Only when the Customer clearly sets the tasks to designers and builders, while those and others are willing to meet each other, projects of modern energy-efficient homes are created.
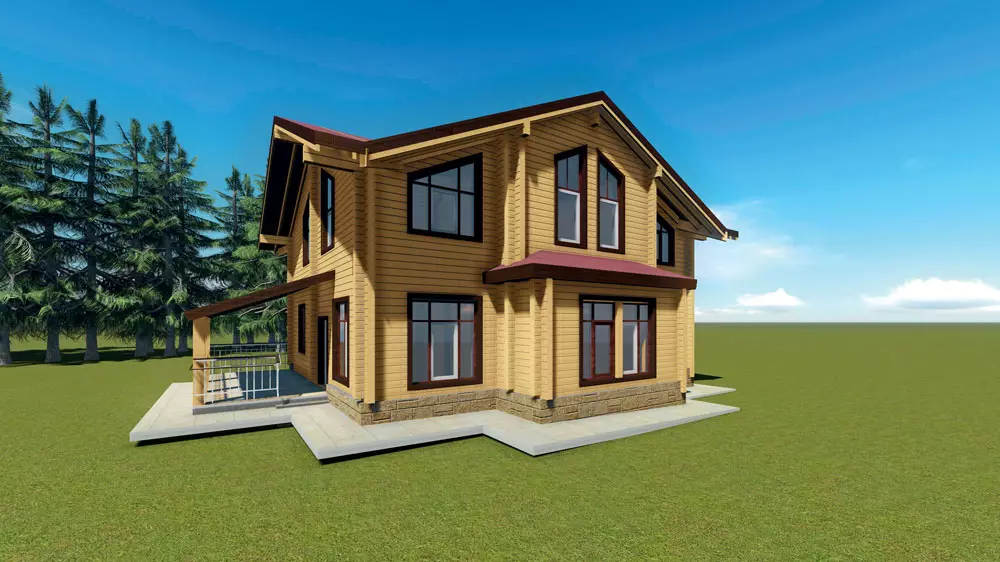


Photo: "Alpbau". Main House (240 m2) and a garage for two cars with a residential second floor (area of 160 m2), on which the host's office and guestrooms are located, are inseparable from each other, because all the life support systems of this complex are located in the garage
The customer initially formulated the following requirements:
- The first is to build a house for a family of five from the glue bar, and next to it a garage for two cars with a residential second floor, in which you need to place all the technical maintenance systems for the main building.
- The second - both buildings should be heated by one pellet boiler, the consumption of which will be maximally economical. The heat source in all rooms of the house will be warm water floors, in the garage - radiators.
- Third - in addition to heating and DHW, equip the dwelling system of ventilation system heated and cooling air, while the electricity consumption must be minimal.
- The fourth is to provide a system of emergency power supply and heating, even in emergency cases (if the pellets supply fully runs out) all its elements were uninterrupted at any time of the year.
Design at home

The specialists of Alpbau, who adopted such an unusual order, did not immediately take up the design of buildings. For a start, heat engineering calculations were performed with the help of which they determined how much heat should produce a boiler heating water floors, and what are the intended heat loss through the building structures of the two buildings. These calculations convincingly proved that the flow of pellets would be economical only if the heat transfer resistance of the enclosing structures will be able to close as much as possible to the characteristics of the "passive" house: walls - 6 m² • ° C / W, base overlap - 4.5 m² • ° C / W, Roof - 9 m² • ° C / W. That is, the walls folded from the glue beam will have to be additionally insulated. The customer approved this idea, and at the same time a number of technical solutions proposed by the Company.
According to the design of the designers, both buildings will make the maximum capacity of 35 kW installed in the garage, equipped with two combustion chambers: one (main) - on pellets, the second (reserve) - on diesel fuel. The coolant and hot water from the garage will be served to the house on warmed highways.
The garage provides for the storage room of the pellets, the supply of which will have to replenish no more than 1 time per month. In the same building there will be a repository of diesel fuel, calculated at least on the crescent volume.
To warm up and cool the air for the ventilation system, as well as partially warm the water for the heating system and the DHW will become a heat pump type "water-air".
Emergency power supply of both buildings will provide a diesel generator, also located in the garage.
From the calculations to the project

After the customer approved the proposed technical developments, the company's experts began to design a complex of two buildings. At the same time, they had to work out a number of original solutions that allowed us to provide energy-saving characteristics of the structure of the house. Briefly consider some of them.
Ground overlap
Heat losses through the base overlap can be up to 20% of the total heat loss through the building structures of the house. Obviously, these losses will not be able to reduce without powerful insulation. But how to combine thermal insulation with sufficiently durable floor, communications and warm water floors, so that the total thickness of the cake has not been too big?The designers created a multilayer structure in which the floor surface was separated from the ground separated from the soil, filled between the foundation ribbons, several layers (bottom-up): 50 mm of extruded polystyrene foam, monolithic reinforced concrete plate with a thickness of 110 mm (it is the main load), 160 mm polystyrene foam density. 300 kg / m³ (communication is laid here) and, finally, a cement-sand screed with a thickness of 70 mm, in the lower third of which pipes for warm water floors are laid. Unusual multi-layer pie fully complies with the requirements of both strength and energy saving - its reduced heat transfer resistance is 4.62 m² • ° C / W.
The project was implemented in several stages. At the stage of construction of the base, the ground, bothering between the foundation ribbons, was covered with plates of extruded polystyrene foam and cast a reinforced monolithic slab on top of them. Next, built a box of the house, laid all the necessary communications along the concrete slab, and then hidden them in the layer of polystyrene foaming thickness of 160 mm. On top of it, the pipes of warm water floors were installed and covered with a concrete tie, the upper level of which was located 50 mm above the surface of the pipes (in accordance with the technology of installation of the selected grade of floors). Well, during the finishing decoration of the premises, the tiles of porcelain tiles were stalled.
Selection of insulation
As a heater, it was decided to use the soaking thermal insulation of the GUTEX THERMOFIBRE based on wood fibers. Raw materials for its production serves chips of coniferous rocks, which grind on wood fibers. After that, the minimum amount of additives that increase the biocoes and fire resistance are already introduced into the composition of almost finished material, package and pack the product.
In terms of thermal conductivity, the material corresponds to modern effective insulation (0.039 W / (M • K), has good sound insulation properties, easy to use. But the main thing - it is "not sitting down" with time and almost does not change its heat-saving characteristics even when the moisture penetration is It is primarily due to the structure of the material. The secret is that the moisture comes primarily in the capillaries of fibers, the space between which is filled with air. As a result, the insulation is able to absorb and evaporate moisture in the amount of up to 10 and even 20 l / m³, and then return it back. The fact that the coefficient of the specific capacity of GUTEX THERMOFIBRE is 2-3 times higher than the similar indicator of mineral wool.
Accumulating heat (or cold), as well as moisture, the insulation contributes to maintaining a healthy microclimate in the premises.
Since the process of planking the material in the cavity of the building structures is quite detailed in the photos, add only that a similar insulation is permissible to lay a 400 mm thick layer, which is resistant to sediment only if its density is not lower than 29 kg / m³.
Therefore, the density of the already stacked layer has to be constantly monitored during the planning process. For this purpose, a device resembling a high metal glass with a sharp top edge is used. Such a glass cut holes in vaporizolation to put the hose in the insulated cavity, according to which the insulation is supplied. They also take samples: After the end of the cavity becomes the cavity with the help of a glass, the insulation column is cut on all its thickness, weigh the density on the table. If it is not sufficient, the joind continues. When the density is normal, the insulation is returned to the place and the cutting hole is stuck.
On the roof, the stuffing thermal insulation is covered with a layer of another material based on wood fiber - with a rainfit suction plates of Gutex MultiPlex-Top with a thickness of 35 mm. This insulation has a slightly higher thermal conductivity than the strangal (0.044 W / (M • K), but it has greater density and durability, and most importantly, due to the introduction of paraffin additives is not afraid of water and can even be used as temporary roofing for 3 months Coatings
Outer walls
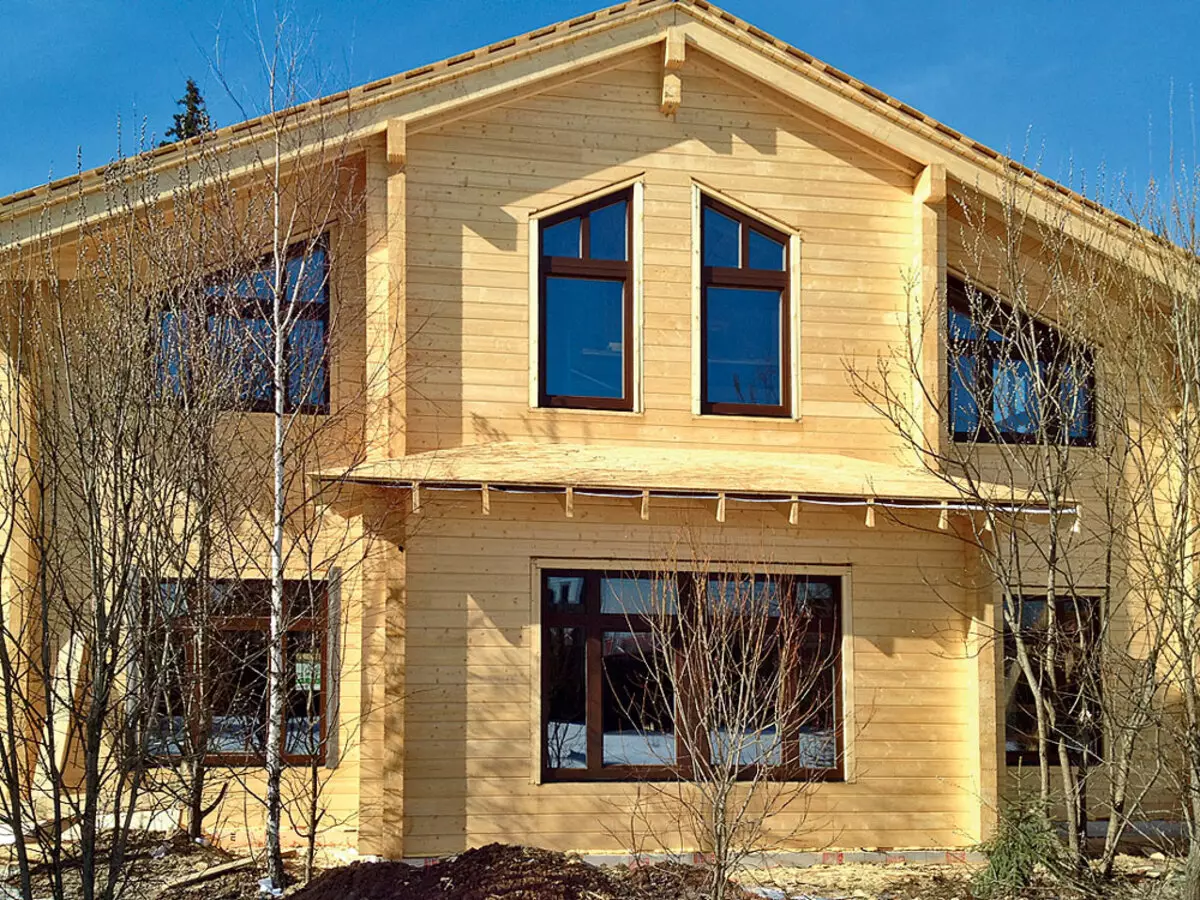

