The beginning of the construction season is not far off, and it's time to talk about popular material - light blocks. What to choose the thickness of the walls? Make them single-layer or multi-layered? How to reinforce the masonry and do you need to strengthen the purses? We answer these and other questions.


Photo: shutterstock / fotodom.ru
In lungs (so-called structurally insulating) blocks a lot of advantages over other materials. This is an affordable price, a good insulating ability and speed of masonry, because each block is equal to several bricks. Of course, there are also disadvantages, such as low strength and moisture resistance (especially this concerns popular products from cellular concrete). However, modern technologies make it easy to overcome these flaws. Sometimes it is more difficult to solve problems that arise before the construction of construction is to determine the choice of block type, thickness and wall design.

Photo: ytong.
Thermal insulating ability of walls from light blocks
According to the current SP 50.13330.2012 "Thermal protection of buildings" required by the reduced heat transfer of the outer walls of the structure (R0), for example, for Arkhangelsk is 3.56 m2 • ° C / W, for Moscow and St. Petersburg - about 3.2 m2 • ° C / W, for Krasnodar - 2.34 m2 • ° C / W.To find out the necessary thickness of a single-layer wall from a certain material, you need to multiply R0 on the thermal conductivity coefficient of this material (we led their values in the table). The solution of this problem is complicated by the fact that the thermal conductivity coefficient of light blocks varies in fairly wide limits depending on the production technology. Thus, in the case of a ceramzite concrete, the gravel fraction is important, and the microstructure of the ceramic stone, the volume and configuration of emptiness affect the thermal conductivity of the paved blocks.
When buying blocks from cellular concrete, you should claim a copy of a certificate of compliance with GOST 21520-89 and independently check the material strength by a shock sclerometer.
It is worth noting that the single-layer block walls of the "reasonable" thickness on the latitude of Moscow do not reach the norm. For example, R0 fencing from gas-silicate blocks of the D500 brand (density of 500 kg / m3) with a thickness of 400 mm is approximately 2.9 m2 • ° C / W. Therefore, many developers choose a multi-layered insulated design.
The insulation of the walls allows to achieve high indicators of heat saving with substantial savings on materials and works, including at the construction stage of the foundation, because the multilayer design is easier and, as a rule, thinner one-layer. In addition, it has a greater thermal inertia: if in the winter it will take to leave the house for two or three days, then you can turn off the heating, without fear that the rooms will disenteen. The main lack of multi-layered walls is a relatively short service life of the insulation (no more than 50 years), that is, with the time the walls will become colder.
Masonry technology
The laying of blocks are carried out in a wastewater and does not apply to difficult work. However, each species of this material - its own installation specificity, and builders are obliged to consider it. Errors when conducting masonry will adversely affect the geometry of the walls, their strength, tightness and thermal insulating ability.
The links between masonry from blocks and brick facing should be durable and durable, but flexible so that the wall does not crack during the shrinkage at home. Optimal options are galvanized steel grid, glass or basaltoplasty.
How to reduce heat loss through masonry seams. To do this, it is necessary to extremely reduce their width and / or use "warm" solutions. If the dimensional deviations of the blocks do not exceed 1 mm, the experimental bricklayer puts them on the layer of the solution with a thickness of no more than 3 mm, and then heat losses through the seams can be neglected. Alas, stable geometry possess only pretty expensive gas-silicate blocks made at enterprises with modern autoclaves and sawing lines (for example, the products of the YTONG brand).
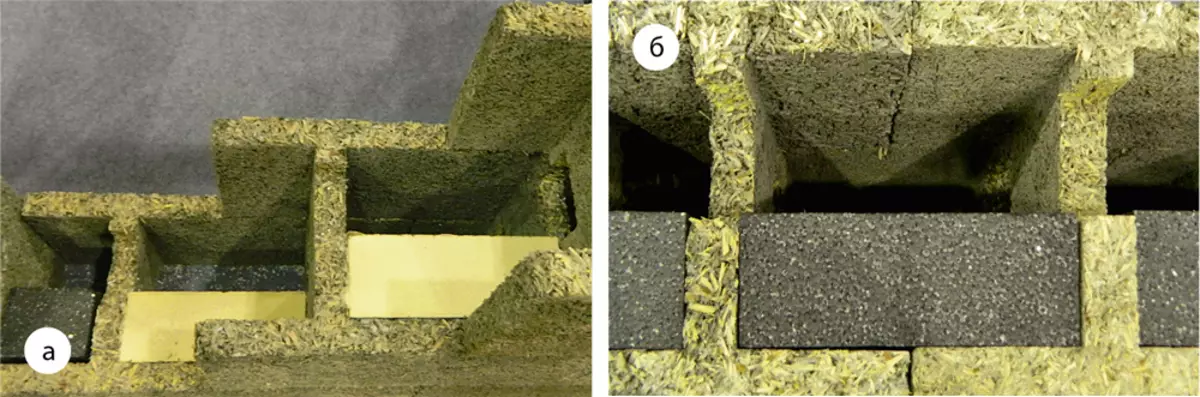
Void Arbolite blocks, insulated expanded polystyrene foam (a) or neuropom (b), are laid without seams. Then a heavy concrete is poured into the cavity. Photo: ytong.
During the construction of ceramic invoked, arbolite, ceramzite concrete and foam concrete blocks, the thickness of the seams is usually 10-15 mm, therefore it is advisable to lead the solution on the "warm" solution. It can be prepared on an object from cement and low-density fillers, such as perlite sand, which is sold in bags and squeezing.
Ready "warm" mixture (Porotherm TM, Knauf LM21, etc.) will cost 2-2.5 times more expensive prepared independently (from 300 rubles per 20 kg), however, during the construction of a small area (up to 150 m2), savings are unlikely Makes himself, especially since plasticizers and sedels of setting have been added to special adhesives, providing good grip with a block.
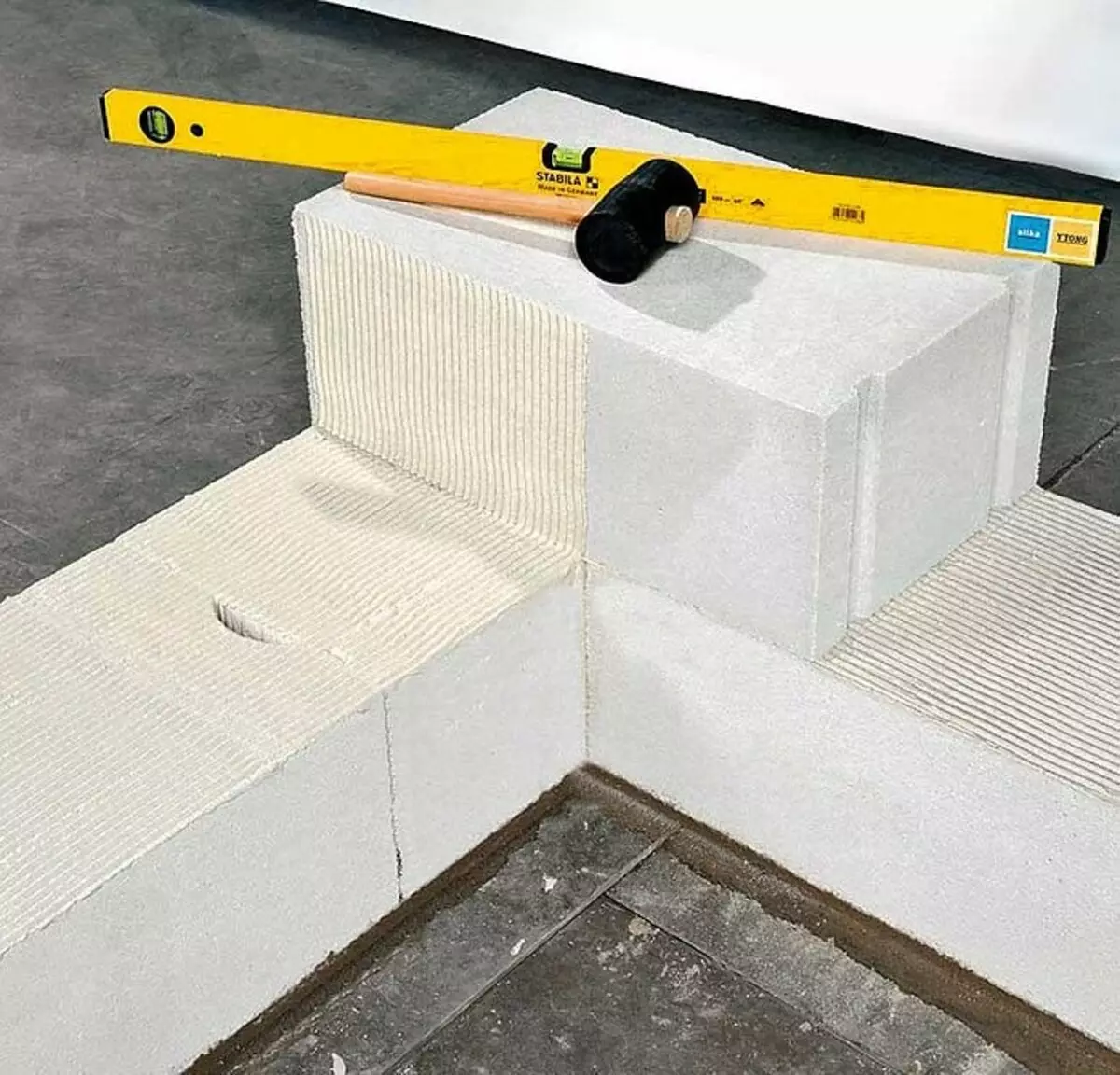




