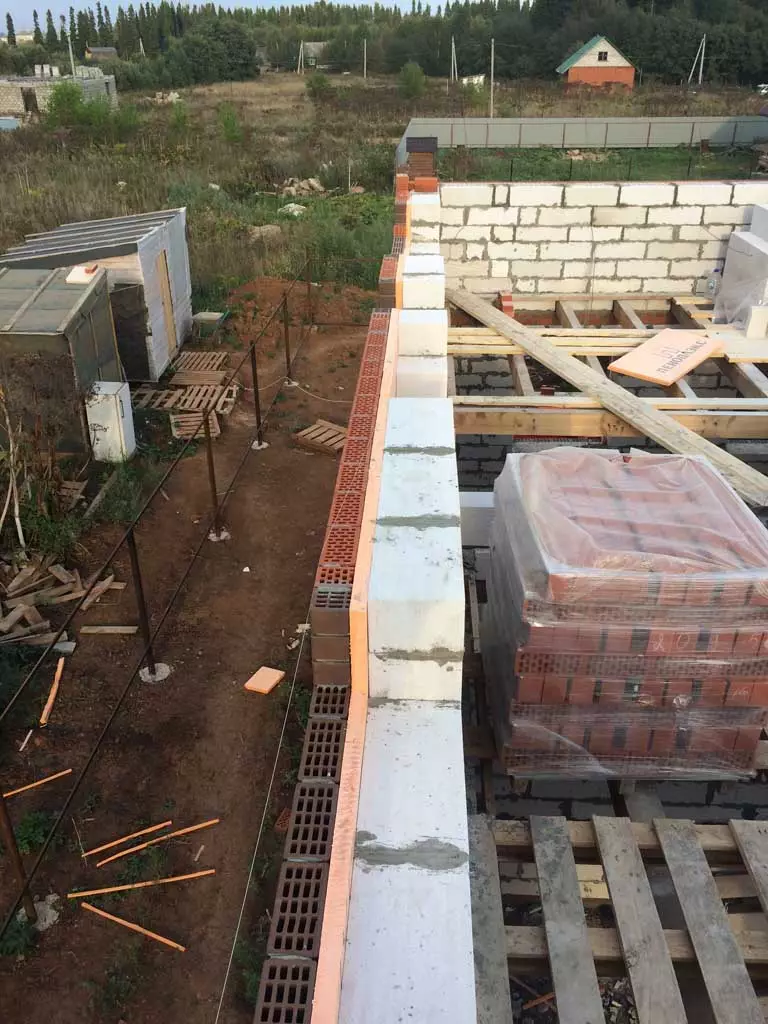
The house from the enrolled blocks cannot be left without moisture-resistant finish - it is required to be placed, put it with a brick (if additional warming is not provided, then without a gap) or mount the mounted facade. Photo: Wienerberger
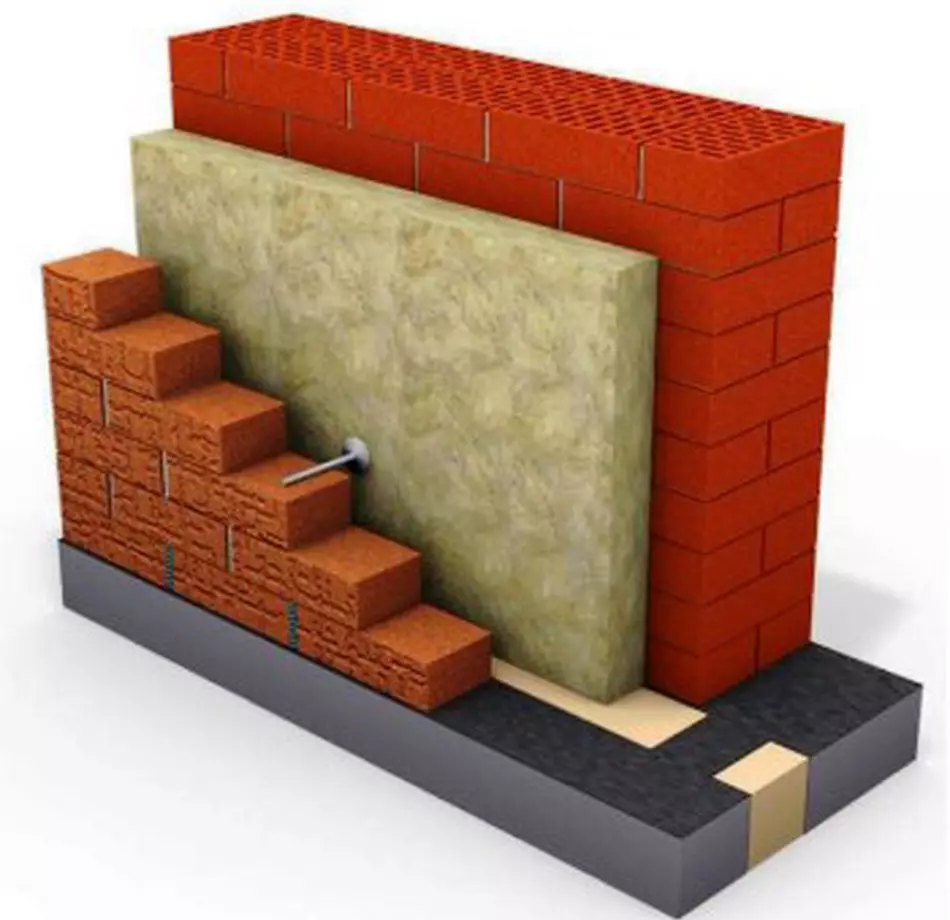
In multi-layered walls with insulation of mineral wool, the ventilation layer is necessary, since the dew point is usually at the heaters of the insulation with masonry or in the temperature of the insulation, and its insulating properties during moisture deteriorate sharply. Photo: Yucar.
Today the market offers a huge variety of building technologies, and in connection with this, confusion often arises. Let's say, the thesis was widely widespread, according to which the vapor permeability of the layer in the wall should increase in the direction of the street: only in this way it will be possible to avoid the mooring of the wall with water