Ecode: history, concept, advantages. Ecode in Russia. How to solve the problem of conservation of heat in an energy-saving home

Scientists and science writers have always worried about the houses of the future ... Today, a conversation is very relevant about a housing that meets the new conditions and the style of life of a modern person. The natural resources of the planet are dried, global warming increases, and the universal energy and economic crisis covered all countries. Therefore, it is so important to preserve energy resources. We will begin a conversation about energy-saving homes.
In October 1973 The global energy crisis broke out, the negative consequences of predatory mining fuels accumulated by decades. I spark, which fled the crisis was that Arab oil producers ceased to supply it to countries supported Israel in an armed conflict against Egypt and Syria. The global price for 1 barrel oil increased 4 times. It was then that scientists announced the size of the explored energy reserves of the Earth. It turned out that oil, gas, uranium enough for only 50-70 years. In addition, the catastrophic results of the global warming began to be manifested due to a constant increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Residential buildings and to this day make their destructive contributions here: the anthropogenic load, rendered by them on the environment, is about 40% of the total. B70-KGG. Hchw. Scientists and architects began to develop projects of the world in the world of eco-leave.
In December 1997 In Japan, with the participation of more than 120 countries, the Kyoto Protocol was signed to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change. Objective - in the period from 2008 to 2012. Reduce the cumulative level of greenhouse gas emissions by 7% due to the development of alternative energy without burning fossil fuels and reduce heat loss. Russia November 4, 2004 Signed the Federal Law on the ratification of the Kyoto Protocol. Relationship with this law is prescribed to limit the total average emissions of six types of gases listed in the Kyoto Protocol: carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrogen pump (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFC), Elegaza (SF6) . The last three types of gases not only create a greenhouse effect, but also actively destroy the ozone layer of the atmosphere.