Externally, the "passive" house is no different from their fellow, erected from a tangled glue bar. Its walls are covered with a decorative protective composition, which preserved the color of the natural tree
Thunderstanding and thermal calculations showed that if we add the outer walls from the glue bar 120 mm wide, and then insulate them from the inside of the house with a stuffing heat insulation based on wood fiber with a layer of 200 mm, then the carrying capacity, and thermal insulation properties will correspond to the desired level. However, the Customer did not agree with this conclusion and decided to use a gluing bar with a width of 160 mm. As a result, the resistance of the heat transfer of the walls after their insulation from the inside of the house with a stratum insulation layer with a thickness of 200 mm was 6.62 m² • ° C / W.
Warm outdoor walls complement energy-saving wooden windows. Their frames and sash consist of four alternating wood layers (pine) and have a thickness of 80 mm. In three-hour glass windows, low-emission glass was used, and the interconnect space is filled with argon. As a result, the coefficient of wind heat transfer is 0.9 W / (m² • K), and the noise reduction index ranges from 32 to 40 dB.
Heating and ventilation
The main source of heat for the heating and DHW system is the Wirbel EKO-CK Plus boiler, equipped with two combustion chambers: main works on pellets, backup - on diesel fuel. Pellets in the burner of the boiler are served from a metal bunker placed in the immediate vicinity of the boiler, there are approximately a week of fuel. Behind the wall of the boiler room there is a storage room (from the calculation for a month) - they are fed to the bunker automatically using a screw conveyor. The transition from the pellets (if they are over) the diesel fuel is also automated. The submission of the latter is carried out from the adjacent space from the boiler room, where two capacity from the polymer material with a volume of 500 liters is installed.In addition to the boiler indoors, two boilers are located, one of which (1000 l) warms the technical water, the second (500 l) - water entering
In the cranes in the kitchen and bathrooms.
Next to the boilers is the thermal pump housing, which is used both for heating or cooling air for the ventilation system (the process occurs in a channel heat exchanger) and to obtain hot water. Moreover, in the summer, when the heating boiler does not work, the heat pump completely takes on the function of water heating. This work is mainly carried out at night, when the electricity tariff is minimal (than and the large capacity of boilers is explained). Switching the heat pump from heating (cooling) air heating and back is automatically executed. The inflow and outflow of air from the residential premises is carried out on plastic heat-insulated air ducts - after exiting the heat exchanger, they rise to the overlap of the first floor and then distributed from the premises of both floors.
To our story about the construction of an energy efficient home, it remains quite a bit. In order to ensure the dwelling with warmth, first of all raised the garage. The latter was built on frame-panel technology, so it was not so warm as the house, but it was collected in just five days.
Floor plan
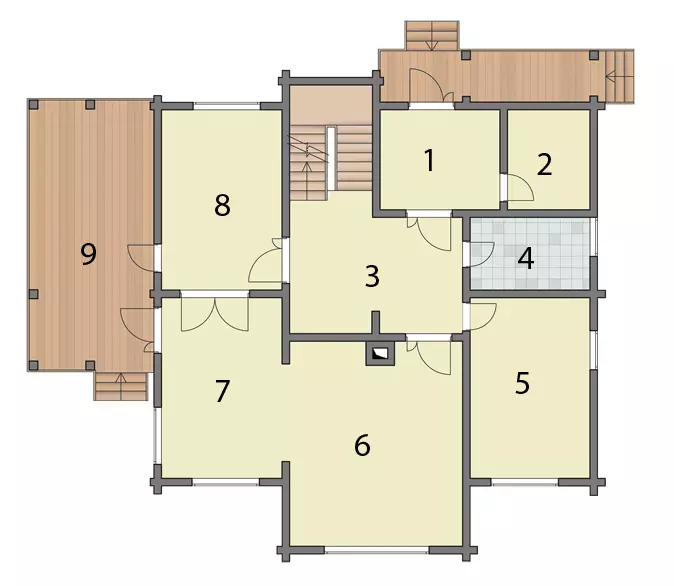
1. Tambour 8 m2 2. Technical premises 6 m2 3. Hall 16 m2 4. Bathroom 6 m2 5. Bedroom 15 m2 6. Living room 26 m2 7. Dining room 15 m2 8. Kitchen 15 m2 9. Veranda 24 m2
Plan of the second floor
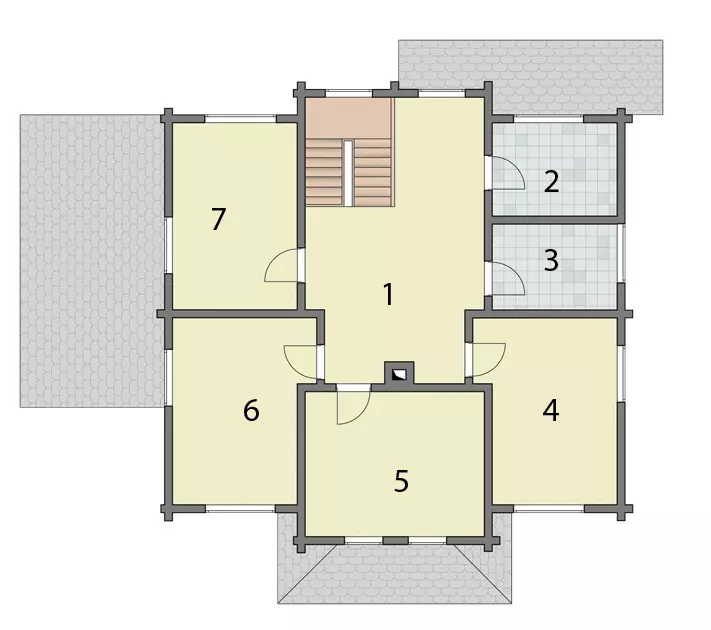
1. Hall 25 m2 2. Squeezing 8 m2 3. Bathroom 7 m2 4. Bedroom 16 m2 5. Bedroom 17 m2 6. Children's 16 m2 7. Recreation area 15 m2
Enlarged Calculation of the cost of arrangement of the house box with a total area of 240 m2 *
| Name of works | number | Cost, rub. |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation, Walls, Partitions, Overlap, Roofing | ||
| Device of a warmed foundation "Plate on a tape" | set | 1 150 000 |
| Filling of polystyrene fibergetone 150 mm and screed 60 mm | set | 210,000 |
| Insulation base and basement base | set | 60 000 |
| Assembling a set of houses on the customer's plot | set | 1,500,000 |
| Warming of outdoor walls, partitions, roofs | set | 425,000 |
| Device of the rafting system and roofing flooring | set | 465,000 |
| Installation of wood windows 62 m2 | 125,000 | |
| TOTAL | 3 935,000 | |
| Applied materials on the section | ||
| Concrete, Armature | set | 450,000 |
| Set of glue parts (beams, pillars, timber) | set | 1 933 000 |
| Set of internal frame walls and partitions | set | 371 000 |
| Set of mounting elements and hardware | set | 98,000 |
| Woodenuminous windows inwido 62 m2 | set | 1,400,000 |
| Cleaning beams, rafters, OSB-slabs flooring | set | 465,000 |
| The set for insulation, etc. (steam-, wind insulation) | set | 370 000 |
| Integrated insulation Gutex Thermofibre | 90 pack. | 337 500. |
| Roofing CatePal Katrilli (On Veranda, Porch, Erker) 267 m2 | set | 210,000 |
| TOTAL | 5 634 500. | |
| TOTAL | 9 569 500. |
* Calculation is carried out without accounting of overhead, transport and other expenses, as well as profit of the company.
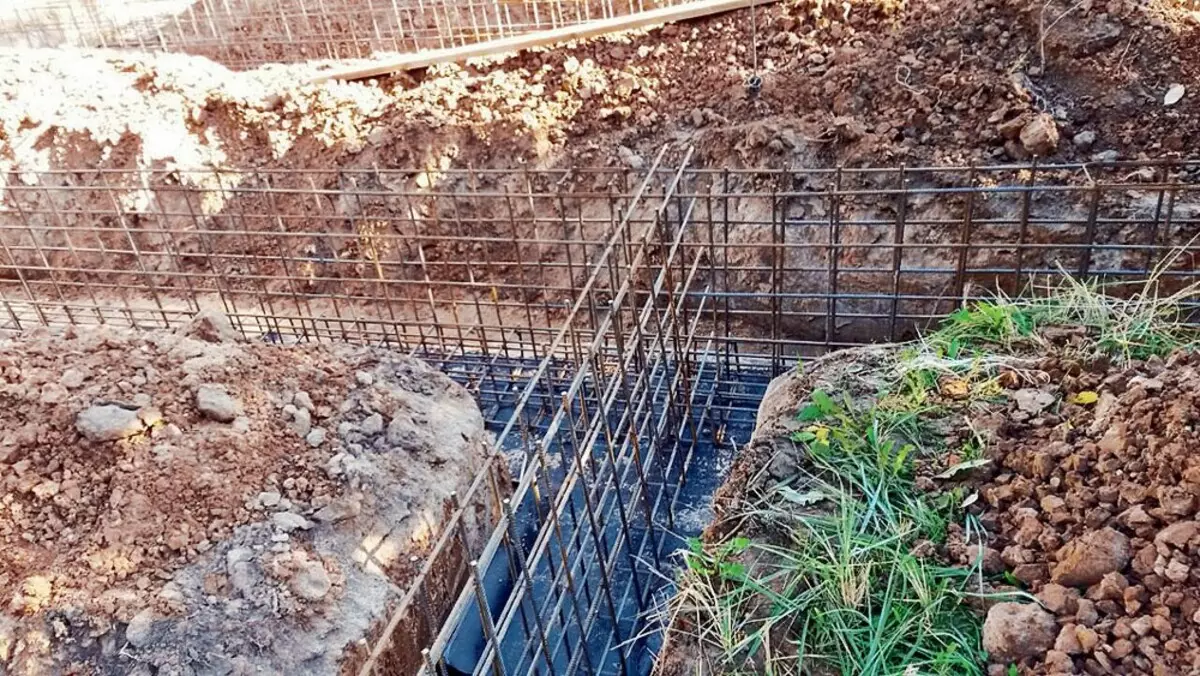



