Gasilicate blocks are one of the most convenient materials in the work. At the beginning of the masonry of the series, an angular stones are exposed and stretched between them with shoelaces. Photo: ytong.
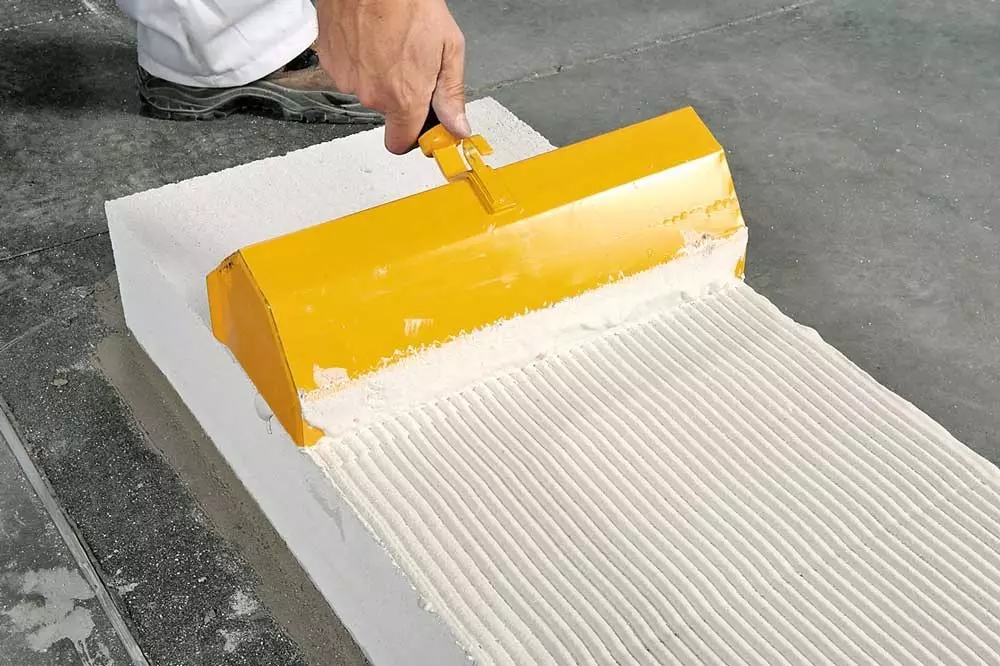

The glue is applied by a special celma-scoop
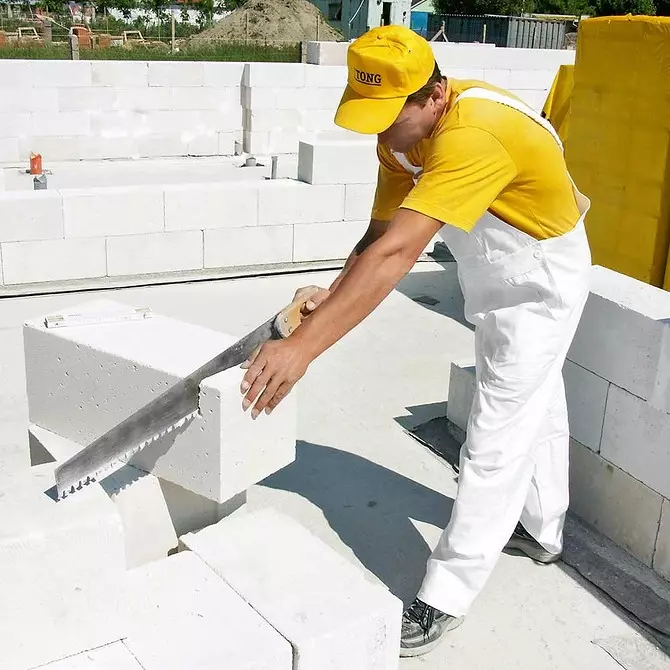