Ecodoma, or passive houses (from English. Passive House), called it because they did not require heating costs. The first house on the project of architects of Nicholas and Andrew Isaakov was built in 1972. In Manchester, New Hampshire, USA). The building had a cubic form, due to which the surface area of the outer walls was minimal, and the glazing area did not exceed 10% of it. Thus, heat losses decreased precisely at the expense of a volume-planning solution. To achieve comfortable microclimate parameters (temperature and humidity), the construction was optimally oriented on the sides of the light and was functionally zoned all the premises. Glass stained glass windows of southern facades were successfully combined with massive inner walls and overlaps. Sun protection was proposed in the form of protruding canopies. The ratio of the length and width of the rooms was 3: 2. Since the roof was made flat and covered with reflective aluminum, it reduced her heating and reduced the need for ventilation during the hot season. On the roof of the house installed solar collectors for water heating in the GVS system.

Rockwool. |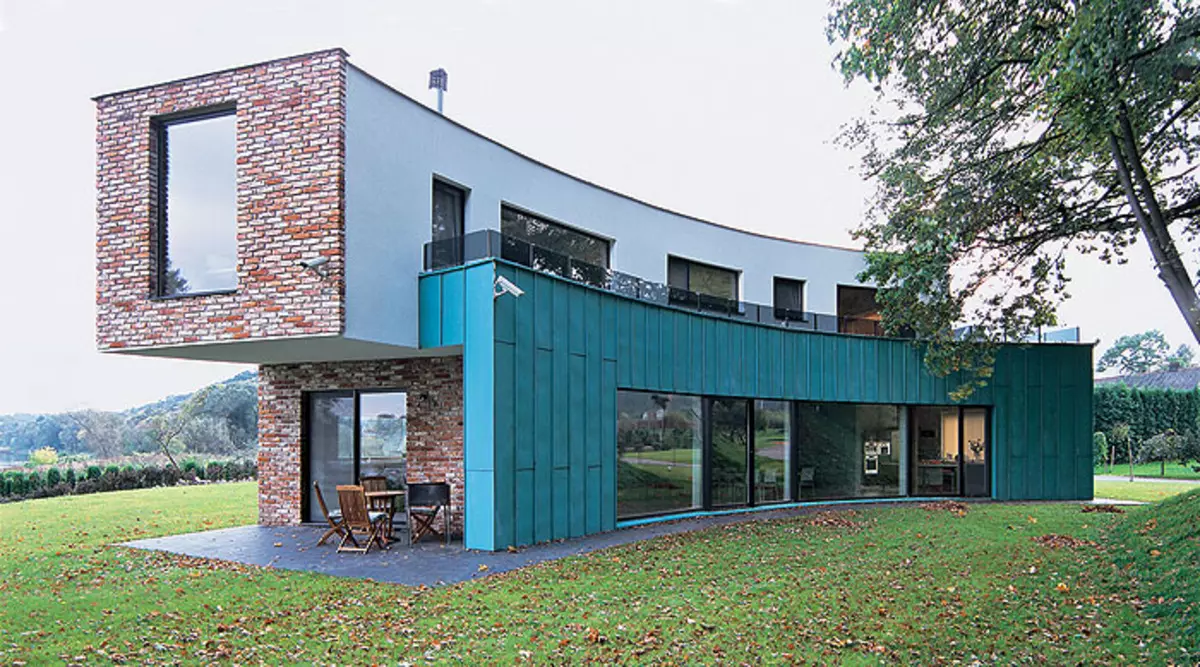 
Architects A.Kancha and Kanchite Photo E.Lichina |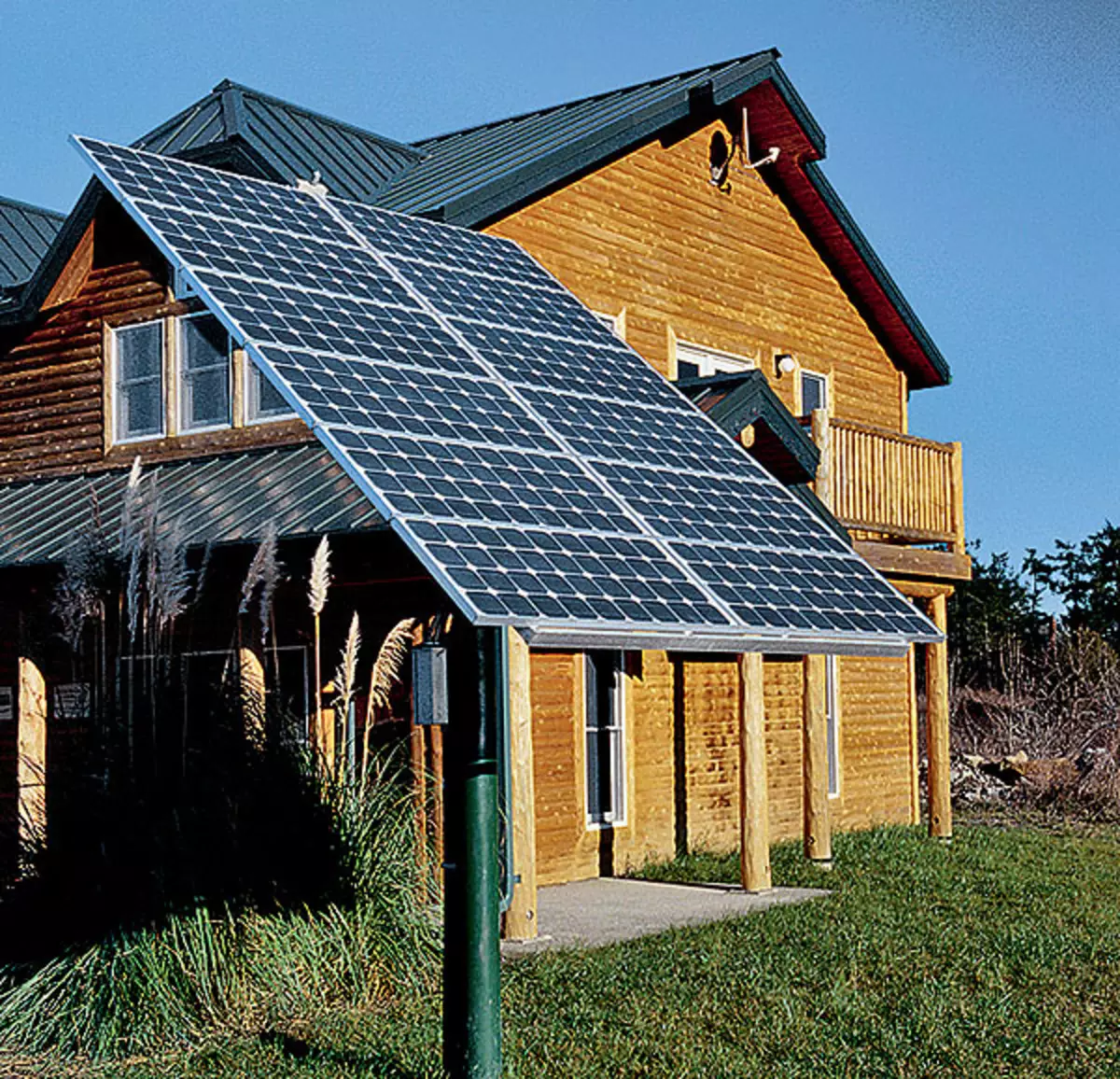 
NGO "Kvant" |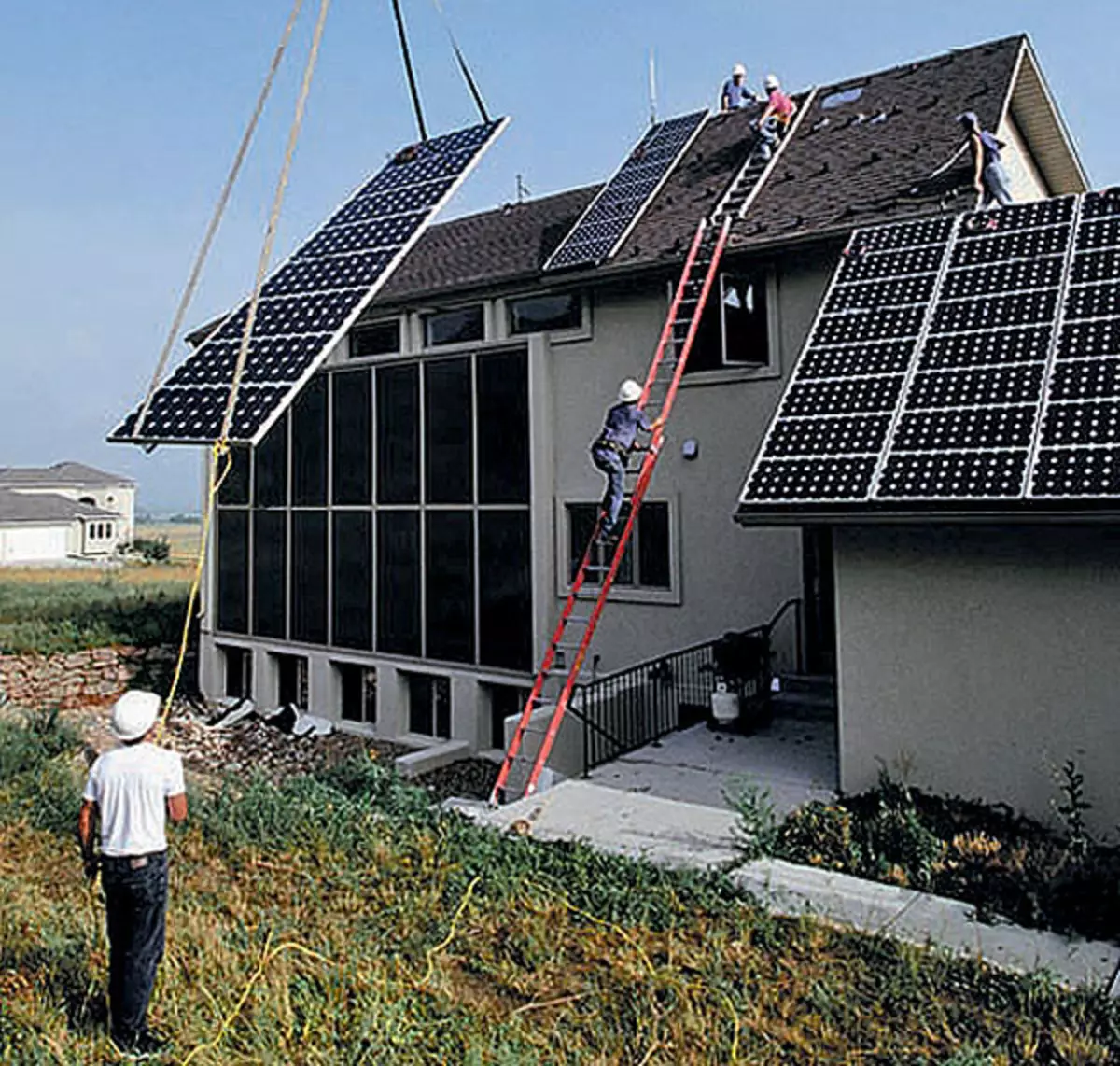 
NGO "Kvant" |
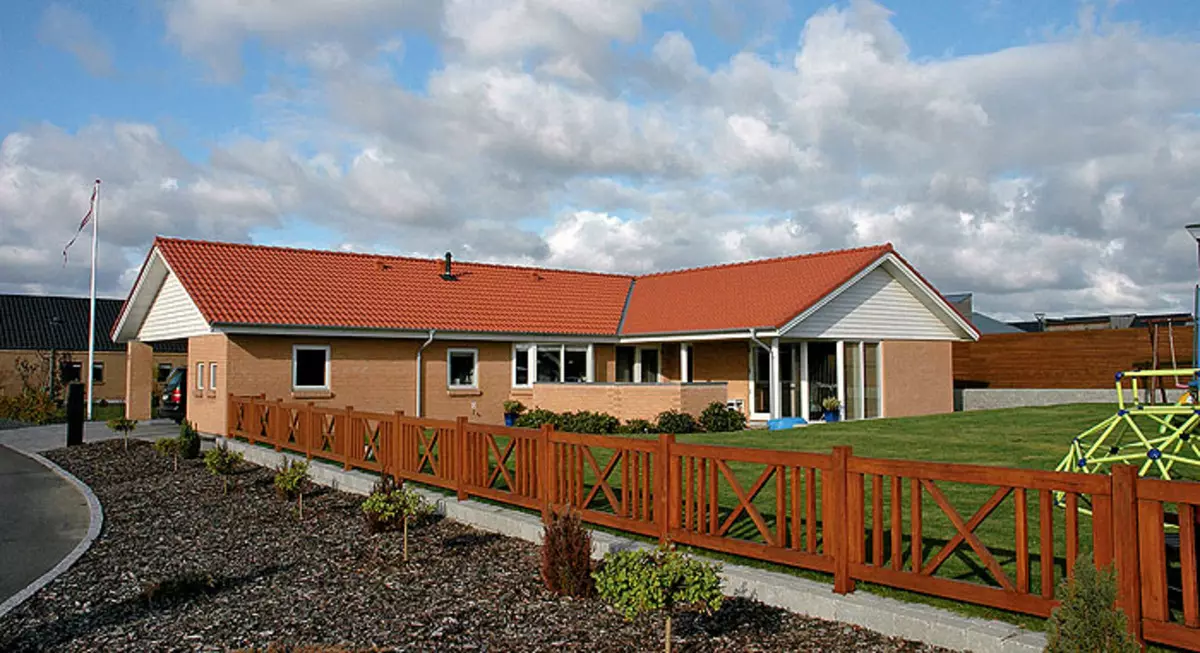
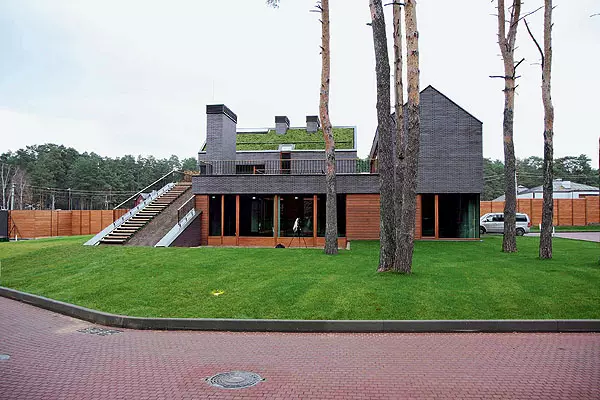
1-2.exodoma sometimes looks deliberately modestly or, on the contrary, avant-garde. But the main thing is that they allow to protect the energy resources.
3-4. Installation of photoelectric panels - eco-ecomoderization in order to increase energy depronience.
History of Ecodom in Russia
In 1972 In Akademgorodok Krasnoyarsk, at the Institute of Biophysics, a hermetic room of 315m3 was constructed to test the closed ecotechnology of the long life support of a person in extreme earth and cosmic conditions. It was divided into four blocks: greenhouse, residential cabins, kitchen, work zone. 10 experiments with crews were conducted, which included 1-3 people. The longest lasted 180 days. Scientists were used special ammunition for carbon dioxide absorption and water regeneration system that cleaned liquid waste to the condition of drinking water. To satisfy up to 80% of the need of the team in food, wheat, soy, salad, chofa (the latter - for obtaining vegetable oil) were grown in a greenhouse with artificial