vapor from the premises. Sometimes it is interpreted: if the outer layer of the wall is made of a more dense material, then a ventilated air layer should be present between it and masonry from porous blocks.

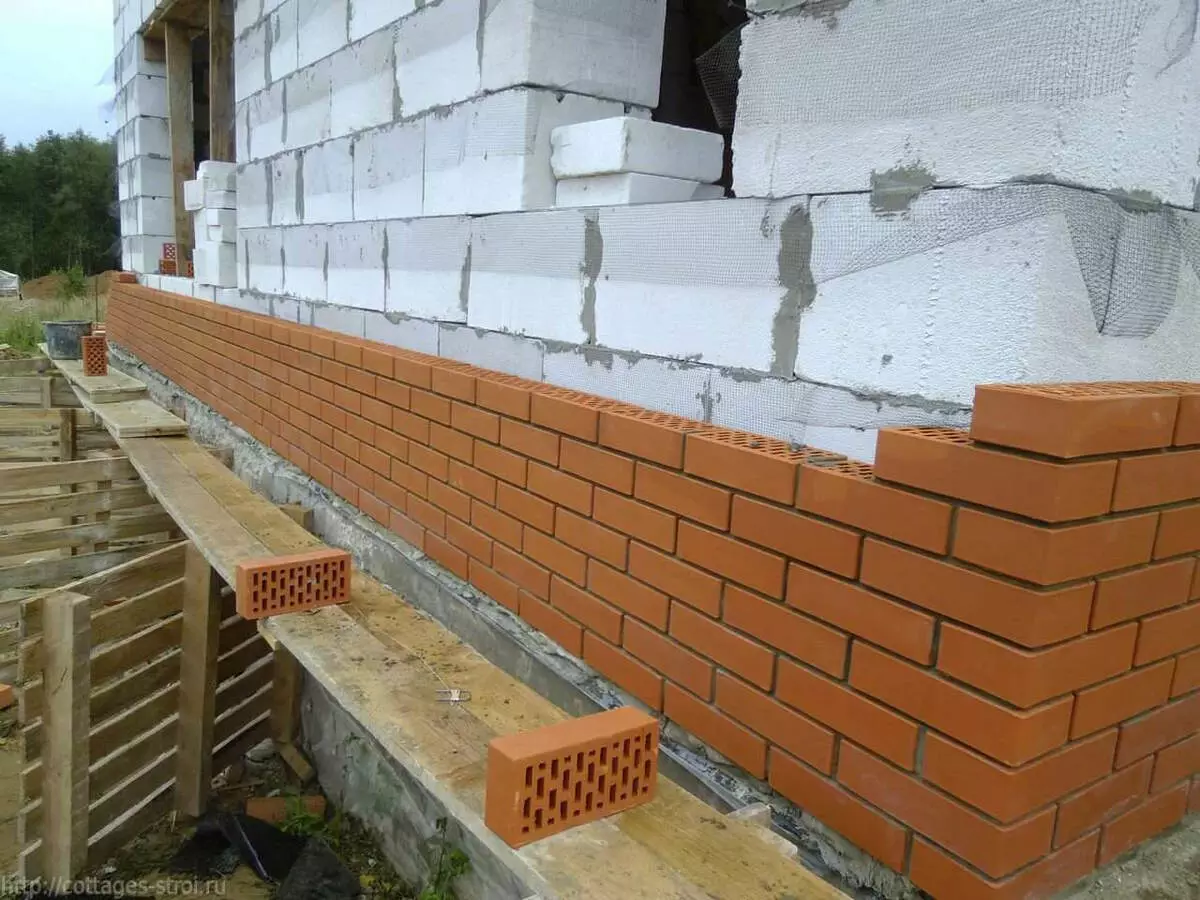
Often the gap leaves in any walls with brick facing. However, for example, the laying of light polystyrene batteries practically does not miss steam, which means that there is no need for a ventilating layer. Photo: dock-52

When used to finish a clinker, the ventilation is usually necessary, since this material has a low coefficient of paroque. Photo: Klienkerhause
Meanwhile, the construction regulations mention the ventilated layer only due to the mounted facades, in the general case, the protection against the mooring of the walls "should be ensured by designing the enclosing structures with the resistance of the internal layers of at least the required value determined by the calculation ..." (SP 50.13330.2012, P. 