Blocks saw a saw with large teeth without wiring. Operas are overlapped with reinforced beams from a higher density aerated concrete
Do you need to reinforce the masonry. When construction from cellular blocks (foam concrete and gas-silicate), the first and every fourth row of masonry, as well as the zones of the supports of the jumpers and a row under window processes. At the same time, steel or composite rods with a diameter of 10 mm are laid in steres, which are made by manual or electric shock. In addition, it is required to arrange volumetric reinforced concrete belts between floors and under Mauerlat. So that these belts do not become cold bridges, they are isolated from the street side by polystyrene foam or mineral wool. In the house from the cellular concrete of the D400 brand, in addition, it is necessary to strengthen the opening of the entrance door, as well as window openings wide and a height of more than 1.5 m. This is done using welded frames from metal or racks and riggers from reinforced cellular foam concrete D700 or D800 that is preferable.
When laying from arbolic and polystyrene bonts, each third row reinforced with a mesh (better - plastic), and between the floors poured the reinforced concrete belt width (height) from 100 mm.




Photo: "SK DOP"
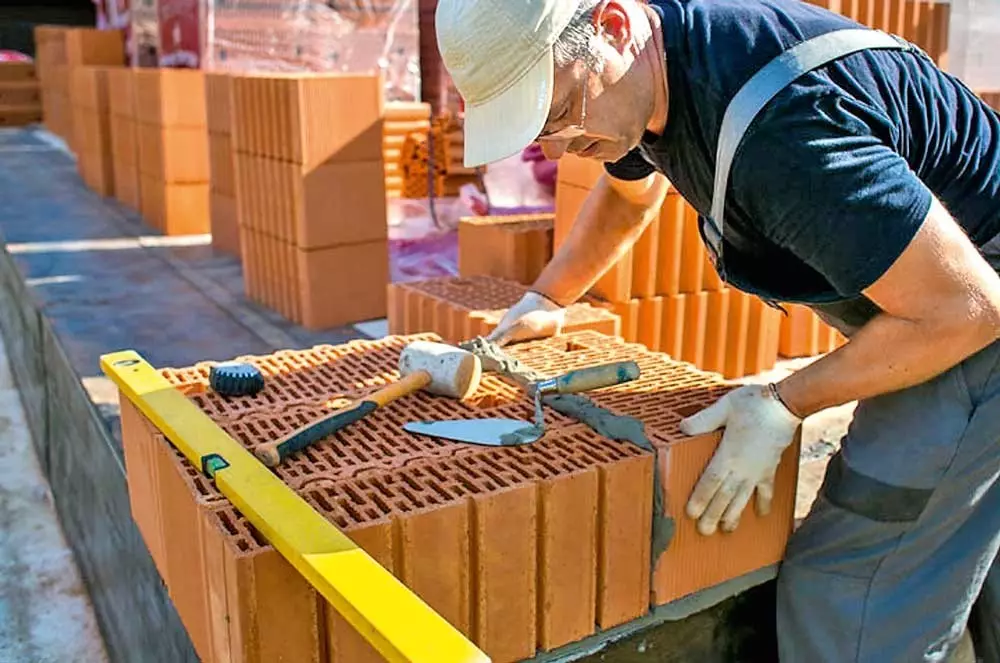

Puzzle compounds of ceramic blocks accelerate the masonry, because the vertical seams need to be filled with a solution only in the corners. Photo: Wienerberger
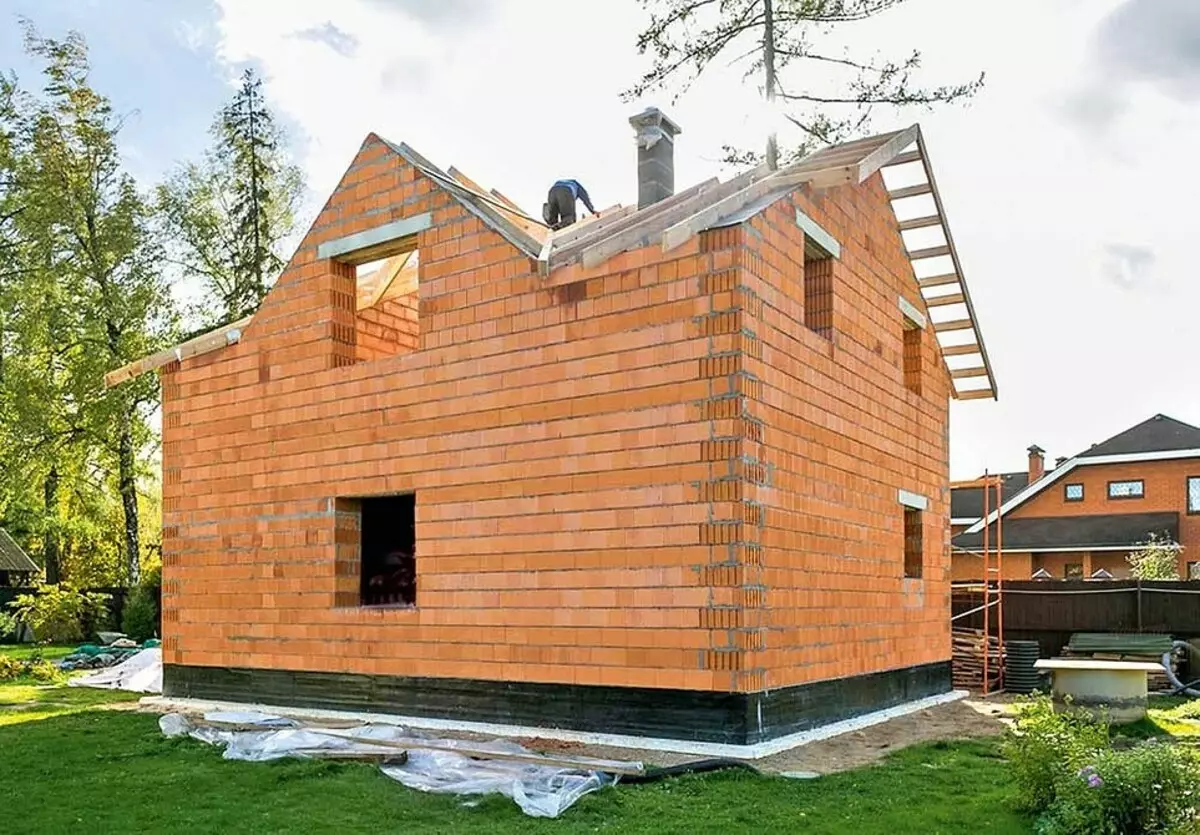