For the foundation device, the trenches depth from 1 to 1.5 m (the site has a slope), the bottom of which weed with rubble. Next, in trenches from concrete B7.5, "preparation" was filled with 500 × 100 mm and, when the concrete harvested, the waterproofing was used on it and the reinforcement frame was mounted.
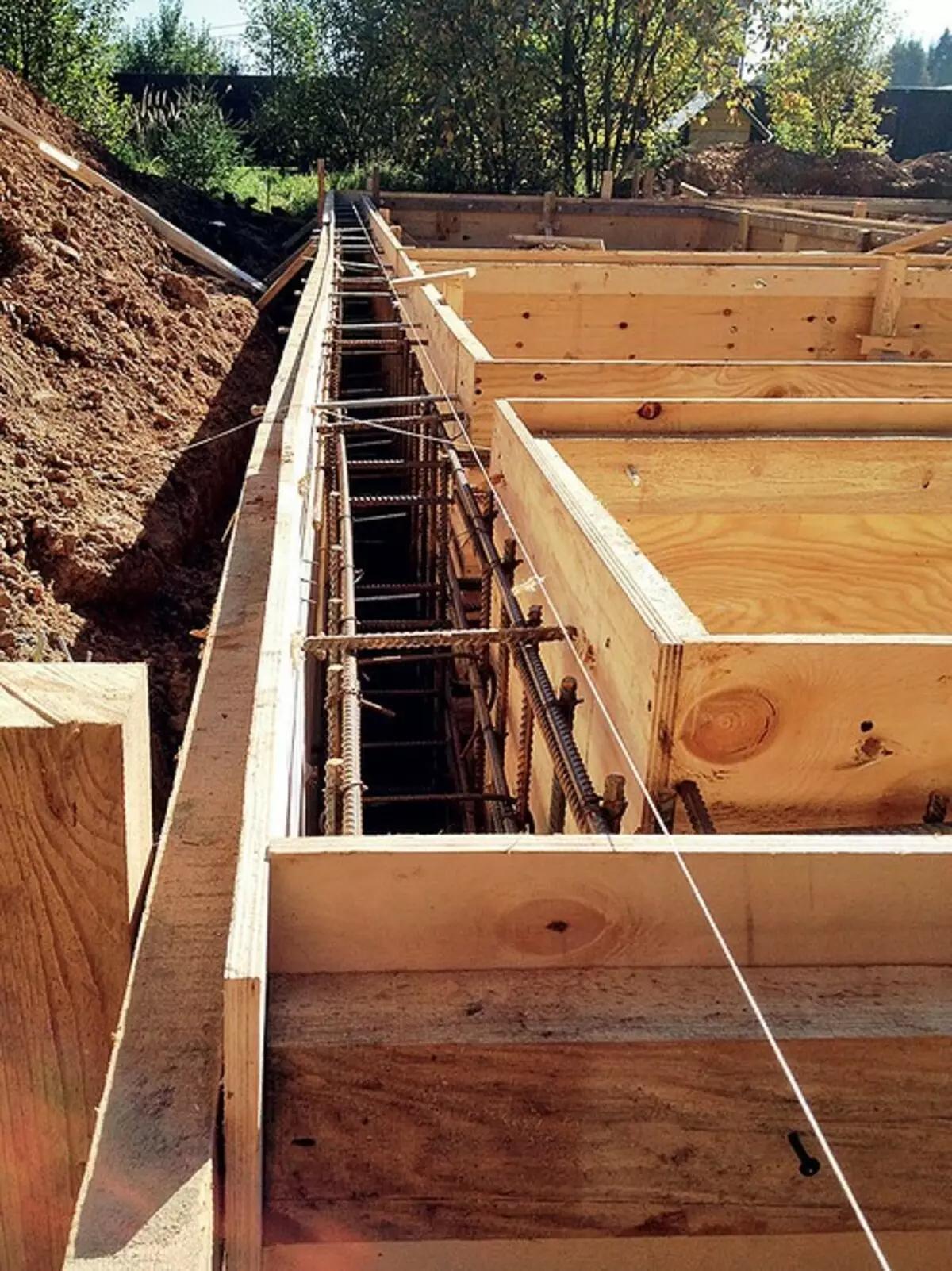

Then in the trenches installed formwork
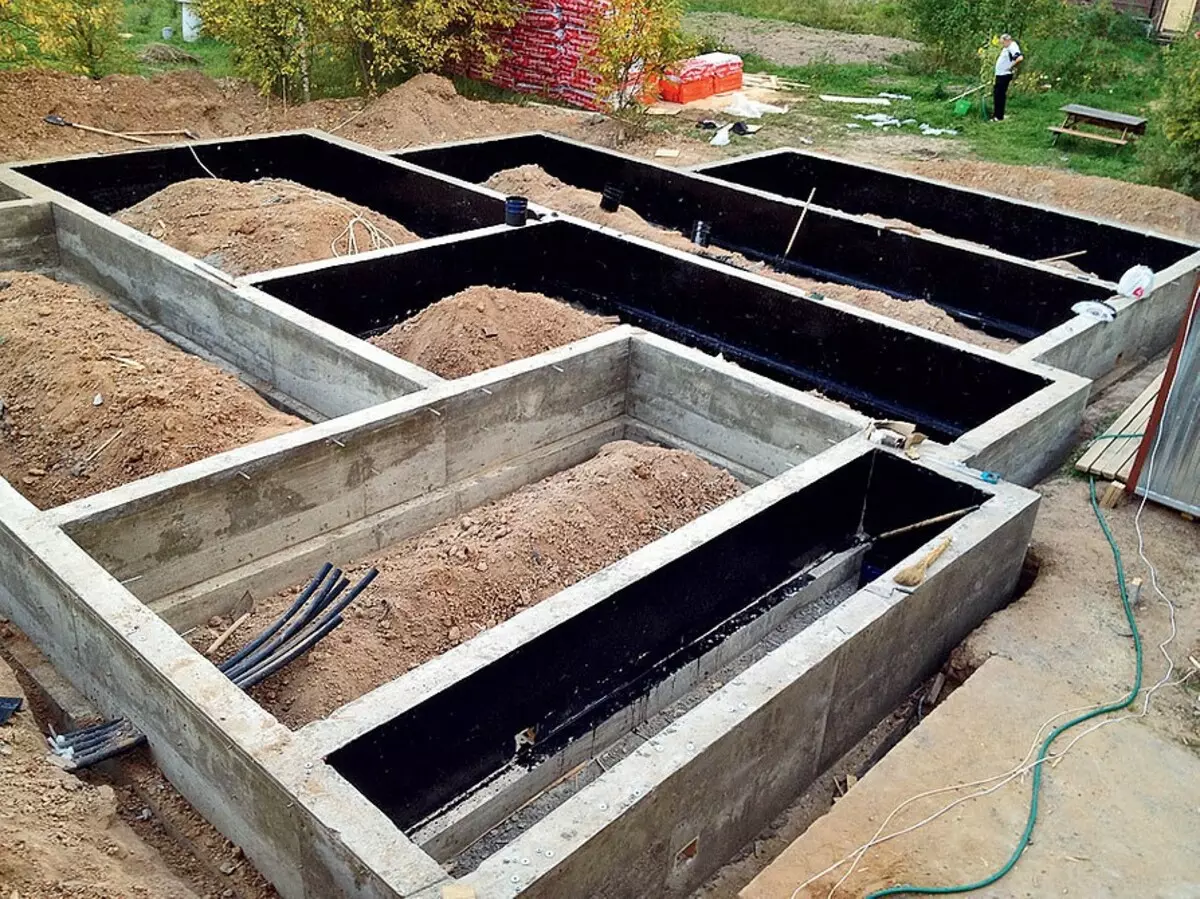

From concrete class B22,5 cast ribbons width 360 mm (height over the ground 200-500 mm)
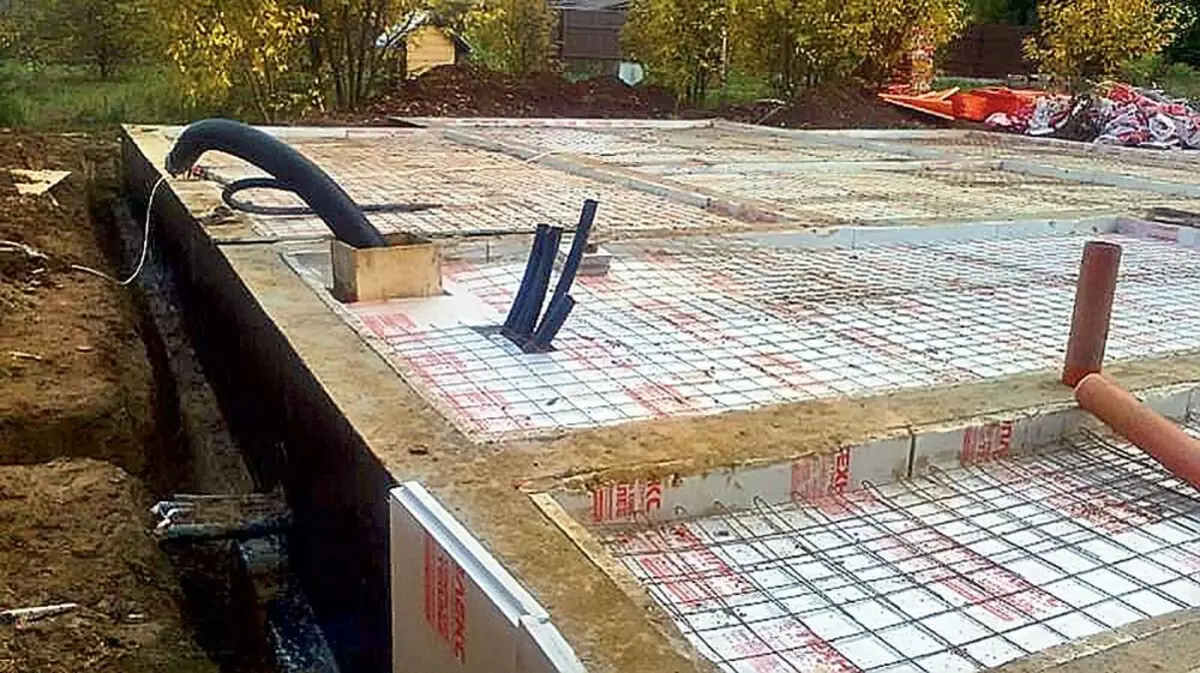

The space between them was covered with sand, on top of the plates of extruded polystyrene foam 50 mm

They laid an armature frame and cast a monolithic concrete slab (concrete B22,5) with a thickness of 110 mm
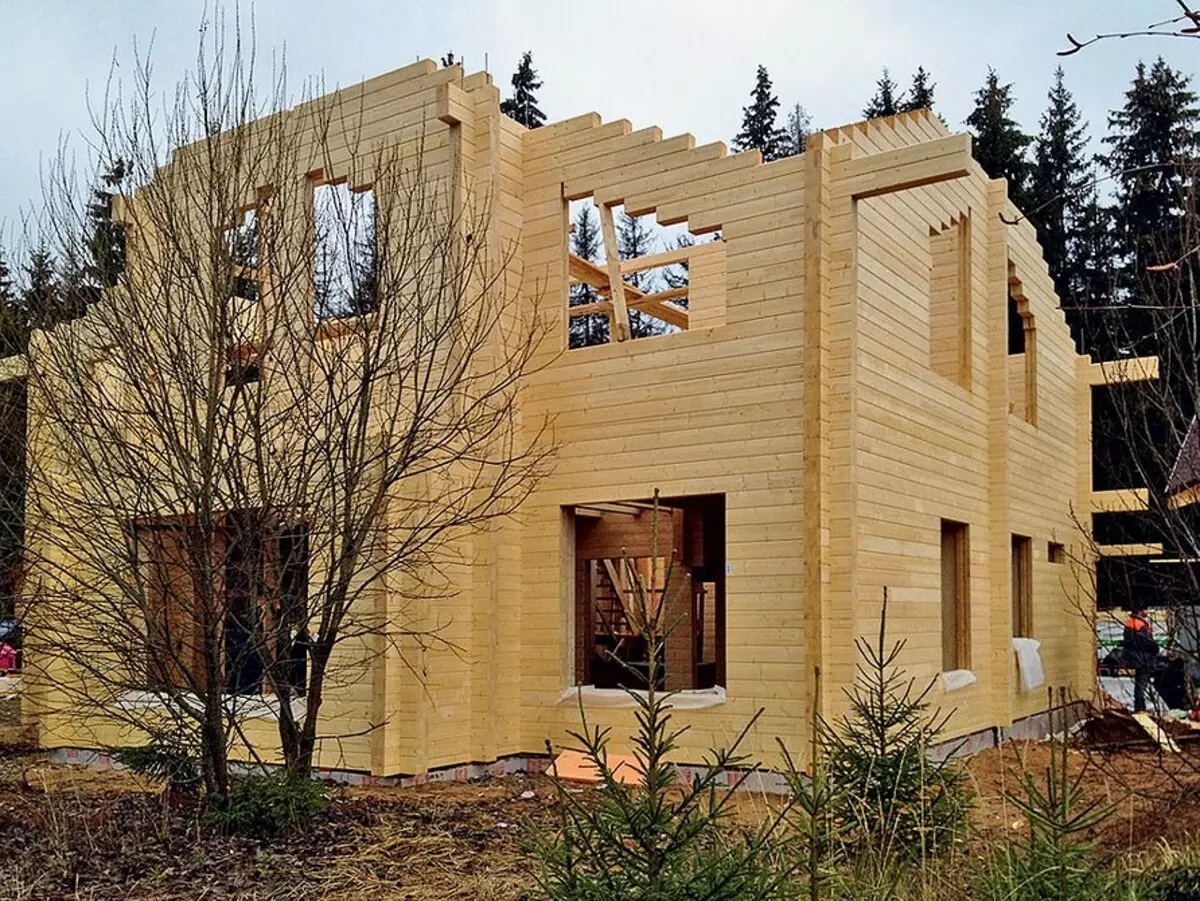