lighting. The plants of certain varieties with shortened stems were used in order to save the greenhouse space. Products of animal origin used in the form of canned food. After this experiment today in 5km from Akademgorodok build the first ecological cottage settlement in the country. At the same time, the task is: to try on the practice of eco-technologies tested at the Institute of Biophysics. Five houses have already been erected, 20 more are being built. Ecotechnologies are used so far only in some buildings and not in full. In the summer of 2009 It is planned to erect another 10 houses that will equip modern eco-equipment. The village is located in one of the coldest regions of Russia, but scientists hope to achieve the absolute non-volatility of buildings, full processing of organic waste into fertilizers and biofuels, as well as self-sufficiency of fresh, environmentally friendly food. Such a house makes sense to be viewed together with the site, and it is correct not passive, but rather, active, because the heat generated should be enough not only for its own heating, but also on the heating of the greenhouse and the work of the biological waste disposal system. If the experiment succeeds, it will be proved by the feasibility of the construction of such ecoposnias in any region of Russia.
Principle of Ekodoma
For the first time, the principle of Sustainable Design ("Designing Sustainable System") was formulated in May 1988. Dr. Wolfgang Faist (founder of the Institute of Passive House in Darmstadt, Germany) and Professor Bo Adamson (Lund University, Sweden). The eco-friendly house (EKODOM) is a building, a comfortable human life, non-polluting environment, non-volatile (using renewable energy sources), resource-saving (saving water and heat consumption) and a resource support (producing eco food and biofuels).
No urban apartment, no country house is able to give a person such a sense of freedom and independence, as its own eco. Of course, the governments of many countries understand that for the sustainable development of civilization you will need to transfer the residential fund to energy-saving technologies. The concept of Ekodoma is developing and improving in numerous research institutes around the world, and today it is based on more than 2 thousand structures in Germany, Denmark, Sweden and other countries in Western Europe, as well as in the United States.