8.1). The normal humidity mode of three-layer height walls is achieved due to the fact that the inner layer of reinforced concrete has high resistance to steaming.

Typical builder error: there is a gap, but it is not ventilated. Photo: Moscow time
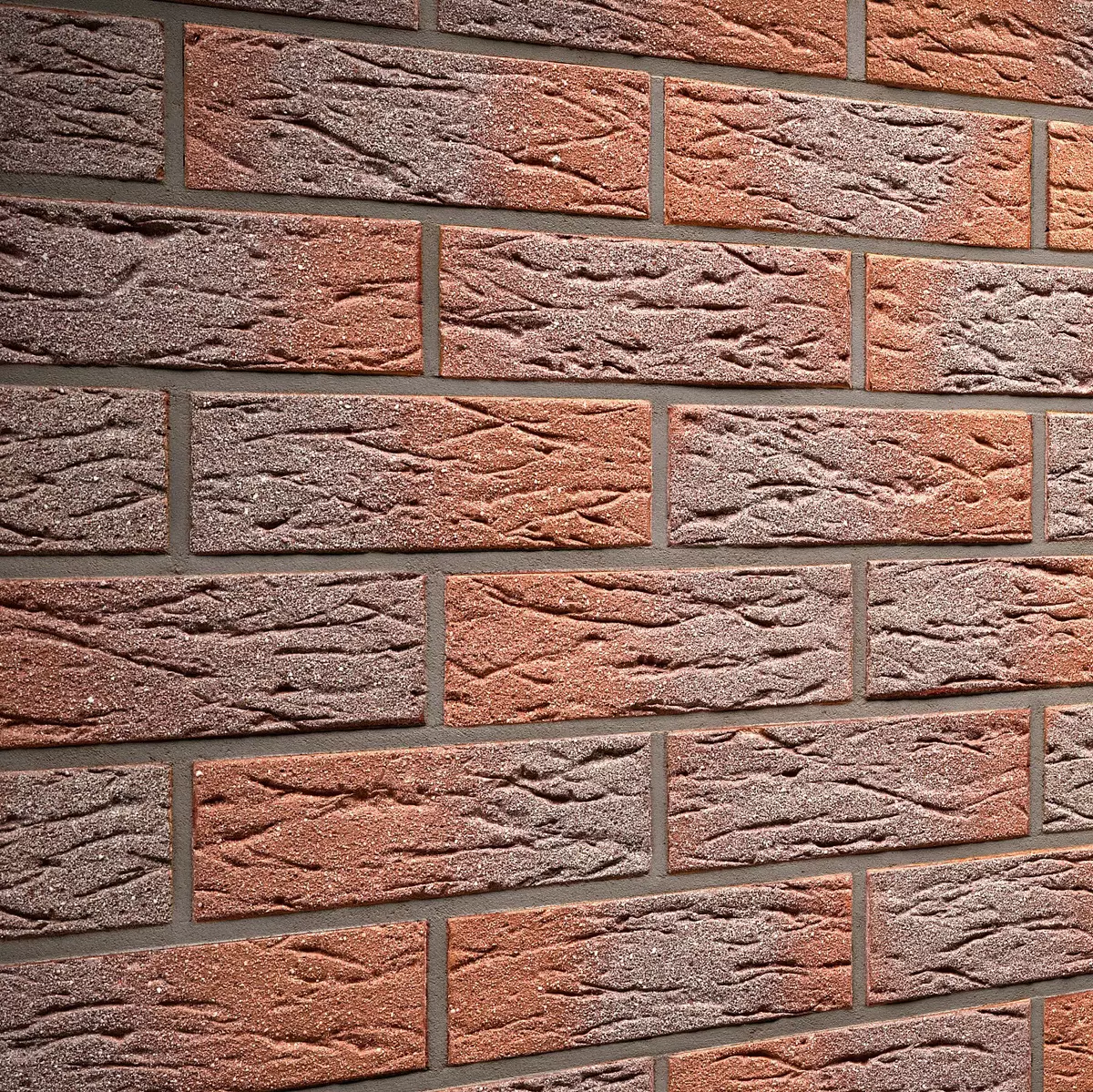

Photo: Klienkerhause
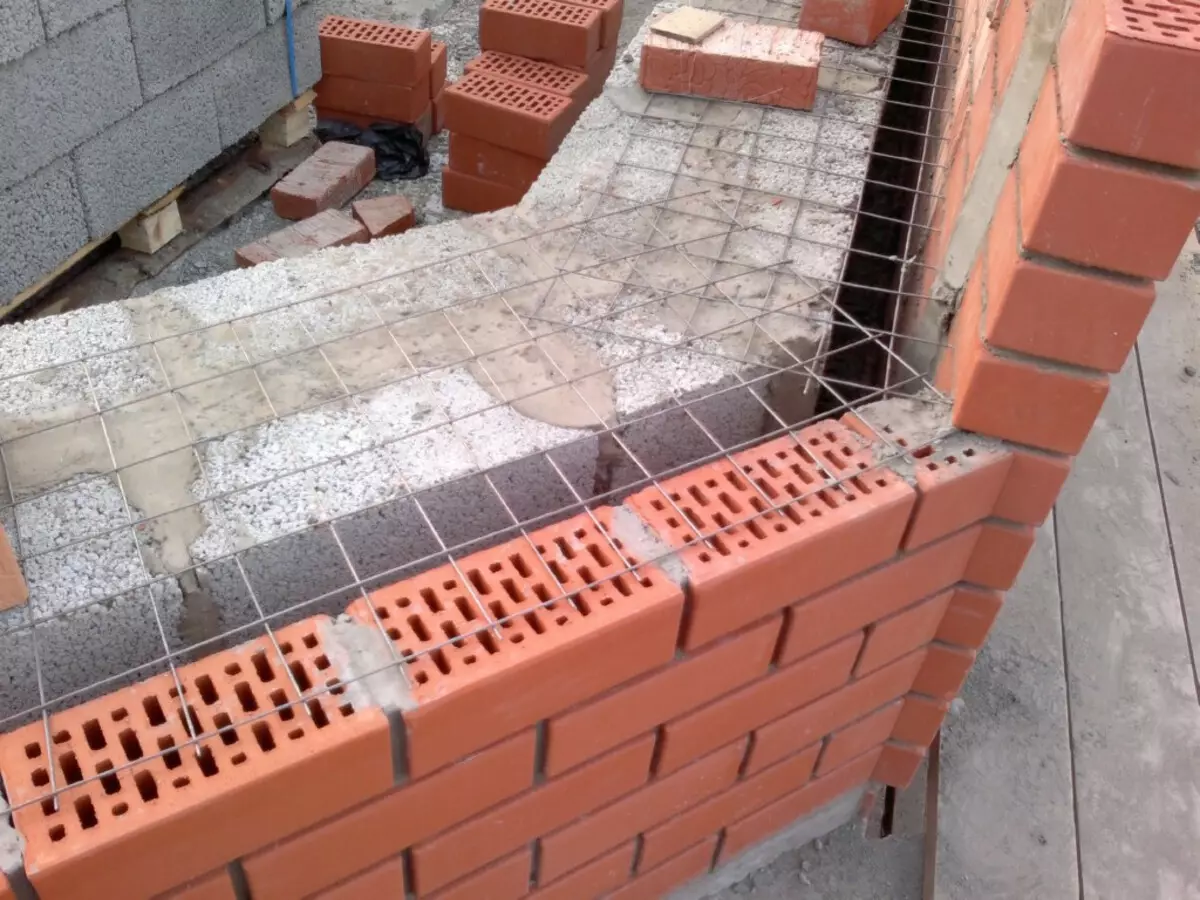
The problem is that some multi-layered masonry structures used in low-rise house-building, according to physical properties closer to the frame wall. The classic example is a wall of foam concrete blocks (in one block) lined with clinker. Its inner layer has vapor-permeal resistance (RP), equal to about 2.7 m2 · h · P / mg, and the outer - about 3.5 m2 · h · v / mg (Rp = Δ / μ, where δ is the thickness of the layer, μ is the material vapor permeability coefficient). Accordingly, there is a chance that the increment of humidity in foam concrete will exceed the tolerances (6% by weight for the heating