The walls of the house were folded from a gluing profiled case with a cross section of 160 × 185 mm (sh × B). Wooden brazening and threaded studs during assembly did not use, which is permissible only with a high-quality bar
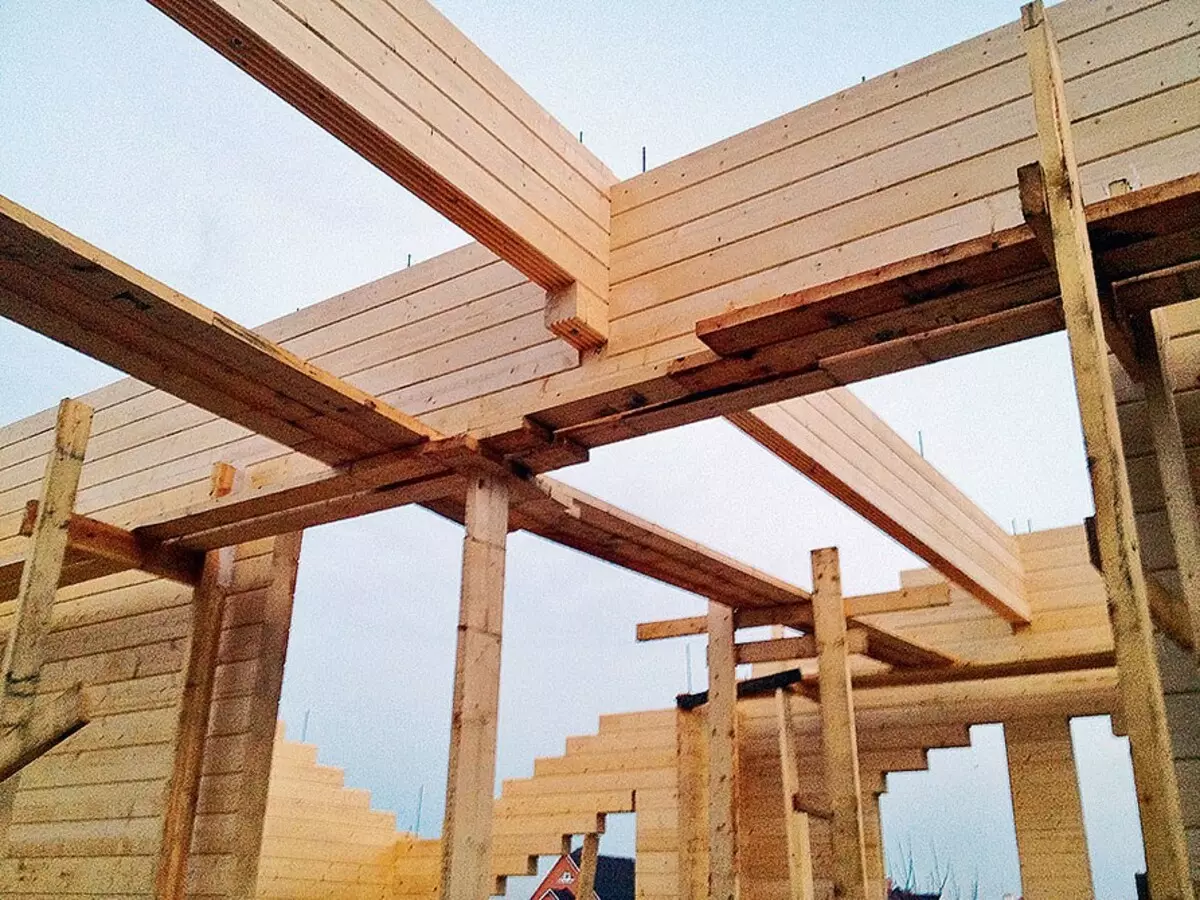

But the precast beams and runs not only pulled the studs, but also pairwise built their components of their bars with self-draws with a length of 400 mm twisted at an angle
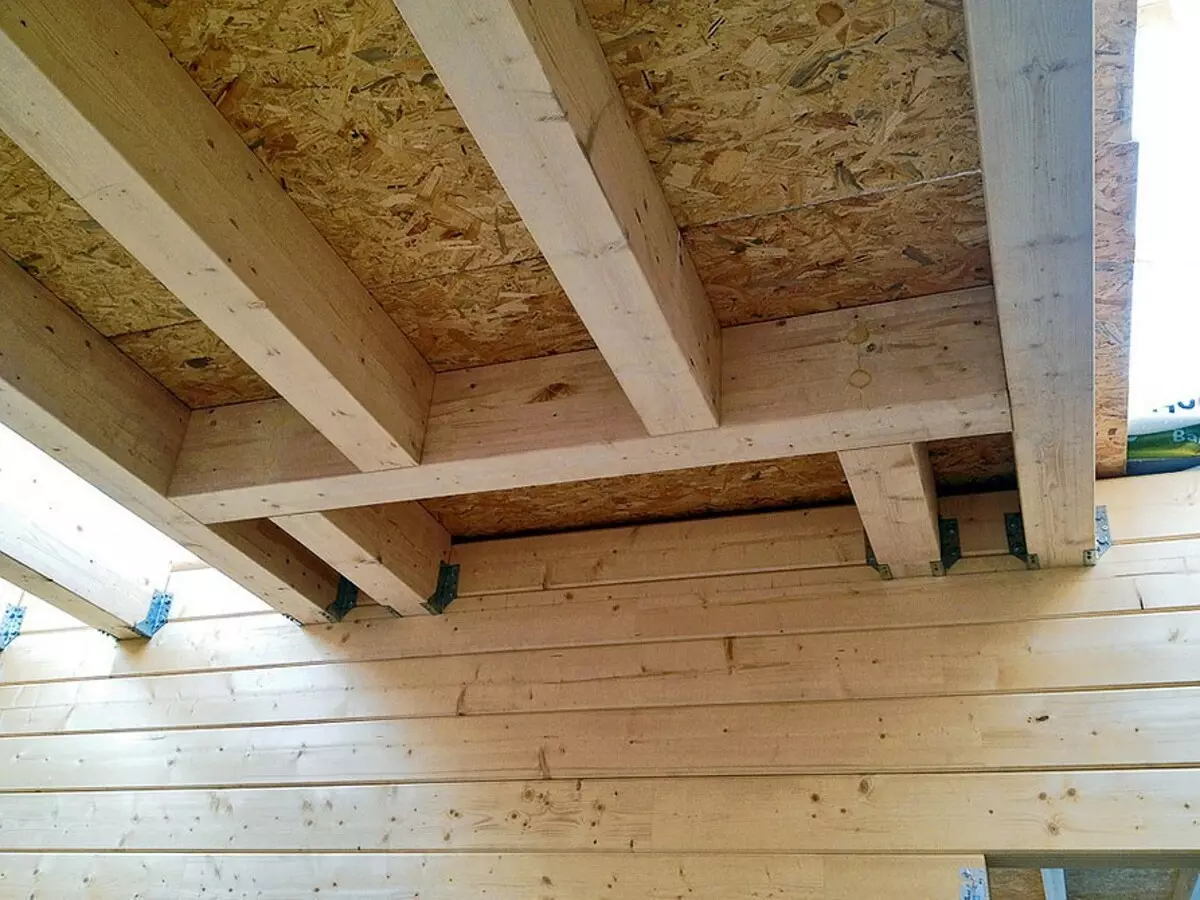

Interconnecting in each room was built individually using wooden beams with a cross section of 240 × 140 or 200 × 100 mm (depending on the length of the span)

To the walls and to each other beams fucked metalloelements
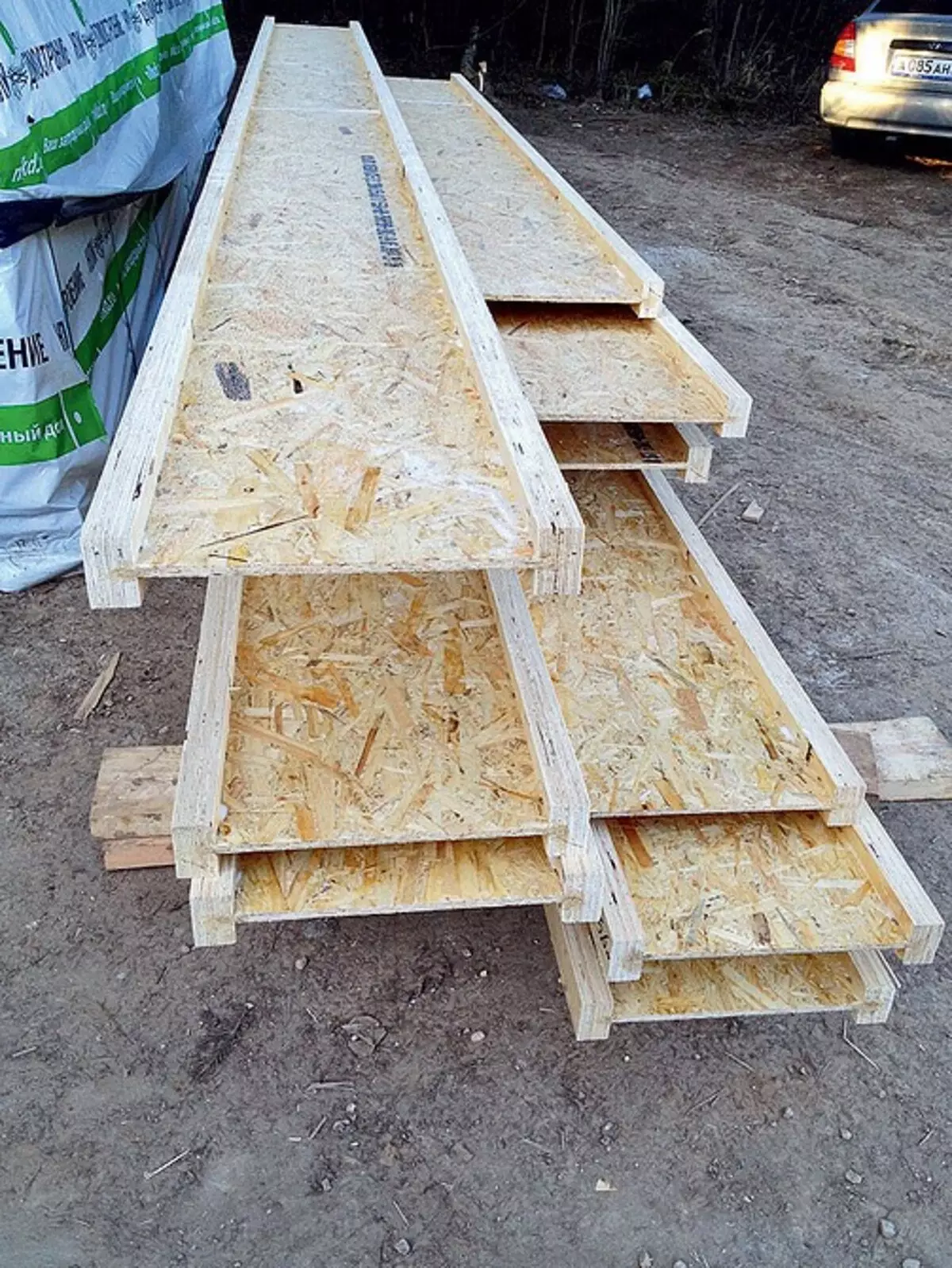