| 
| 
| 
|

| 
| 
| 
|

| 
| 
| 
|
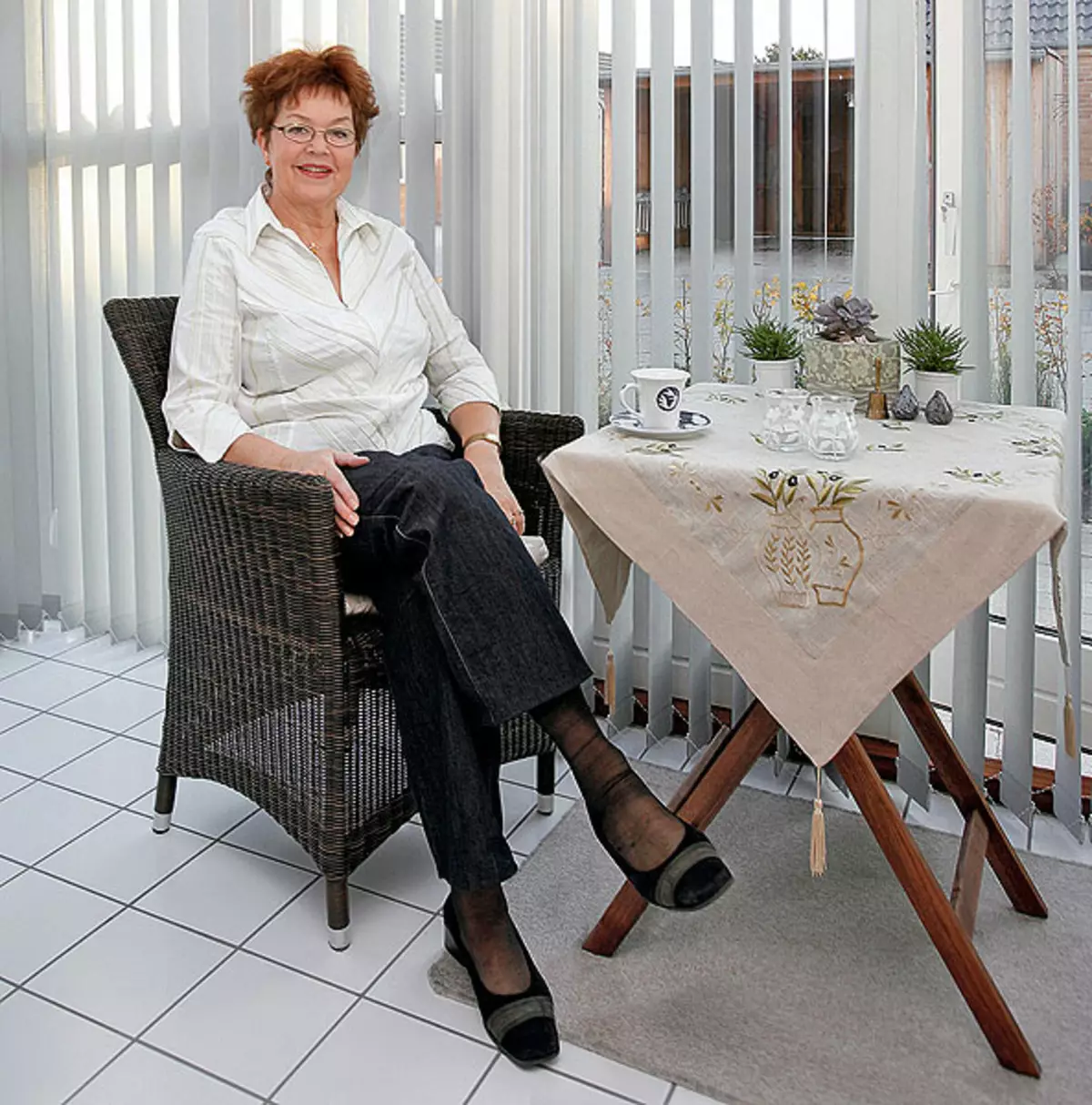
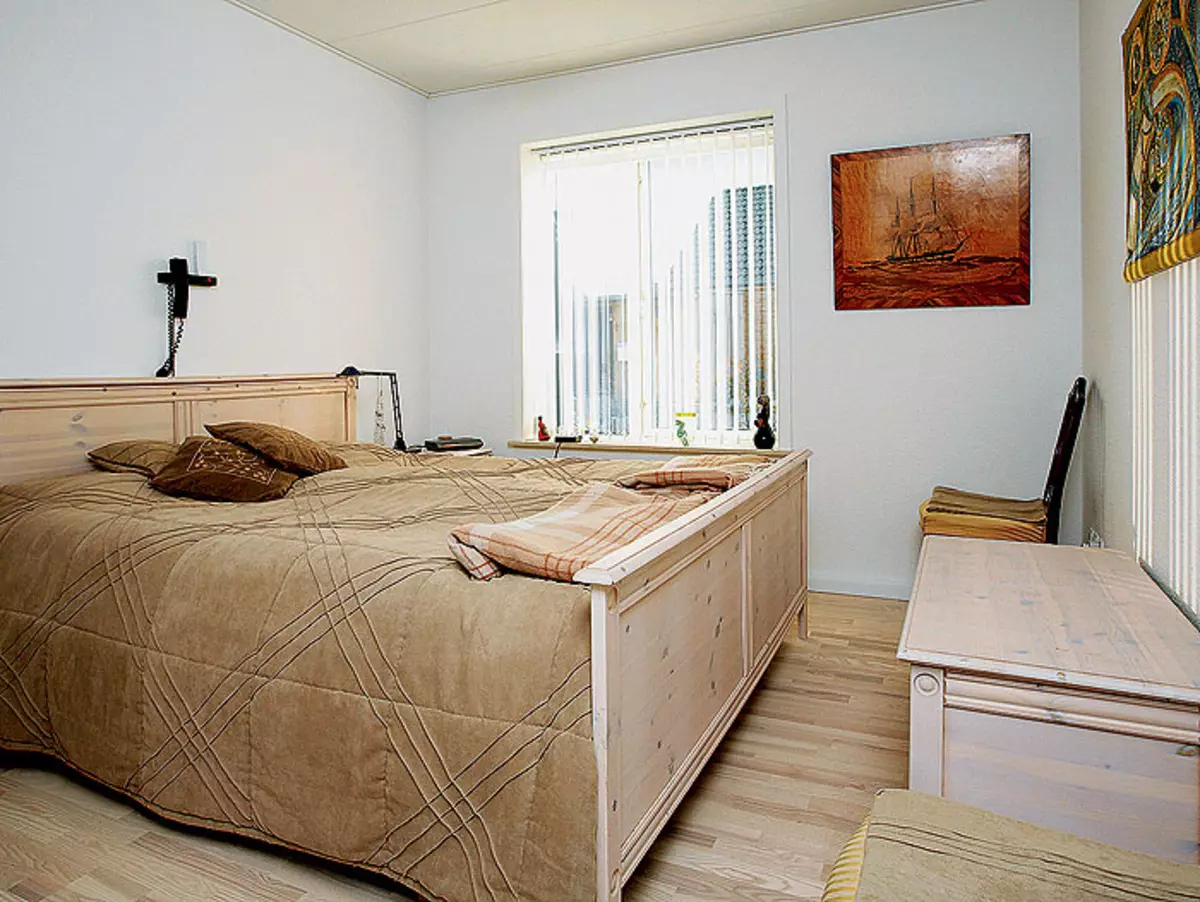
5.Ingrid hill is the mistress of the energy-saving house in the village of Stena (Denmark).