period). This may affect the microclimate in the building and the service life of the walls, so the wall of such a design makes sense to put with a ventilated layer.

In such a design (with insulation of sheets of extruded polystyrene foam), there is simply no place for the ventzazor. However, EPPS will prevent gas silicate blocks to dry, so many builders recommend falling such a wall from the side of the room. Photo: SK-159
In the case of a wall from POORTHERM blocks (and analog) and conventional slotted facing bricks, the vapor permeability indicators of the internal and outer layers of masonry will be distinguished insignificant, so the ventilation gap will be harmful, as it will reduce the strength of the wall and requires an increase in the width of the base part of the foundation.
Important:
- The clearance in the masonry loses its meaning if the inputs and outputs are not provided. At the bottom of the wall, immediately above the basement, it is required to embed ventilation grilles into the facial masonry, the total area of which should be at least 1/5 of the horizontal section of the gap. Typically, 10 × 20 cm lattices are installed in a step of 2-3 m (alas, the grids do not always decorate the facade and require periodic replacement). In the upper part, the clearance is not laid and not filled with a solution, but is closed with a polymer masonry grid, even better - perforated galvanized steel panels with a polymer coating.
- Ventilation clearance must have a width of at least 30 mm. It should not be confused with technological (about 10 mm), which is left for alignment of brick cladding and in the process of masonry, as a rule, is filled with a solution.
- There is no need for a ventilated layer if the walls are tightened from the inside with a vapor insulating film with subsequent trim of HCL or other material. In this case, for a comfortable microclimate in the building requires forced adhesive ventilation.