Externally and for some properties, the picked block resembles a brick, but it does not possess moisture and frost resistance of the brick, so the house from this material requires finishing. Photo: Wienerberger
In the walls of ceramic concrete and ceramic pricked blocks, the seams are not required. The need for intermediary armices is determined by the calculation of loads from overlaps and roofs.
How to make jumpers over the battles. Large manufacturers of modern ceramic and gas-silicate blocks, such as Wienerberger and Ytong, offer reinforced jumpers, but these products are quite expensive and are not available everywhere, therefore, more often, the proceeds are overlapped by segments of metal products - corners and chambers covered in stages.
Options layered masonry
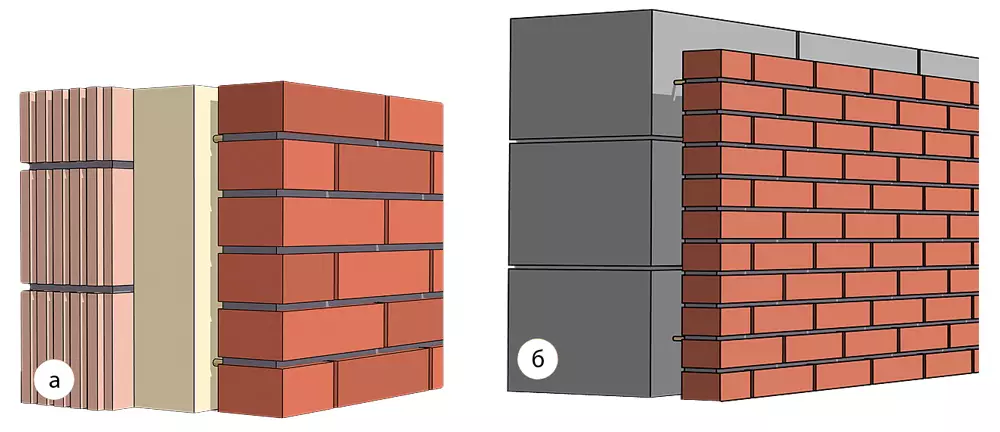
Laying from the recipient blocks with a thickness of 250 mm with insulation of mineral wool (100 mm) and facing bricks. Between the insulation and brick left the ventilation gap 50 mm (a). A wall of foam concrete blocks with a thickness of 400 mm with cladding in the Pollipich; Flexible connections (thin steel plates or rods) are located in a step of 400-600 mm vertically and horizontally (b). Visualization: Igor Smirhagin / Burda Media
Climate in the house
The walls made of light blocks provide a comfortable microclimate in the rooms, as the extra moisture is taken from the air (with the exception of polystyrene bonts). This quality is especially valuable in the absence of a modern ventilation system.Many professionals do not recommend tightening block walls from inside with vapor insulation films, as this will worsen the microclimate in the house. It is necessary to ensure intensive evaporation of moisture from the outer surface of the walls. From this point of view, the optimal way to finish a house of light blocks is a cladding with a brick with a ventuzor or mounting of the mounted facade.
Warming and decoration
Light blocks, including ceramic, are not decorative enough and also need protection against atmospheric moisture. The most common ways of finishing block walls are facing (tring) brick, plastering, cladding with tiles on adhesive solution and mounting the mounted facade. All of them allow additionally to insulate the walls.
Use for insulation of walls from light blocks polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam plates, as well as sprayed polyurethane foam undesirable. These materials have low vapor permeability and interfere with the wall to give moisture, penetrating into the design with room air.
Walls with brick facing belong to the building "classic" and to this day are popular, despite the fact that it is a rather expensive and time consuming method of finishing, besides, it is necessary to increase the design width of the foundation for 150 mm for its implementation), and if provided for insulation, then 200/250 mm.
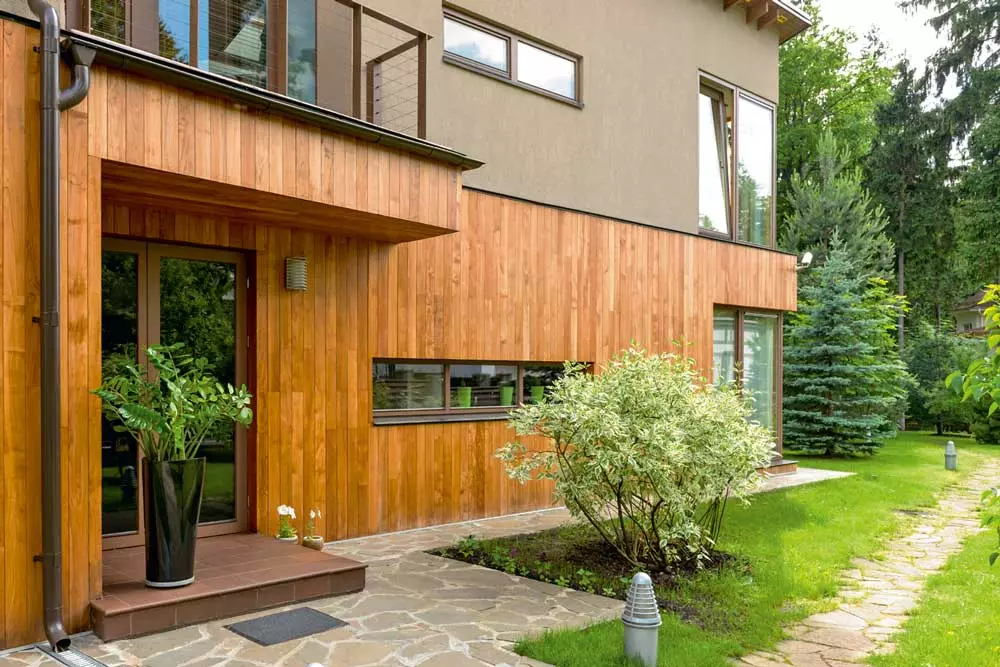