6. Installation in the house of the family Hill is very simple, practical and cozy.
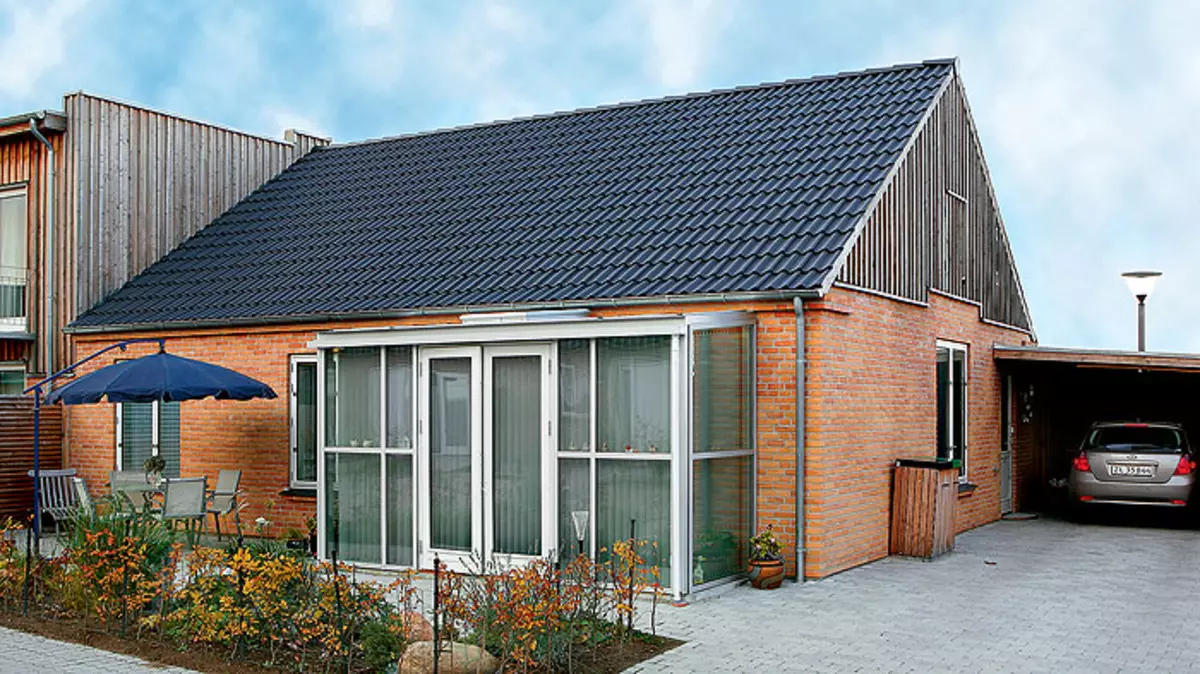
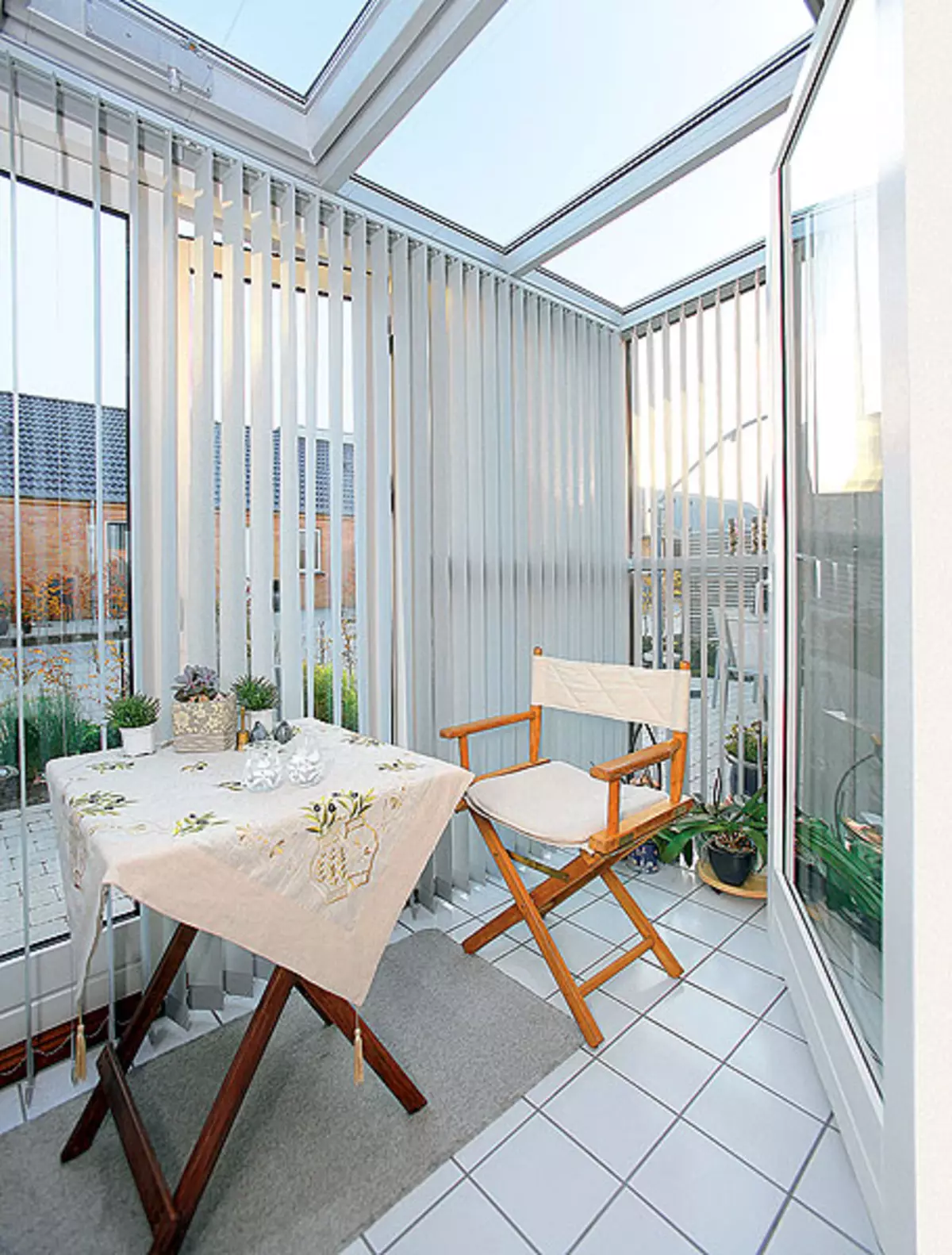
7. General view of a house with a summer glazed extension.
8. The cuisine can be included in the mining; Rainwater from a tank, located in the basement, comes into the washing machine.
9. Semis the hill living in the house of 138m2, pays for electricity 3 times less than it would have to go in an ordinary house. There are no radiators, in the rare cold days, the spouses include warm electric floors mounted under laminate.