The rafal system of the octal roof is elevated using 2-letter beams with a height of 400 mm with shelves (width 64 mm) from the tree and connecting them by the walls from the OSP plate with a thickness of 10 mm
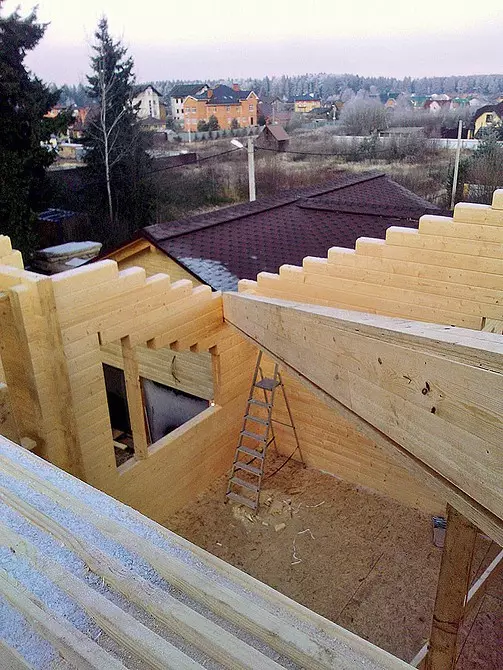

Installation of the design began with the installation of beams in endowes - tweed 2-meter structures with a length of 9 m, the walls of which were reinforced by boards with a thickness of 24 mm. Rafters from single dual-level beams mounted in a step along the axes of 600 mm
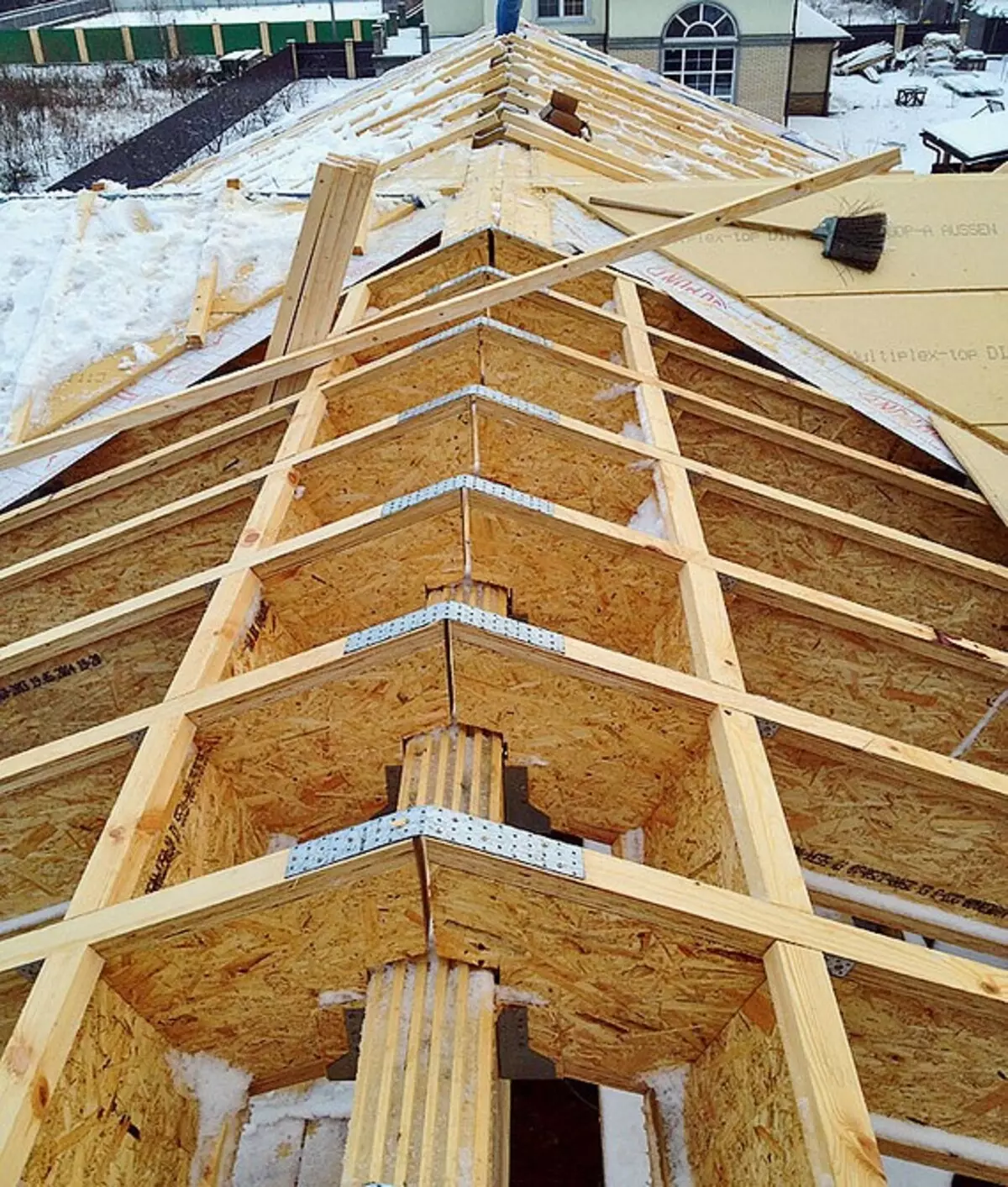

Boots and external brusade beams, runs and external brusade walls with metalloelements
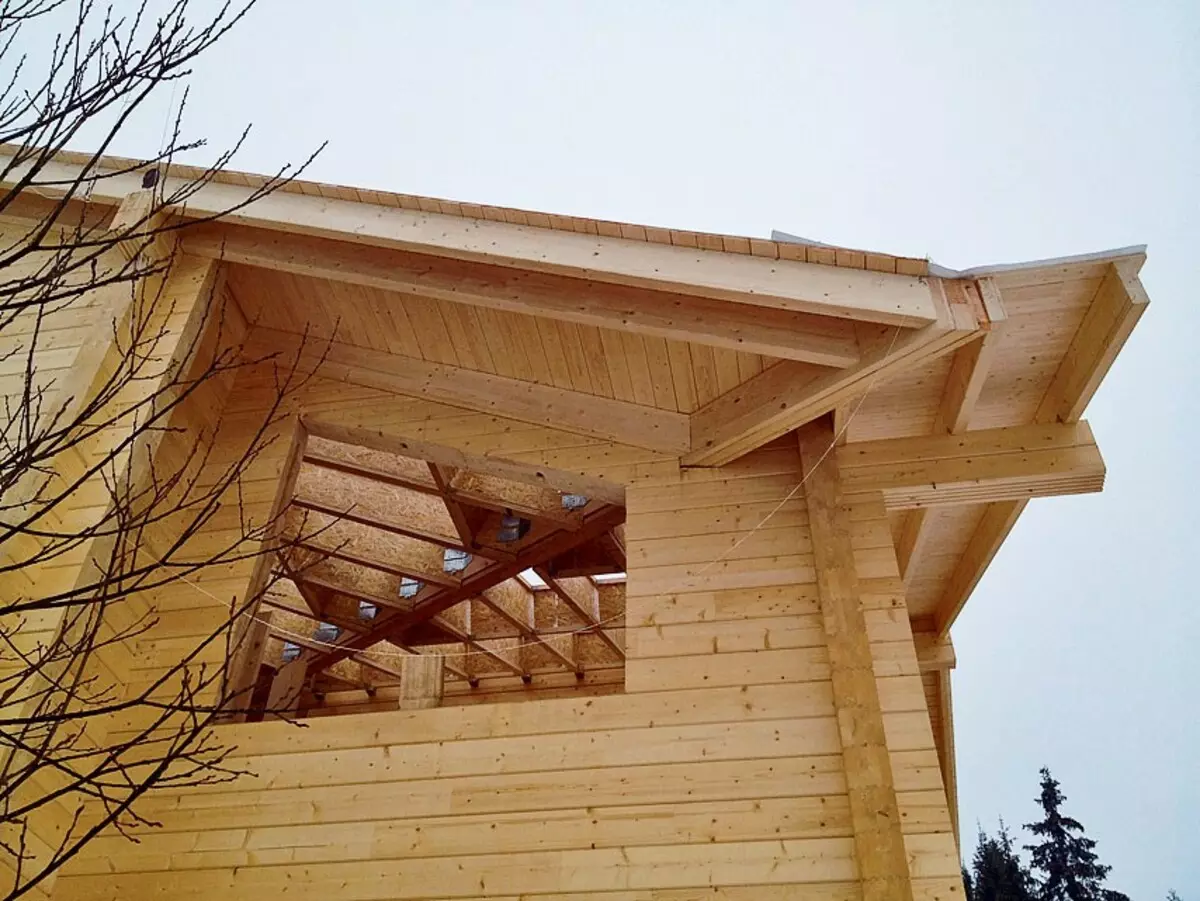

On the overlooks of the roof staged a solid flooring of a cross section of 97 × 20 mm
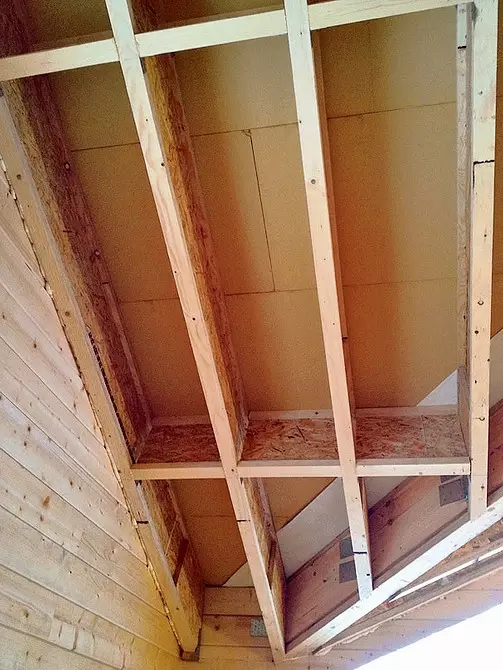