In Russian cities, over the centuries built at home with the first stone and second wooden floor. Modern finishing techniques allow "architectural inversion". Photo: "Planken.ru"
The vapor permeability of the brick facing is small, and it can locate moisture inside the carrier wall. Therefore, between brick and blocks, an inventory value of 20-40 mm is provided. If the masonry of the walls and cladding is carried out at the same time, the brick is associated with blocks of mortgage jumpers.
When cladding already built house use anchors. The insulation is most often pressed against the blocks using plastic washers worn on the rods-jumpers.
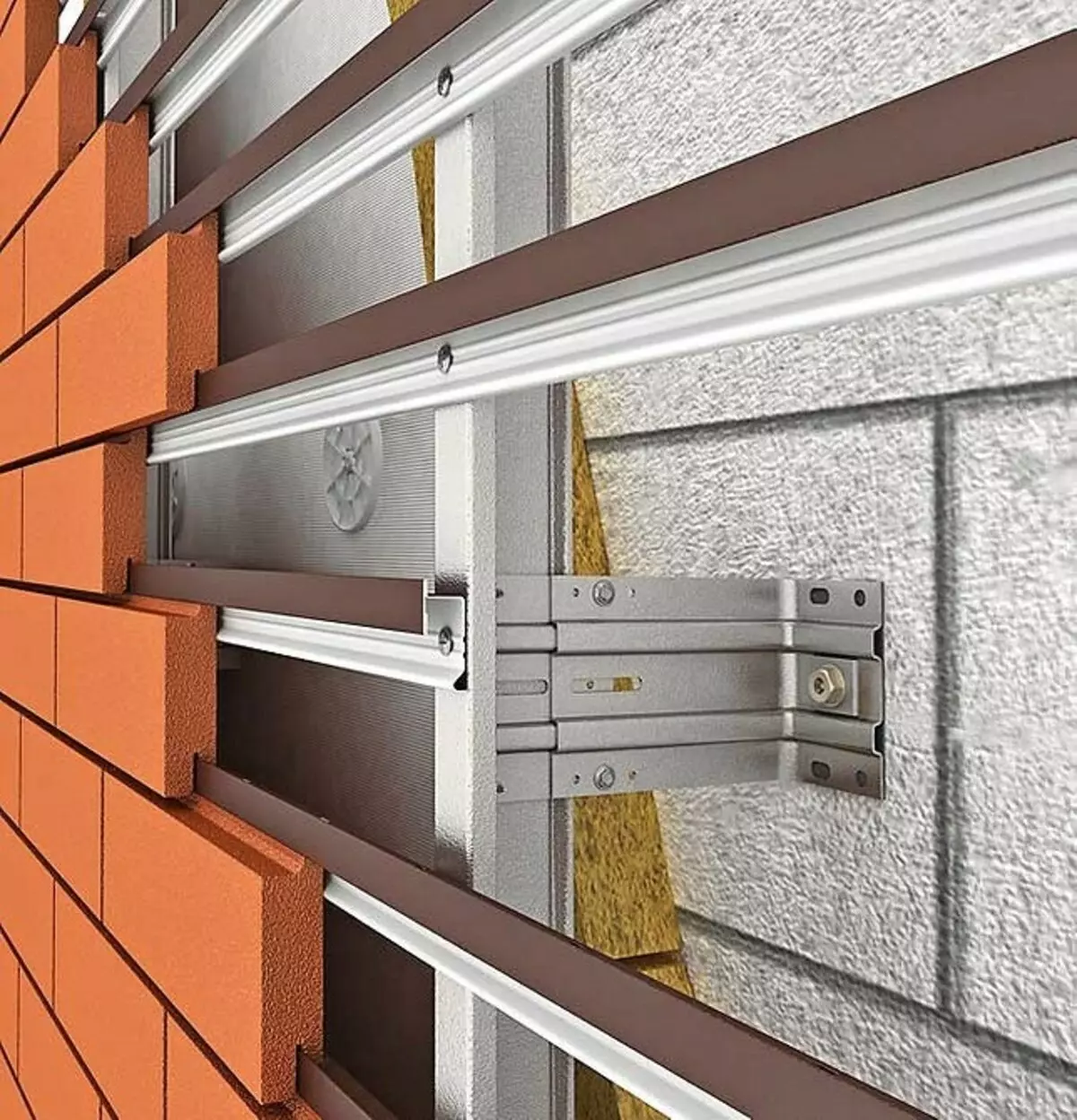







Diseases made of aluminum or steel galvanized profiles are convenient in the installation and serves to 50 years. Photo: Ronson
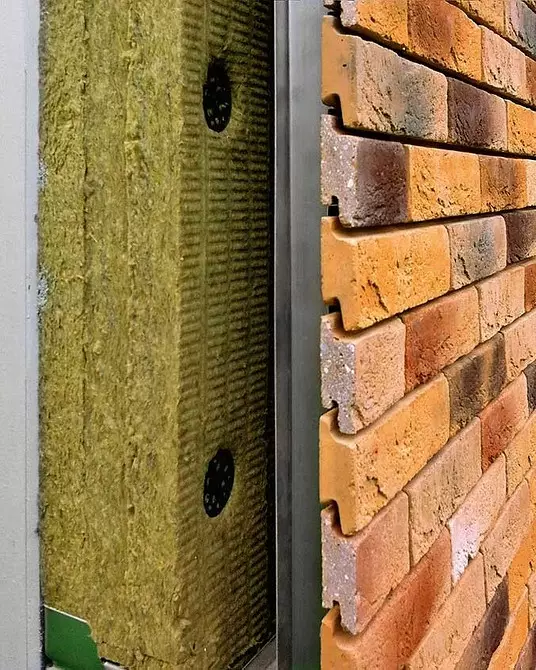

When the device of the mounted facade between the insulation and cladding must necessarily be provided in the vent. Photo: Ronson
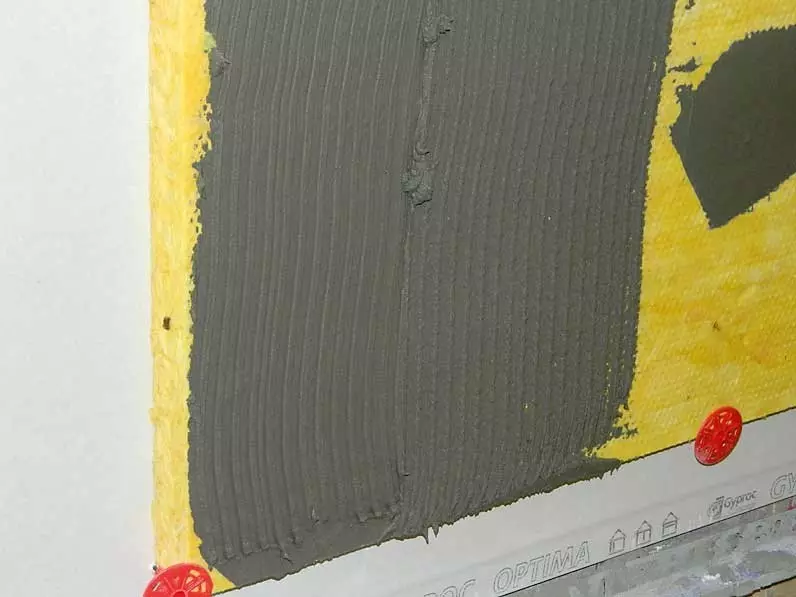