10. Lady extension is for recreation and tea drinking. At the time of year, the door is closed into it.
11. Conducting kitchen mini-post.
12. The resultant heater.
13. Guest has good ventilation and insolation.
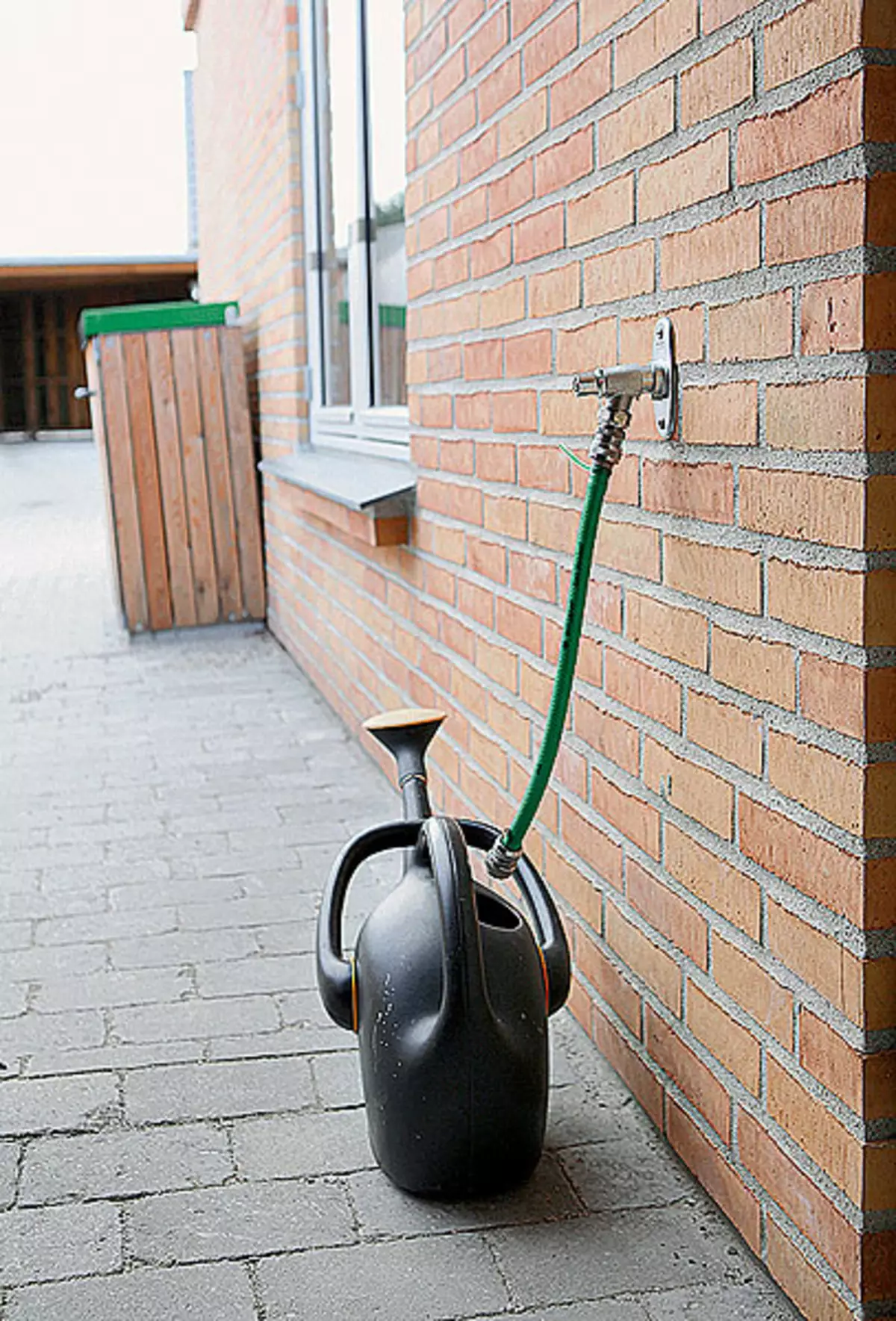
14. Along the rainwater drops are not disappeared - for the garden watering can be made special conclusion.
15. The thickness of the walls of this energy efficient home is equal to 410mm.
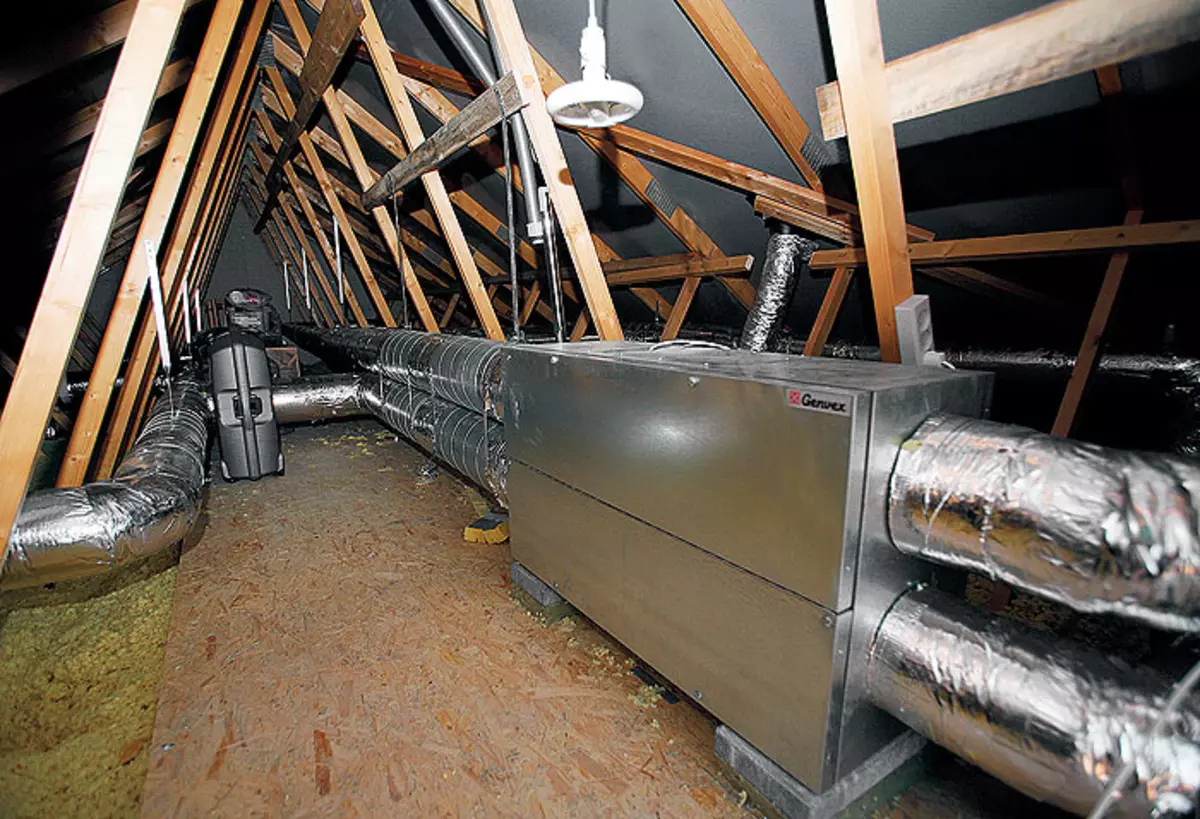
16. The small attic room of the house is occupied by the recuperator of the supply and exhaust ventilation. Thanks to him, a healthy microclimate is supported in the house, which is so important for the spouses of the aged age.
Shot of the house in the Stena (Denmark) was held by Rockwool
The relevance of Ecodom in Russia
The specifics of our country lies in the harsh climate, in which the extreme can not do without additional heating. In addition, in Russia, in contrast to the West, there are no state programs and regulatory documents for the construction of eco-houses. However, some enthusiasts hope to solve these problems, creating ecoposalias. Ecommodernation of houses in Russia is mainly due to the fact that energy tariffs began to grow (according to forecasts, in 2009 they will increase by 20%). It is unlikely that the global economic crisis, the exhaustion of world oil reserves, gas and coal by themselves will force Russians to invest in Ecodom. But the eco-component of the housing (even if not in full) in the future can be a fairly profitable event: this is an opportunity not only to save on electricity, DHW and heating, but also earn, selling excess biofuels, compost and agricultural products.