On the insulated areas of the roof on top of the rafter, we made a solid flooring from the rains the underpants heat insulating plates based on the Gutex Multiplex-Top Wood Fiber Top 35 mm thick

Plates are connected to each other using a spike system and grooves (which allows them to have their joints, without conforming to the rafted step) and are attached to rafters galvanized self-draws.
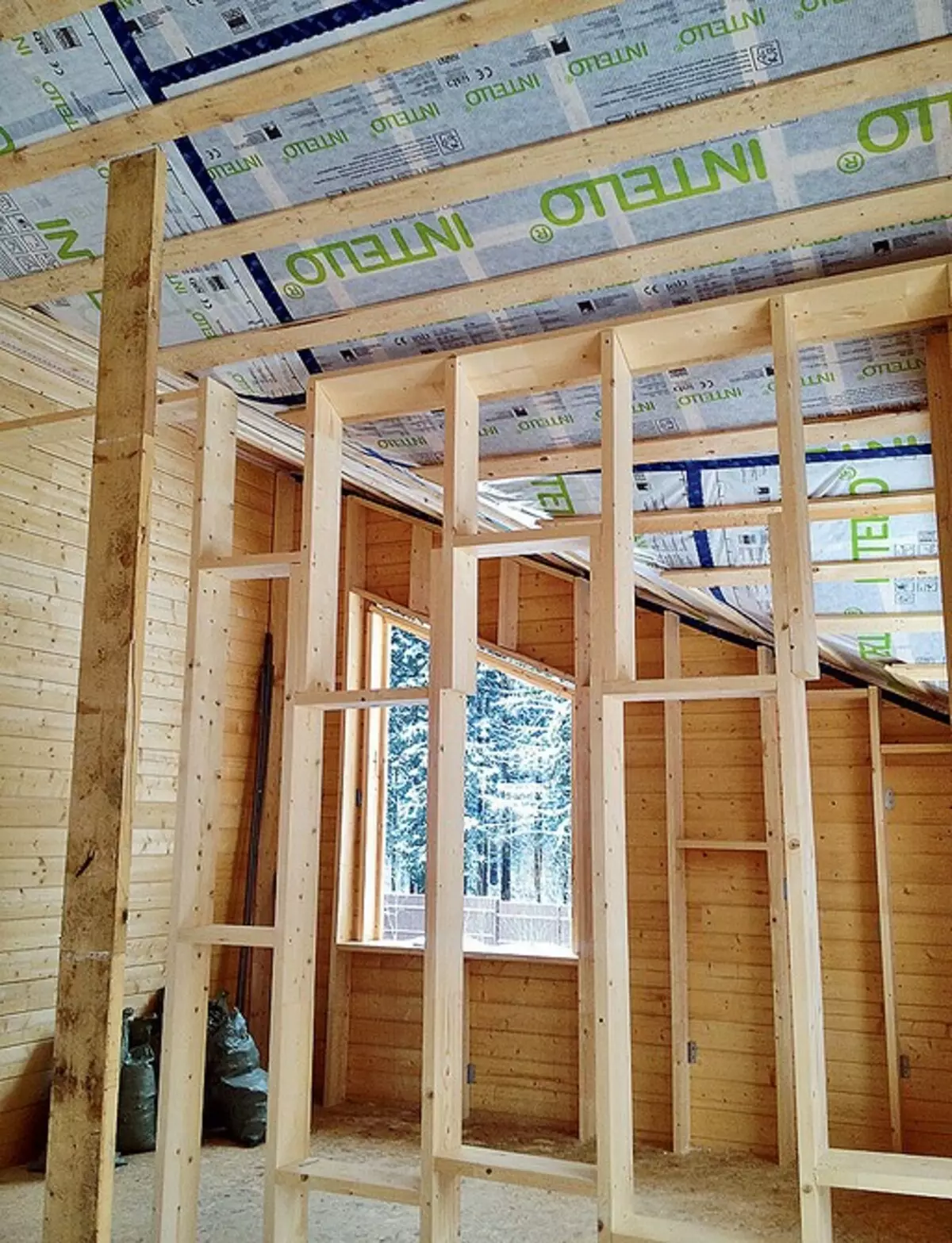

The bottom to the rafters were attached to the Intello Plus membrane and pressed it with a cut from the board with a cross section of 90 × 20 mm. Next on both floors built the framework of interior partitions from the board with a cross section of 150 × 45 mm

On the perimeter of the external walls from the inside of the house attracted frame structures from the board 200 × 24 mm (22, 25), connecting them with a sliding method (23, 24)
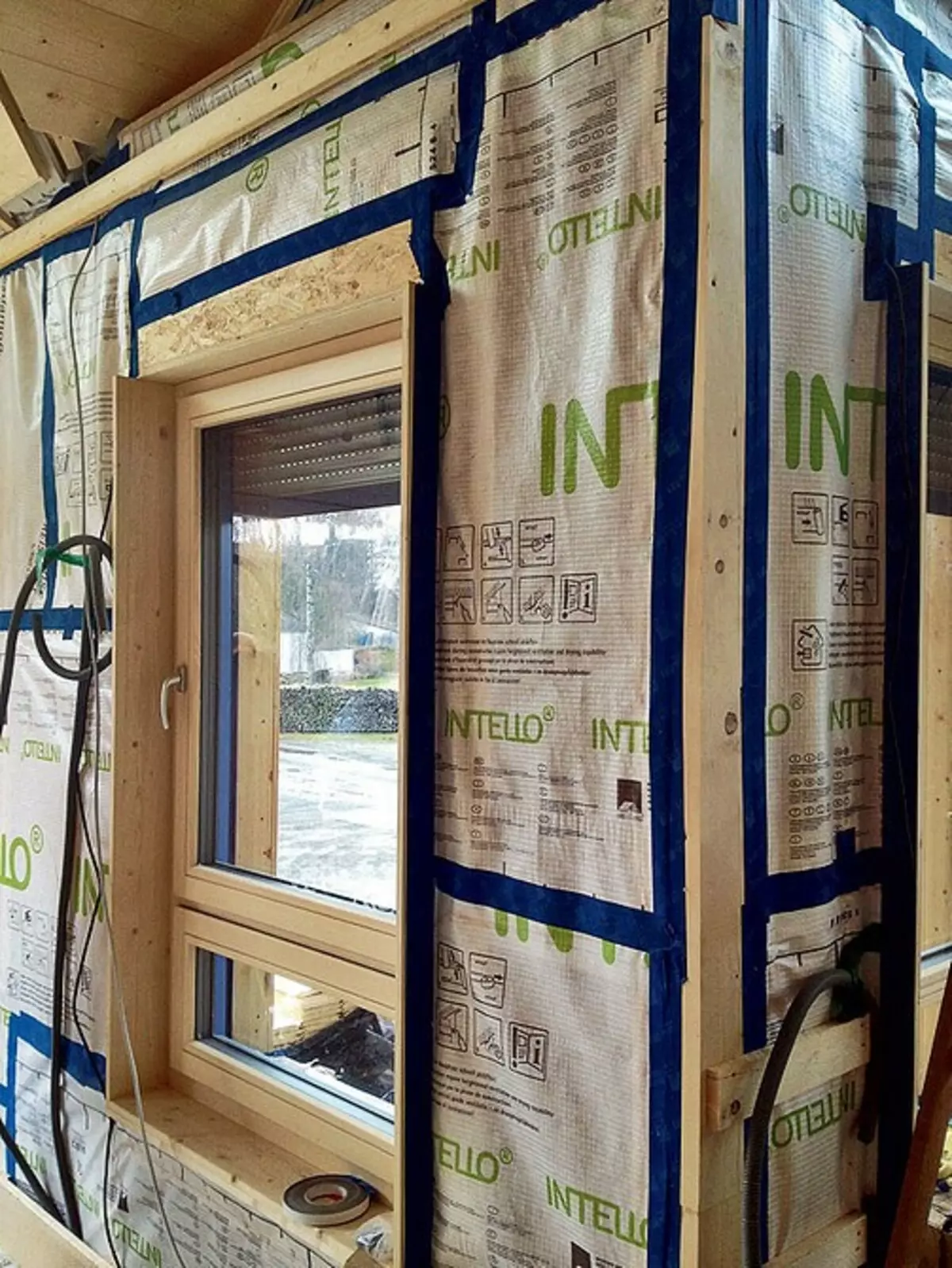

To the frame of the exterior walls attached vaporizolation

Gaming the joints with a special scotch, and pressed her lands
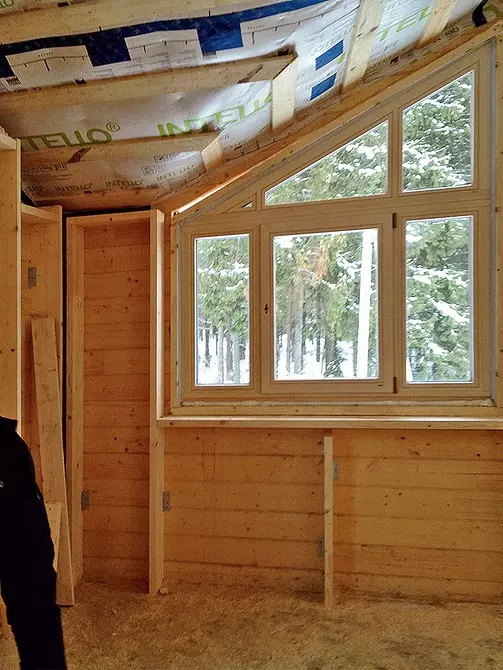

Before proceeding with the insulation of the outer walls and roofs, casing boxes were installed in window caps on the sliding landing, and then the frames of energy-saving windows were attached to them (heat transfer coefficient U = 0.9 W / (M2 • K)

The basis of energy-saving windows are frame structures from glue wood. From the side of the room, their wood is protected only by a decorative and finishing layer. Outside it is covered with aluminum lining
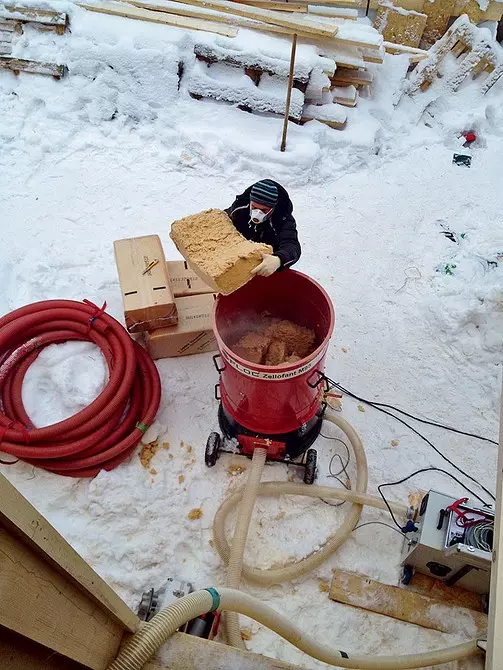