When installing a warm plaster facade, first the walls of high density mineral wool plates (either two-layer), using support profiles, special glue and disc dowels for this. Next, the first layer of solution is applied to the insulation. Photo: Vladimir Grigoriev / Burda Media
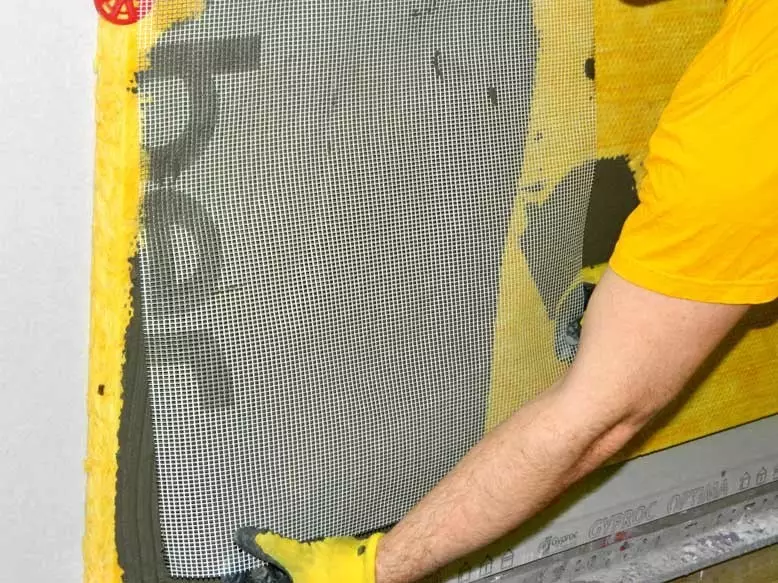

The reinforcing grid is pressed into it. Photo: Vladimir Grigoriev / Burda Media
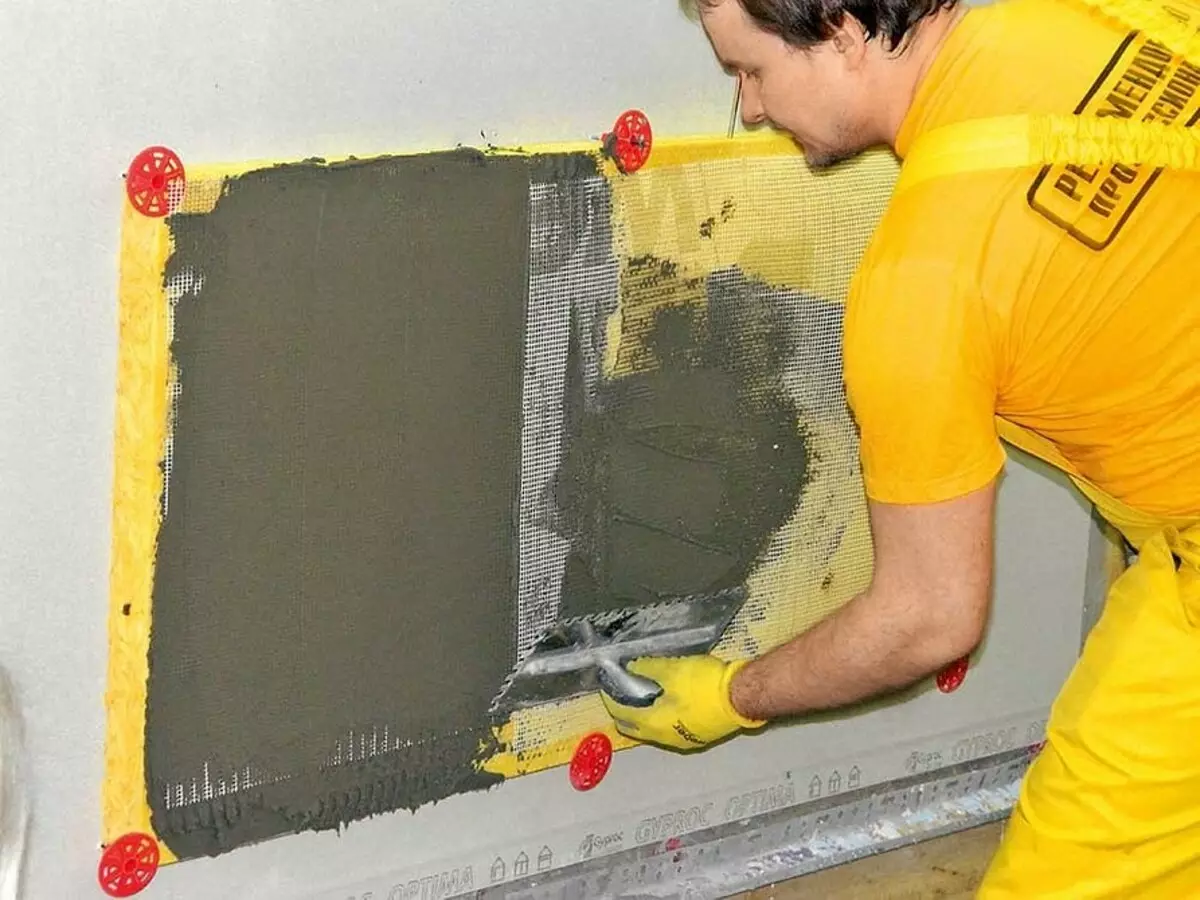

The grid is closed with the finish layer of plaster. Attempting to apply plaster in one layer (on top of a fixed grid) will lead to a stratification of the structure. Photo: Vladimir Grigoriev / Burda Media
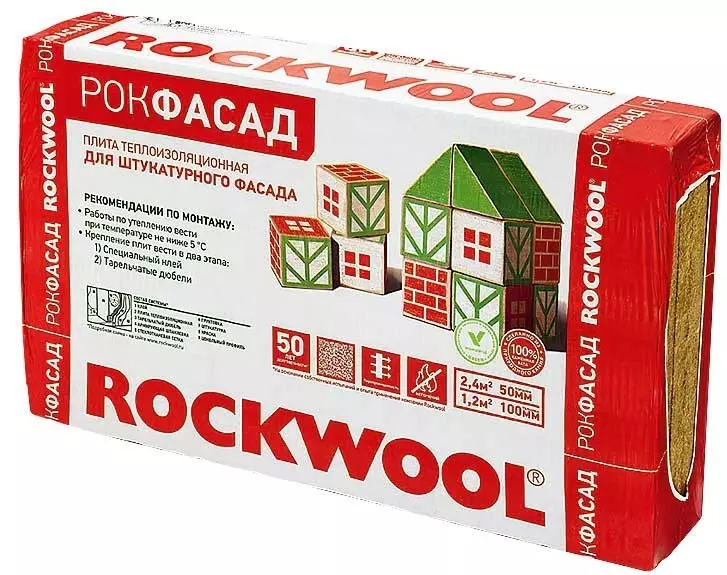