At home, the market for alternative electricity in Russia is not yet, as not and tax benefits for the use of such sources. Abse them The construction of power supply systems on renewable resources is low-apparent. Erectomic eclipses (like any new technology) at this stage costs much more expensive than traditional residential buildings. However, the refusal of large-scale engineering networks and thermalommunications makes the mass construction of eco-leaves cheaper the construction of other types of housing, which has already proved Western experience. For more than a time, accidents are accidentally occasionally, as a result of which thousands of people are deprived of heat. For the repair of worn pipes in frozen land requires large material costs.

| 
| 
Philips Lighting | 
Philips Lighting |
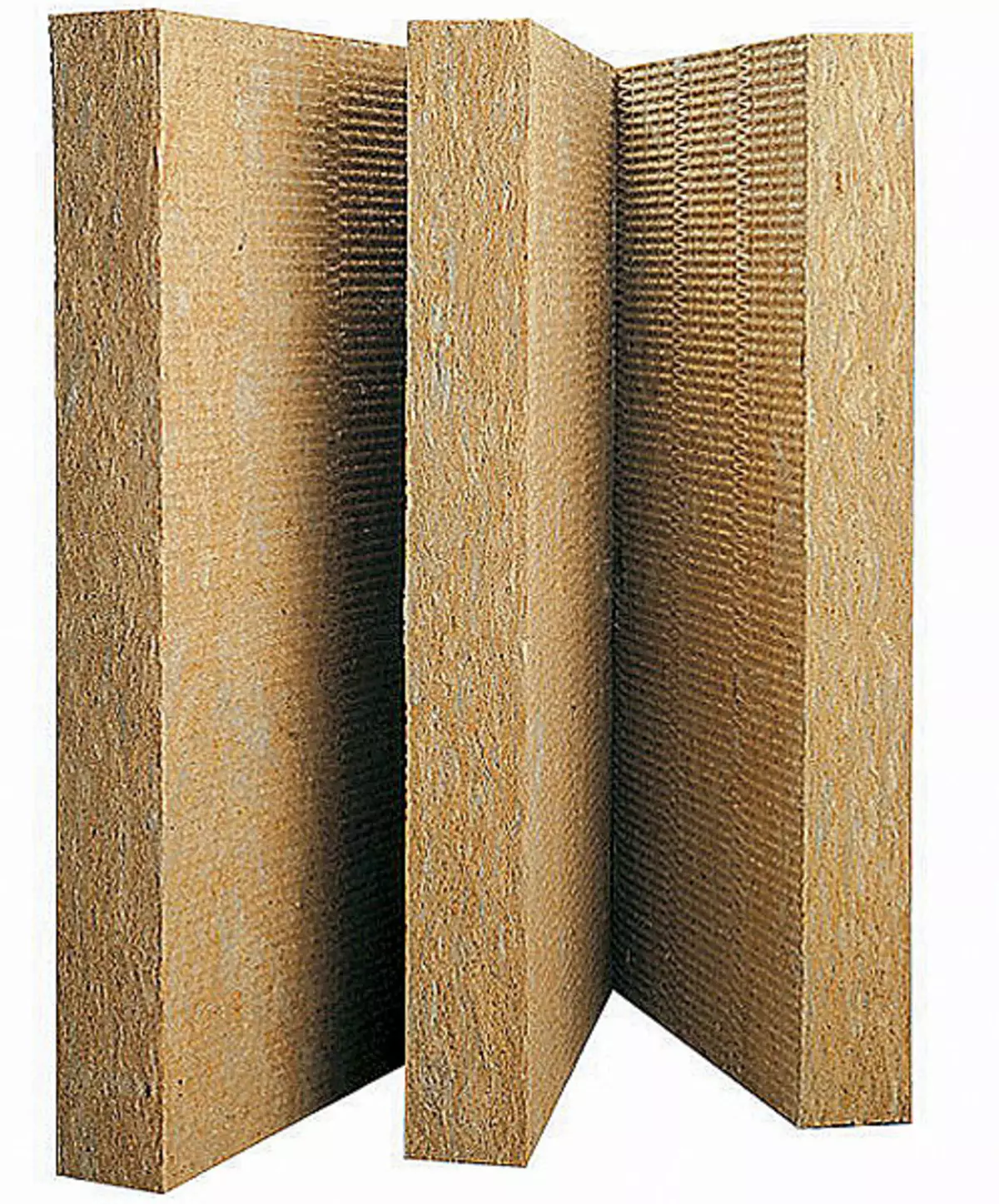
17-18. Materials from stone wool are most often used to insulate houses.
19-20. It is important to solve the problem of energy saving in the dwelling complex. The use of energy-saving lamps instead of usual very soon will be tangible for your wallet: they rarely burn out and consume little electricity.
Advantages of eco-leave
Fertile microclimate without radiators and air conditioners (their role is performed by warm floors and a primer recovery);independence from heatpets due to the use of solar energy and alternative heat sources in the autonomous DHW system;
Due to the autonomous biological treatment of wastewater, it is possible to abandon poisoning nature and emitting methane (it creates a greenhouse effect) of irrigation fields;
biogeneratory system of disposal of biological waste, transforming them into biogas and fertilizer will provide an opportunity to reduce land polygons (solid household waste), which are the source of "greenhouse" methane;
biogas and pyrolysis gas allow to achieve non-volatile and remain in harmony with nature;
Collecting and using rainwater reduce dependence on water supply (plus savings of the precious natural resource drinking water).
Specialists of the Institute of Passive House in Darmstadt are considering an extract as a thermal fortress: the thermal insulation qualities of the walls, roofs and the foundation, the energy efficiency of the windows and the ventilation system allow such a building to retain heat like a thermos.
Reliable walls
Well insulated thick walls, of course, the first and main condition for the existence of Ecodoma. Specialists of the Institute of Passive House in Darmstadt recommend the following values of the coefficients of heat transfer coefficients of the enclosing structures of the ECODOM: outer walls - 9-12; roof - 14-16; Foundation - 8-10cm2 / W. These parameters will not be able to achieve, remove the walls by traditional methods from most thermal insulation materials. For example, a wall from the blocks of "Düsisol" with a thickness of 375mm has the magnitude of the heat transfer coefficient only 3, CM2 / W, and a wall of gas-silicate blocks (cellular concrete) with a thickness of 400mm and is less than: 2, cm2 / W.