- The humidity regime of the premises (and therefore enclosing structures), subjective factors associated with the operation of the building have significant impact. Air humidity in houses with chimney heating is usually much lower than the norm, and the active baths and saunas are actively used sharply increase moisture. In rooms with high humidity, it is necessary to set the exhaust, and the walls are advisable to protect from water vapor films or tiled trim.
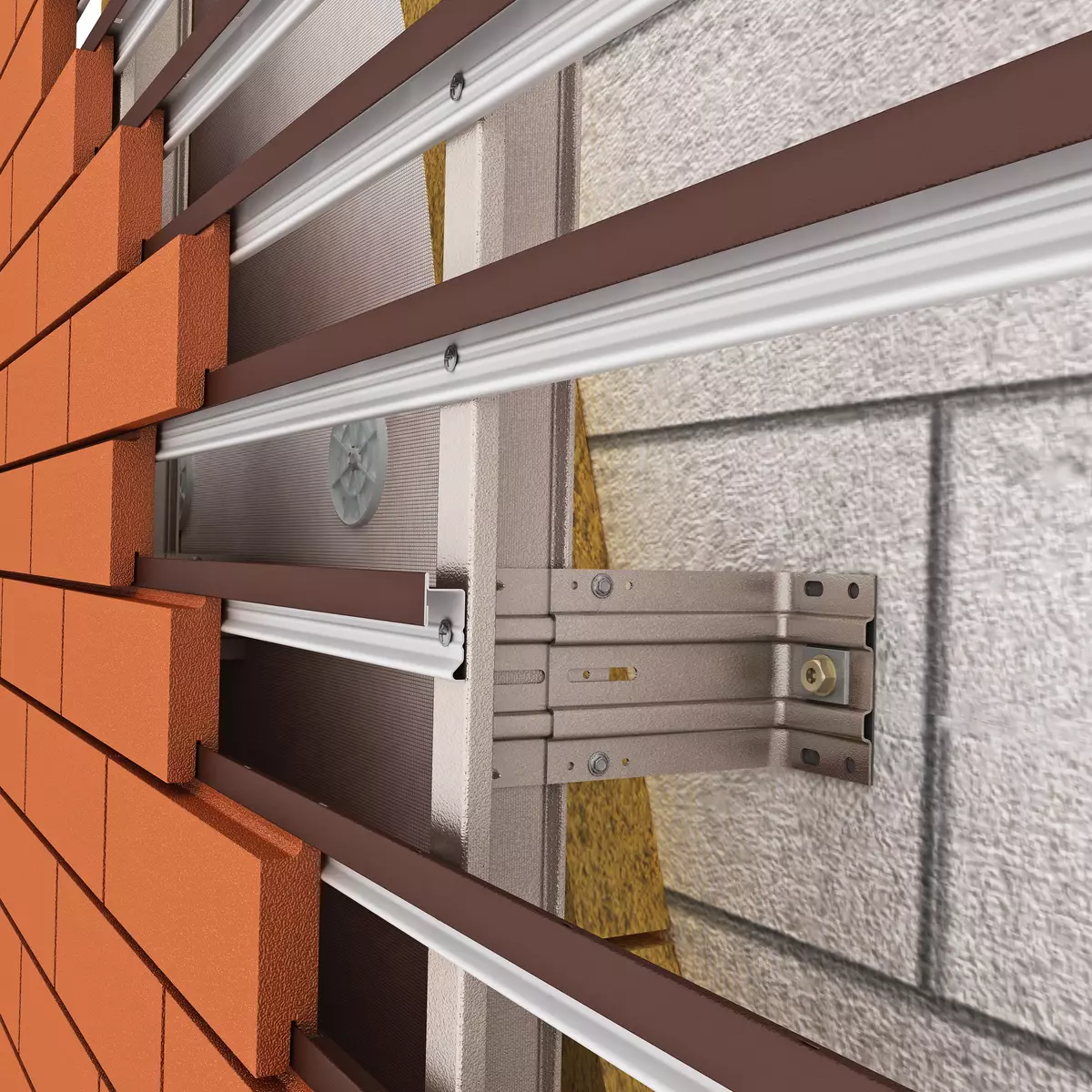

The mounted facade is always mounted with a gap. It is important not to overlap ventilation with details of the root. Photo: Ronson
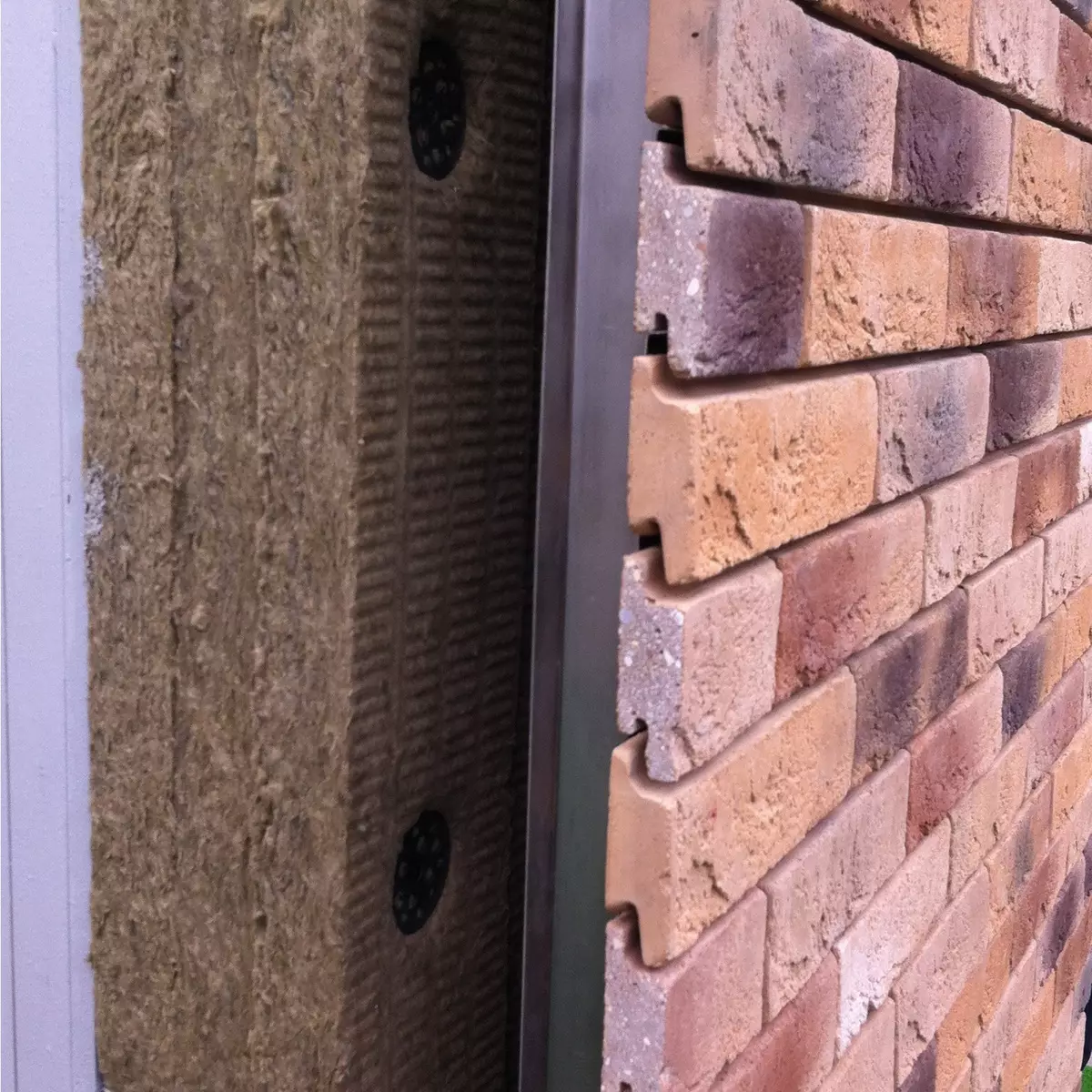

Photo: Ronson