Leading companies produce special products for facade insulation. Let's say Rockwool for layered masonry offers "Kuvii Batts", and for plaster facades - "Rocafasad". Photo: Rockwool.
The plastering facade should have resistance to peeling and vapor permeability of at least 0.09 mg / (m • h • PA). The most precisely use ready-made cement and cement-lime compositions, such as Cerzit ST24, Weber.Stuk 411. Walls made of foam concrete, aerated concrete, polystyrene and ceramic blocks. It is recommended to plaster on the grid.
Clinker cladding has been in fashion due to a certain decrease in the price of this beautiful and durable material. Clinker tiles are glued to the wall aligned with the base plastering layer. When insulation, first with the help of special glue fasten the plates from high density mineral wool, then the plaster layer is applied and the tile is mounted.
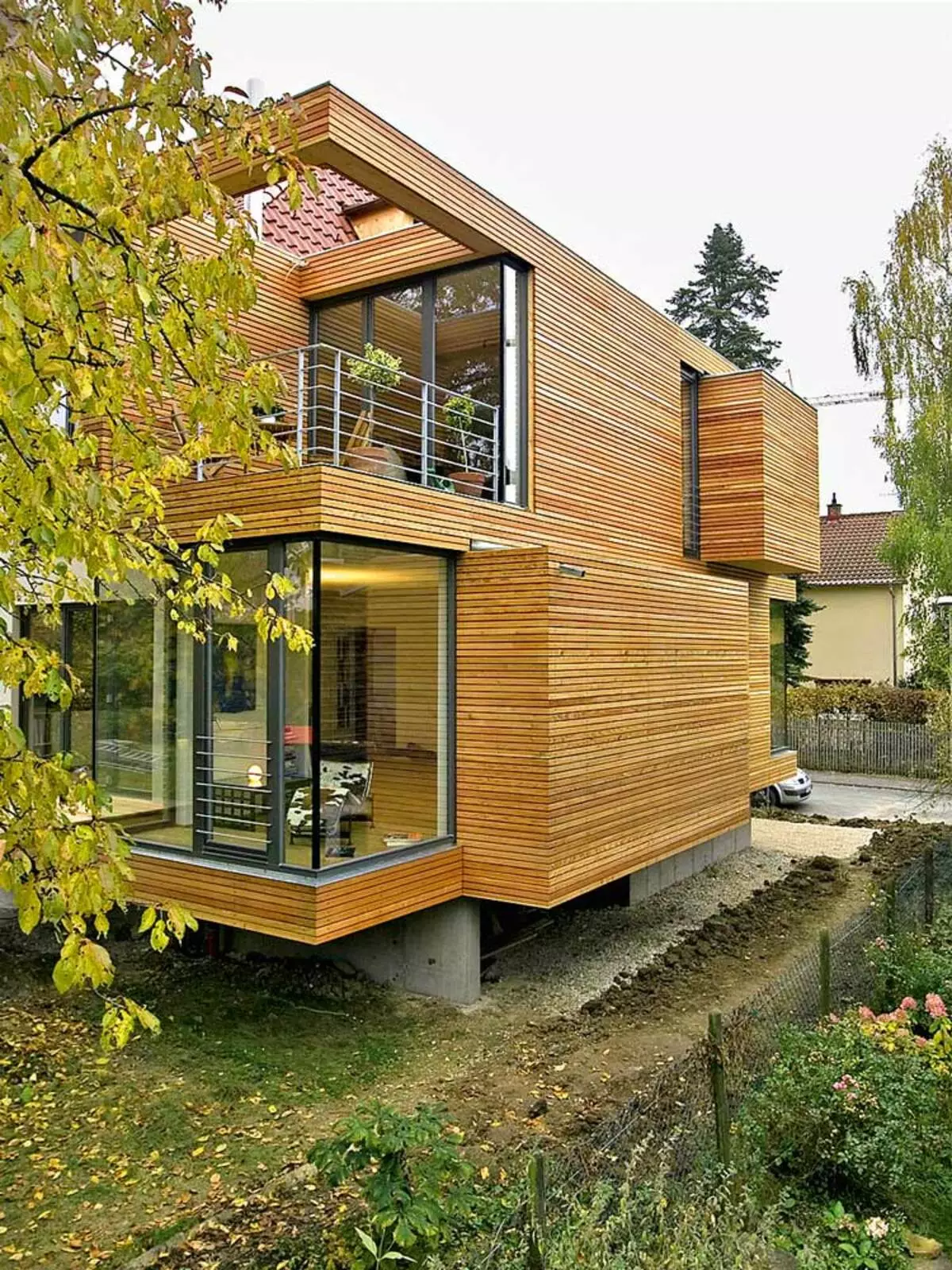