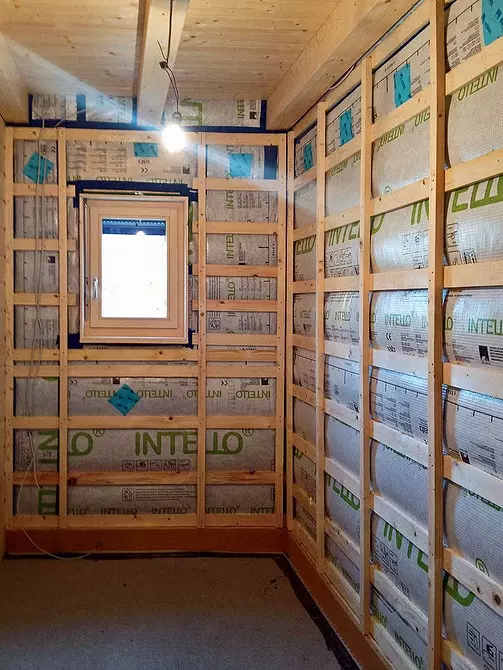
For the insulation of the roof (layer 400 mm) and the outer walls (layer 200 mm), the enlarged thermal insulation of the GUTEX THERMOFIBRE based on wood fibers was applied. Material loosened in a special polar machine
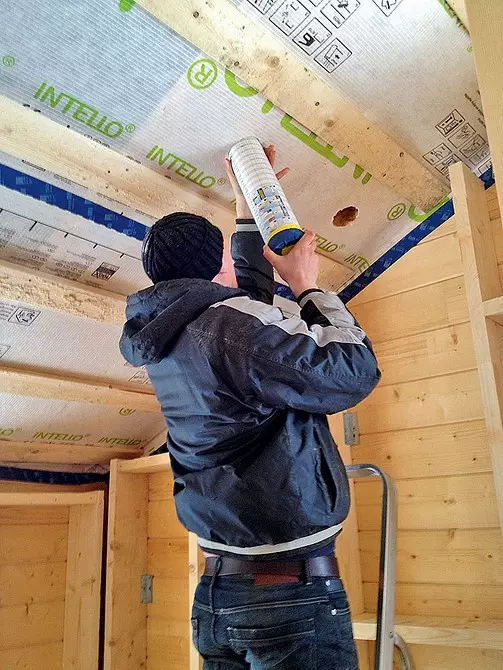

The insulation fired alternately into each cavity formed by the frame, for which the holes were cut in vapor insulation
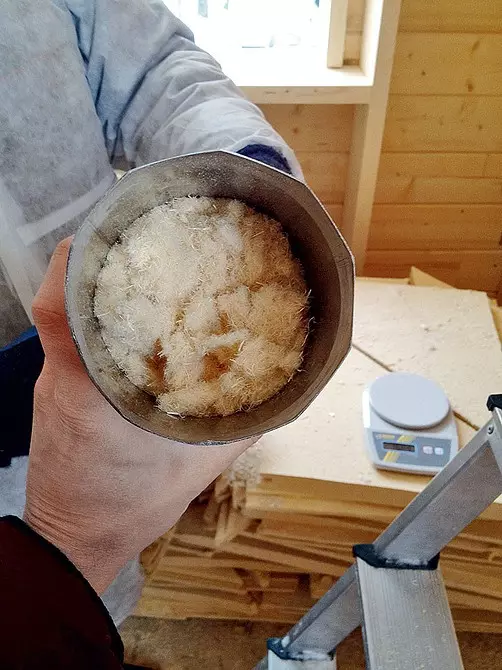

The hose was applied to the place of installation
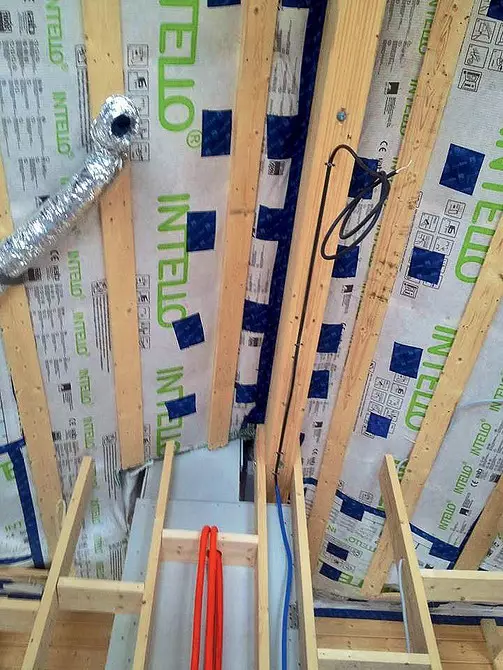

After soaking, they taped scotch
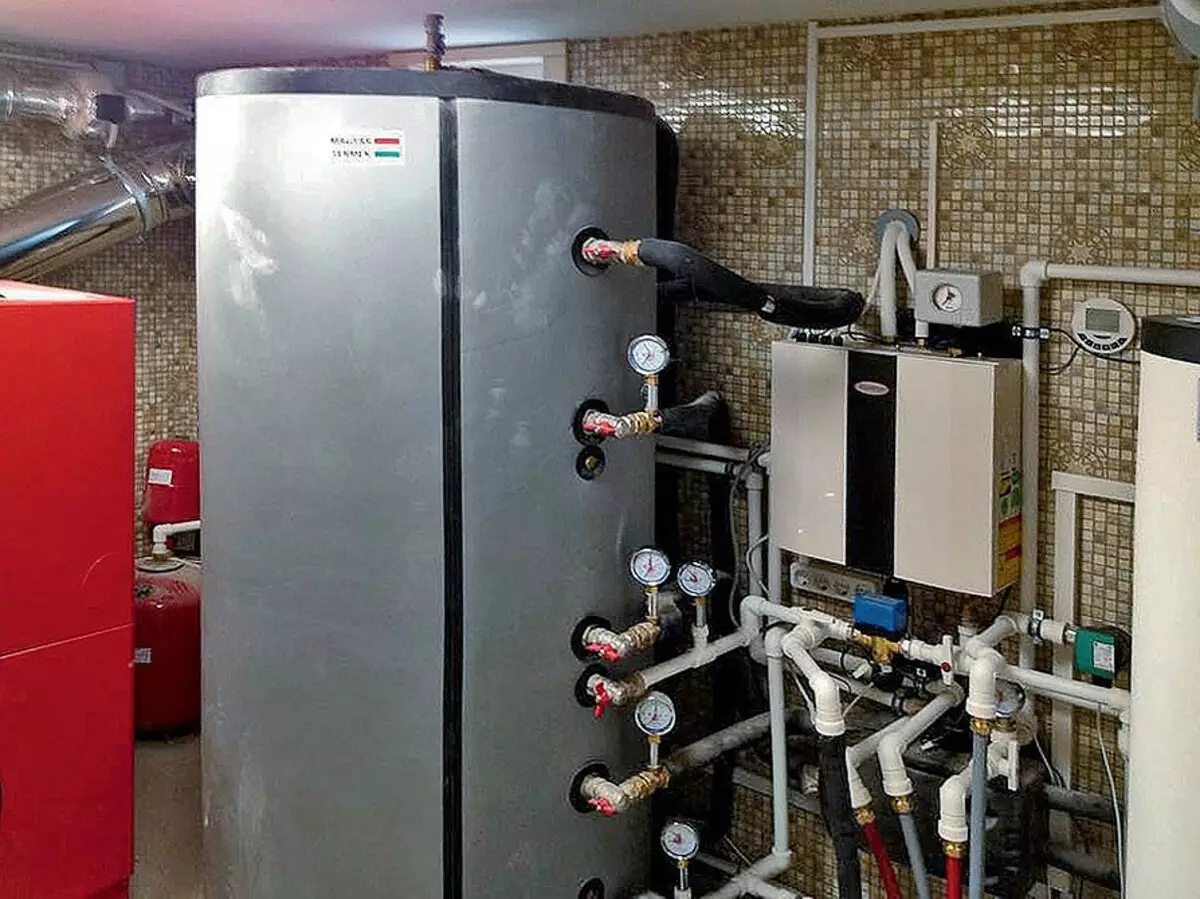

In the operating room located in the garage, the body of the heat pump, two boilers (one for the GVS system, the second for the heating system) are compactly located.
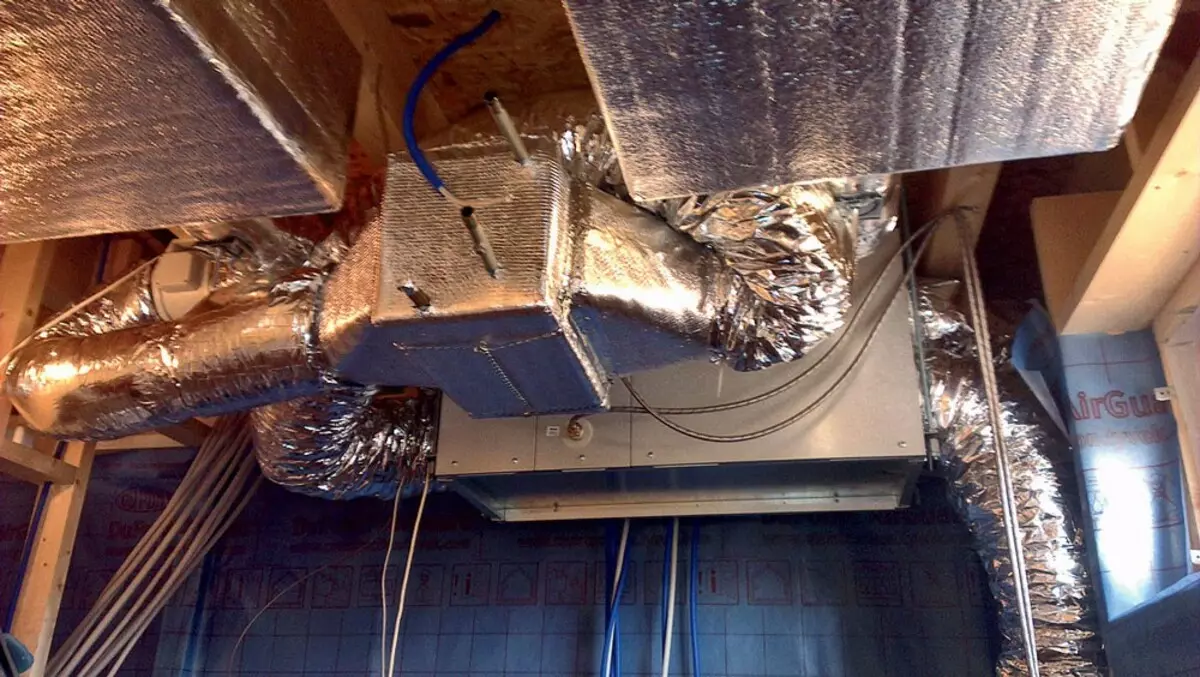
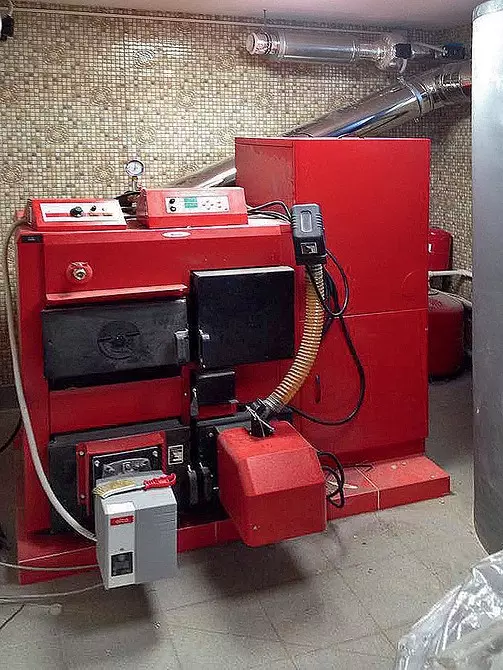