One of the fashionable finishing materials today is a wooden plaquen. The boards are napped with gaps, so the skin is not extended at moisture. Photo: Dörken.
The mounted facade is mounted faster and allows you to separate the house with a variety of materials - block key and lanken, vinyl and metal siding, panels made of fibercement and wood-polymer composite, concrete and stone tiles.
Option of mounted facade
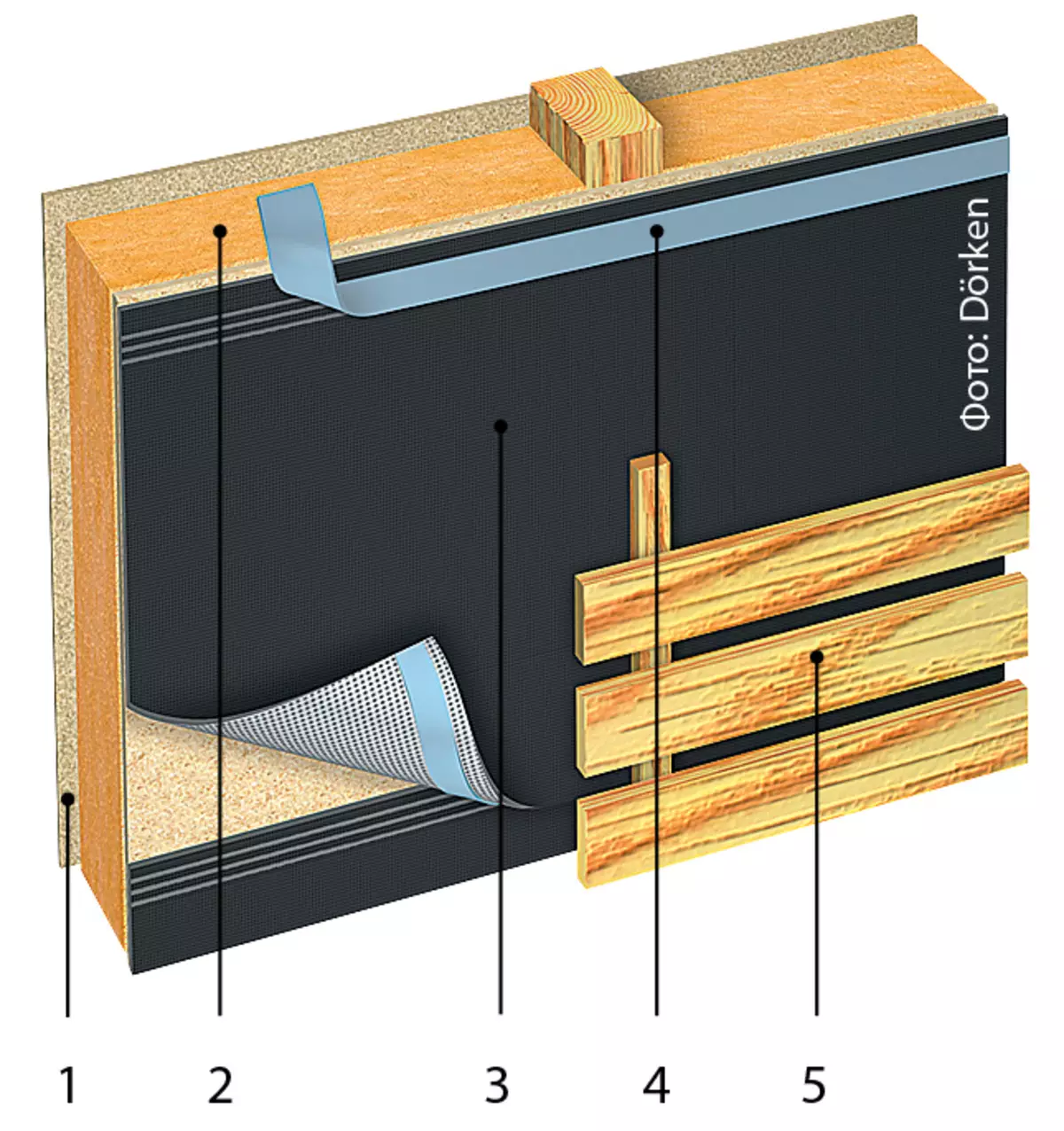
Design elements: 1 - carrier wall; 2 - insulation (wood-fibrous plates with a thickness of 100 mm); 3 - hydraulic protection membrane; 4 - bilateral scotch for joints; 5 - Facade board. Photo: Dörken.
Types of light blocks
Arbolitov
Arbolite (sometimes not quite correctly called opilk concrete). It is produced from a sand-cement mixture and wood chips. Material is impassable and does not support burning, dug with a hacksaw, but at the same time it keeps fasteners well (unlike aerated concrete).Gas concrete
Raw materials for its production serve small quartz sand, binders (lime, plaster, cement) and aluminum powder. When aluminum reaction with alkaline cement or silicate solution, hydrogen bubbles are formed, due to which the material acquires a cellular structure. A clumsy variable monolith saw into blocks, which are then dried in an autoclave or an electric furnace. Technology allows you to vary the density of the blocks. Structural (that is, capable of perceiving power loads) consider the products with a density of 500 kg / m3 and more.
Gas-silicate
The type of a gas-concrete block is manufactured without the use of cement binder. It is this technology that the leading manufacturers are used (for example, Ytong). Silicate blocks are somewhat less durable than cement, however, they differ more uniform structure.Ceramzitobeton
It is made of sandcotent and clay gravel as a filler. There are vigilant (double-frequency, four-row) and full-scale blocks. The first is cheaper and easier, but the presence of large cavities makes some construction work, such as fin fat. The main disadvantages of ceramzite-concrete blocks are relatively low thermal insulating capacity and instability of geometric dimensions (tolerance of up to 5 mm).
Ceramic picked block
Otherwise, a ceramic priced multi-duct unit. It can be considered the last step of the evolution of the red slit brick. The block is also manufactured from the slightweight clay, but its size is 5-8 times more, and the void achieves 55%; Voids have the form of narrow channels, and intensive convective heat exchange, which improves insulating ability. The ceramic unit must be put only on a plastic solution that does not fill emptiness. The material is harder than the cellular concrete, however, it has much greater strength and durability.Foam concrete
This cellular block for the main characteristics is similar to a deplete, but differs in production technology: synthetic or organic foaming agents add to the cement and sand mixture. According to the strength, foam concrete is superior to a gas-silicate, but has a less homogeneous structure.
Perliteobeton
As a filler in it, used pulp sand. By heat insulating capacity, the block is not inferior to a gas concrete, while significantly more thermosters and is durable. The material is produced in the territory of Russia in extremely small volumes, and its price is clearly overestimated (from 6 thousand rubles per 1 m3).Polystyrevbeton
The polystyrene foam granules occupy more than 50% of its volume. This block is very "warm", but has low vapor permeability.
Slag concrete
Today, it is produced only in some regions of non-black earth. The material is very dry, but has low thermal insulation characteristics.
Characteristics of lung building blocks
View of the wall block | Arbolitov | Gas-silicate | Ceramzitobeton | Ceramic picked | Foam concrete | Polystyrevbeton |
Compressive strength, kgf / cm | 240-70 | 10-20. | 50-120 | 30-50 | 10-30 | 15-30 |
Density, kg / m3 | 400-850 | 400-600 | 700-1400. | 550-650 | 400-900 | 400-600 |
Thermal conductivity, W / (M • ° C) | 0.12-0.30 | 0.10-0.25 | 0.28-0.40 | 0.16-0.25 | 0.10-0.31 | 0.10-0.24 |
Water absorption,% | 60-80 | 100 | fifty | 15-30 | 95. | 5-15 |
Cost, rub. / M3 | 4000-4200 | 2600-4600 | 2600-2800. | 5100-6000 | 2500-3400. | 2700-3000 |