Combined pellet and diesel boiler
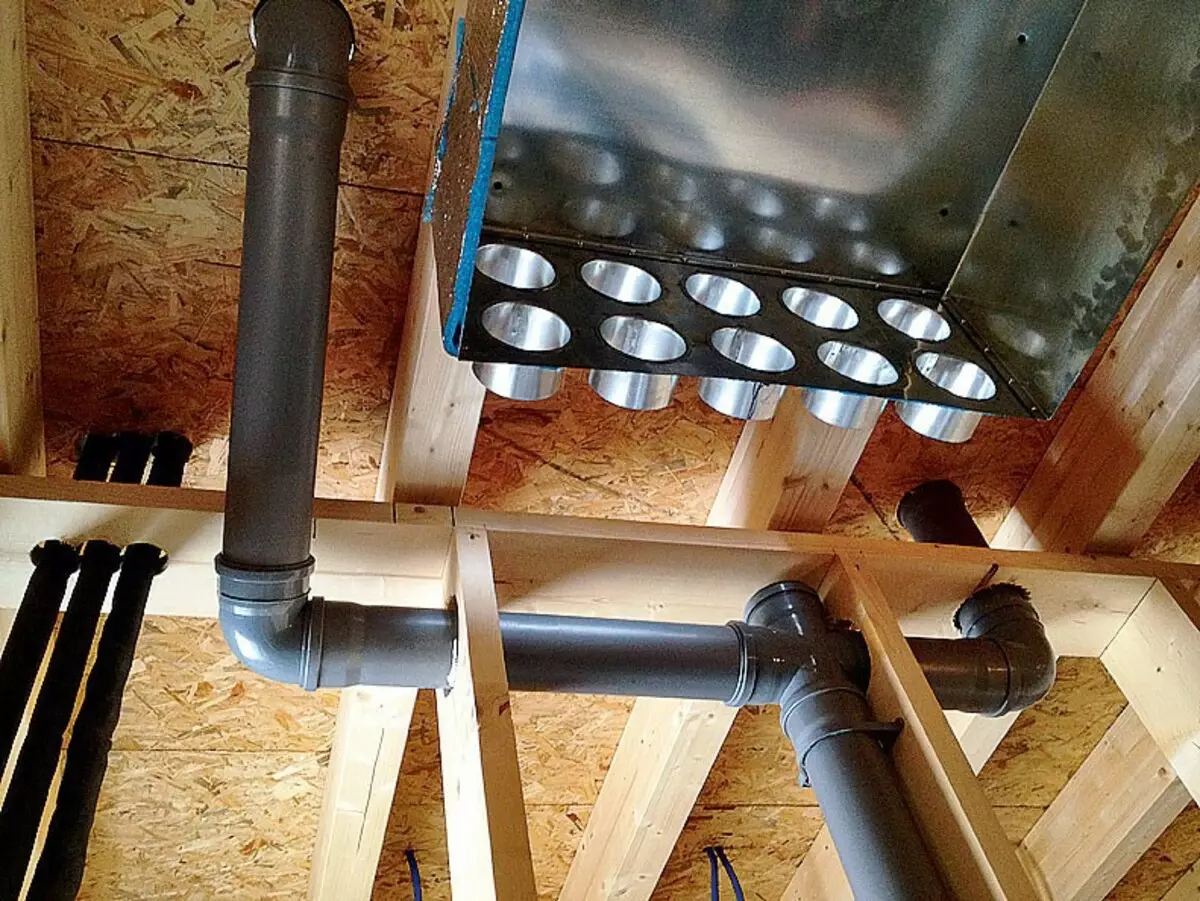

Warm air enters the switchgear, from where the hoses enters the room
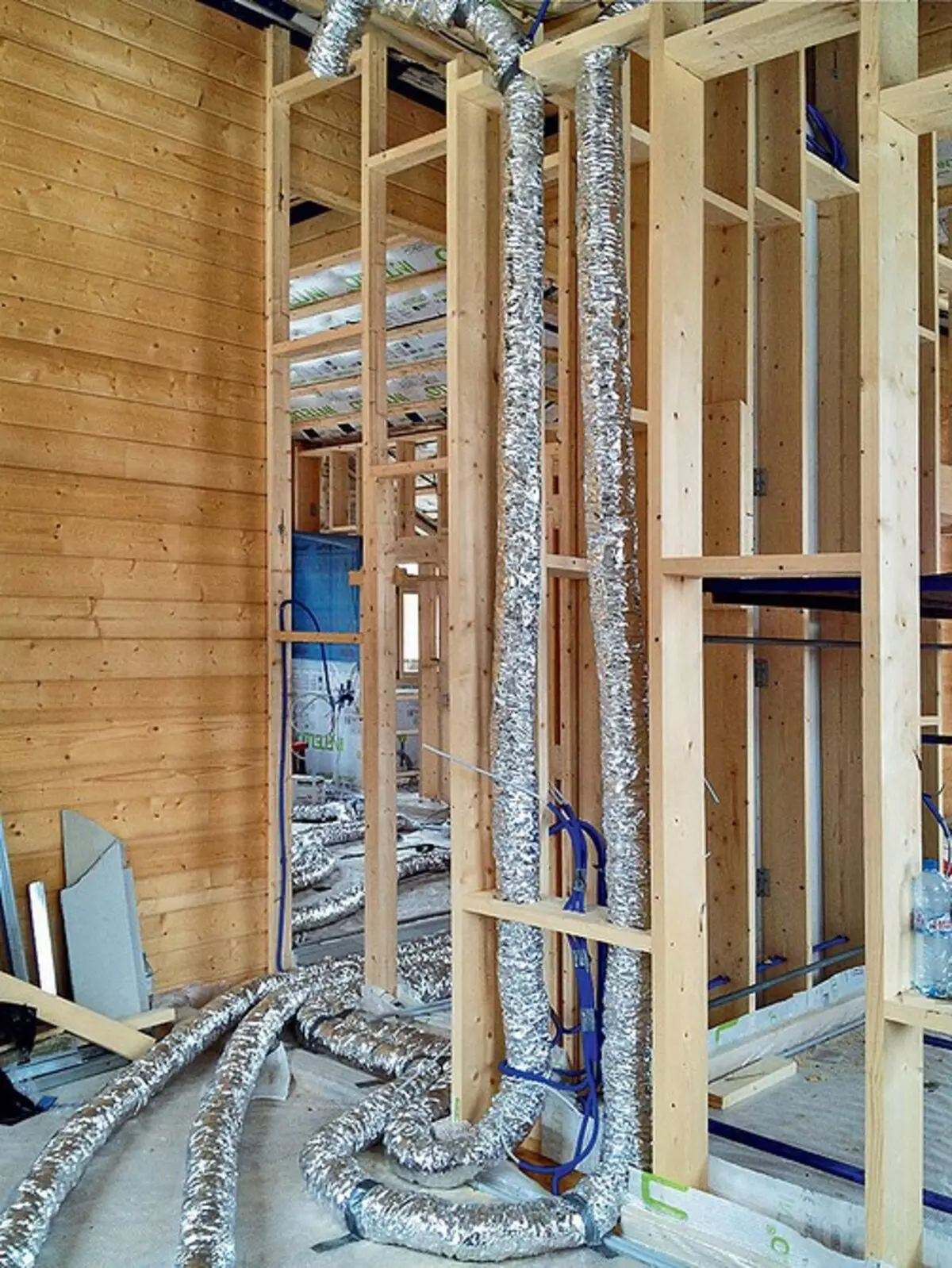

Air ducts-hoses supplying air into residential premises of both floors are laid around the first floor overlapping, as well as inside frame partitions
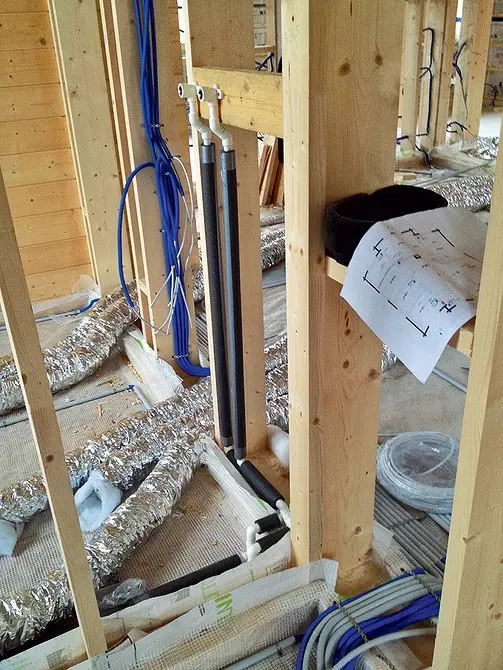

In the same way, engineering communications were conducted

External and interior walls, ceilings of the first floor and roofing races from the inside of the house are trimmed by a blackboard imitating the slope of the outer walls
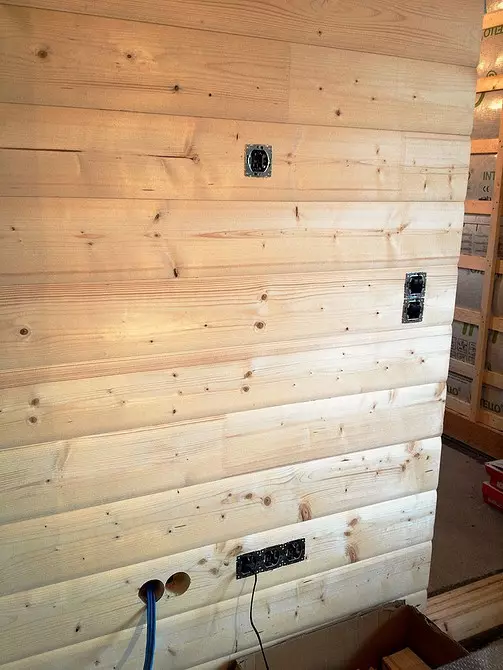

On the insulation of the outer walls, only their thickness is evidenced, which is noticeable only in the pro
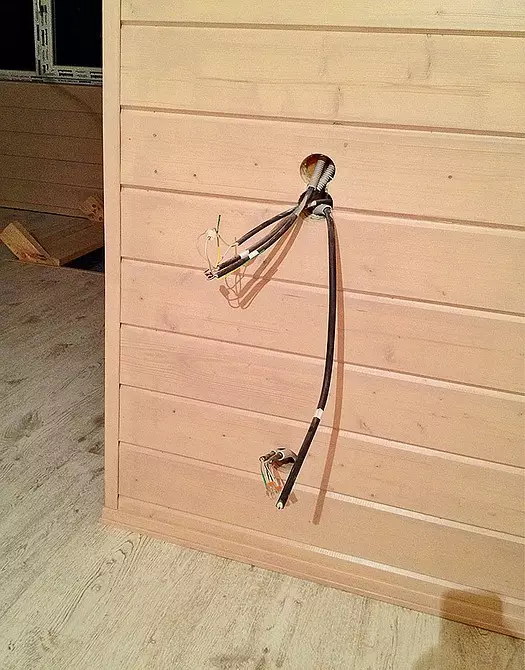

Passed in space under the skin electrical and weakly-accurate cables are removed into rooms through the holes cut in the wood, the diameter of which corresponds to the size of standard wiring boxes