The method of manufacturing thick clairger blocks, of which some American ecodom are built, not received distribution in Europe. Effected by Western European Ecodomes "passed" a system consisting of a carrying wooden or stone frame, insulated with a thick (at least 500mm) layer of hard or semi-rigid slabs from stone wool. The walls of the walls can usually be judged by the depths of window openings. Most often as insulation materials are used by materials such as Rockwool (international concern with headquarters in Denmark), Paroc (Finland), Knauf, URSA XPS (both - Russia). Ecology shoulders for ecology for Ecodom, the most attractive can be considered slabs made of stone wool. They possess the following advantages:
non-toxic and non-carcinogenic, in contrast, for example, from such a material as asbestos fiber;
Basalt fiber does not break, does not ourselves and it does not roll like fiberglass;
Ungigroscopic (water absorption is no more than 1.5%) with simultaneous good vapor permeability;
Over time, stone wool plates are not compressed in the amount in contrast to glass or silver plates;
The material is not subject to fungi and insects;
The non-combustibles and heat-resistant plates from the stone wool are withstanding the temperature to 1000c.
Rockwool produces various heat insulating materials from stone wool "for all occasions." Light plates Rockwool Light Batts small density (37kg / m3) are designed for partitions, overlap, mansard insulation, scanty roofing, facilities for lags, frame walls. This material does not have a large load on the walls and overlappings well passes through itself steam, pulling out the excess moisture. The advantages of rigid hydrophobized heat-insulating plates Rockwool Flor Batts (density is 125kg / m3), intended for insulation of floors and foundation, consist in the top of them you can pour a bitumen or cement screed.
The role of methane in greenhouse effect
Greenhouse effects of atmospheric gas gases radiated by the Earth. The Wkyot's protocol notes that it is methane to blame for global warming, although its emissions into the atmosphere is much smaller than carbon dioxide. This is motivated by the fact that for the same greenhouse heating of the atmosphere, it takes 21 times less methane than carbon dioxide. Greenhouse effect attachment is even simple incineration of methane instead of its emissions into the atmosphere. Valid dreams from carbon dioxide absorbed by plants, methane, occasionally in the atmosphere, there are dozens of years in it, slowly split by solar radiation. Effective solution to the problem of global warming - the collection and use of methane as an alternative renewable fuel.
"Right" windows
The coefficient of resistance of the windows of windows should be at least 1.5 cm2 / W, this is the second necessary condition for the thermal tightness of the ECRODOM. The requirements for the windows are following:
The design of the window profile must have low thermal conductivity and not have "cold bridges"; Preferred three-chamber or five-chamber profiles 62-130mm thick;
It is desirable that two-chamber hermetic double-glazed windows are filled with inert gas (crypton or argon), and metal oxide low-emission spraying is applied on the glass (for example, with titanium oxide);
Windows with a large glazing area should go to the south;
To reduce heat losses through the windows in winter at night they are better to close them with shutters, roller shutters or dense curtains.
The windows that meet these requirements even in winter provide a flow into the solar heat house, since a special coating on the glasses does not prevent the penetration of sunlight, but reflects a significant part of the heat that is out of the room (greenhouse effect). When the sun is not and this effect is missing, the windows should be closed by shutters to avoid heat loss.
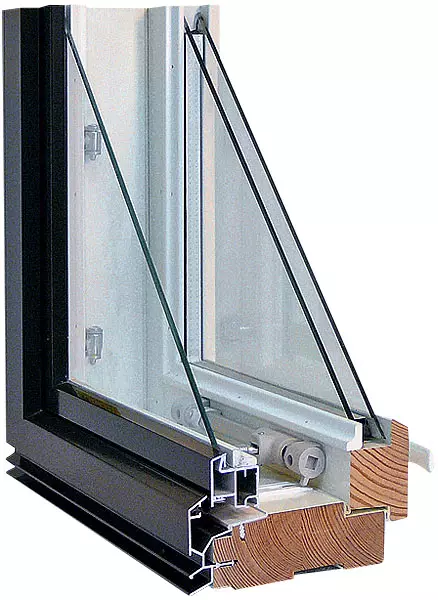
Wood or combined (wood aluminum or plastic windows with aluminum overlays) is used in vacepomos. Plastic windows have hollow frame profiles with a large number of partitions, such as three- or five-chamber: DeceUninck (Belgium), Kbe, Rehau, Veka (all Germany).
The most successful designs are window systems that fully appropriate heat transfer resistance standards even for the coldest regions of Russia. Three-chamber glass windows must have a thickness of at least 46mm. Installation depth of profile is not less than 70mm. A significant number of cameras in the window profile provides minimal thermal conductivity and minimizes the "cold bridges".
In the early time, wooden windows are becoming popular again (the best material for them is a Siberian larch). Causes of this:
They do not accumulate static electricity and do not attract dust;
They are formed less frosty and moisture is not condensed;
The hardness of the Siberian larch is close to the hardness of oak and over the years even increases;
The unpretentious tree of a specially glued window profile can "breathe" and therefore creates a healthy climate in the house.
Wooden windows with double-chamber windows are best suited for Ecodom (three low-emission glass, the intercole cameras are filled with Crypton). The glass must have thermal insulation with the heat transfer coefficient 2cm2 / W.

WinFin. | 
Rudupis | 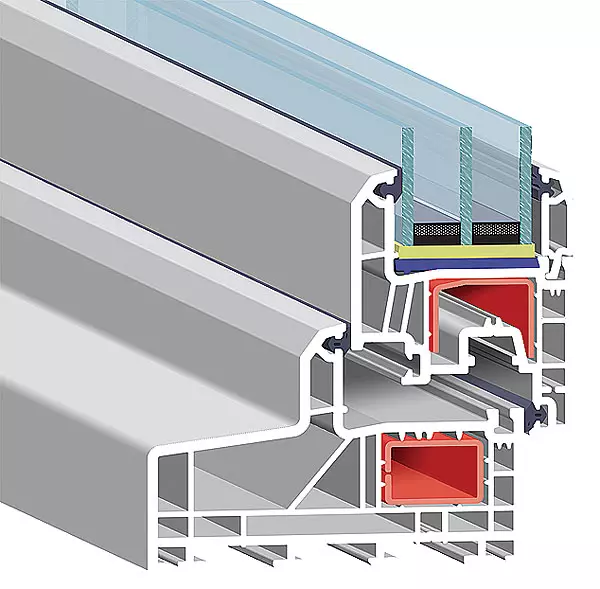
"PROFIN RUS" |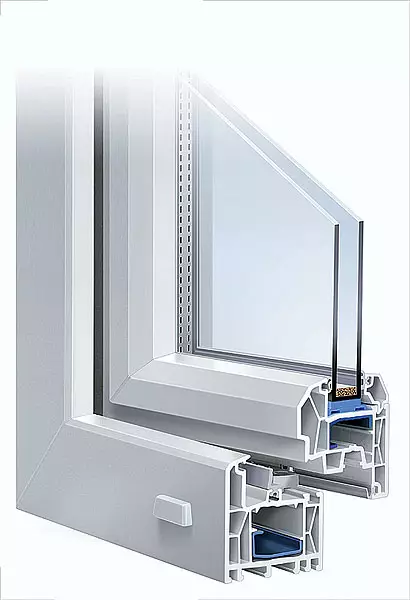 
Exprob |
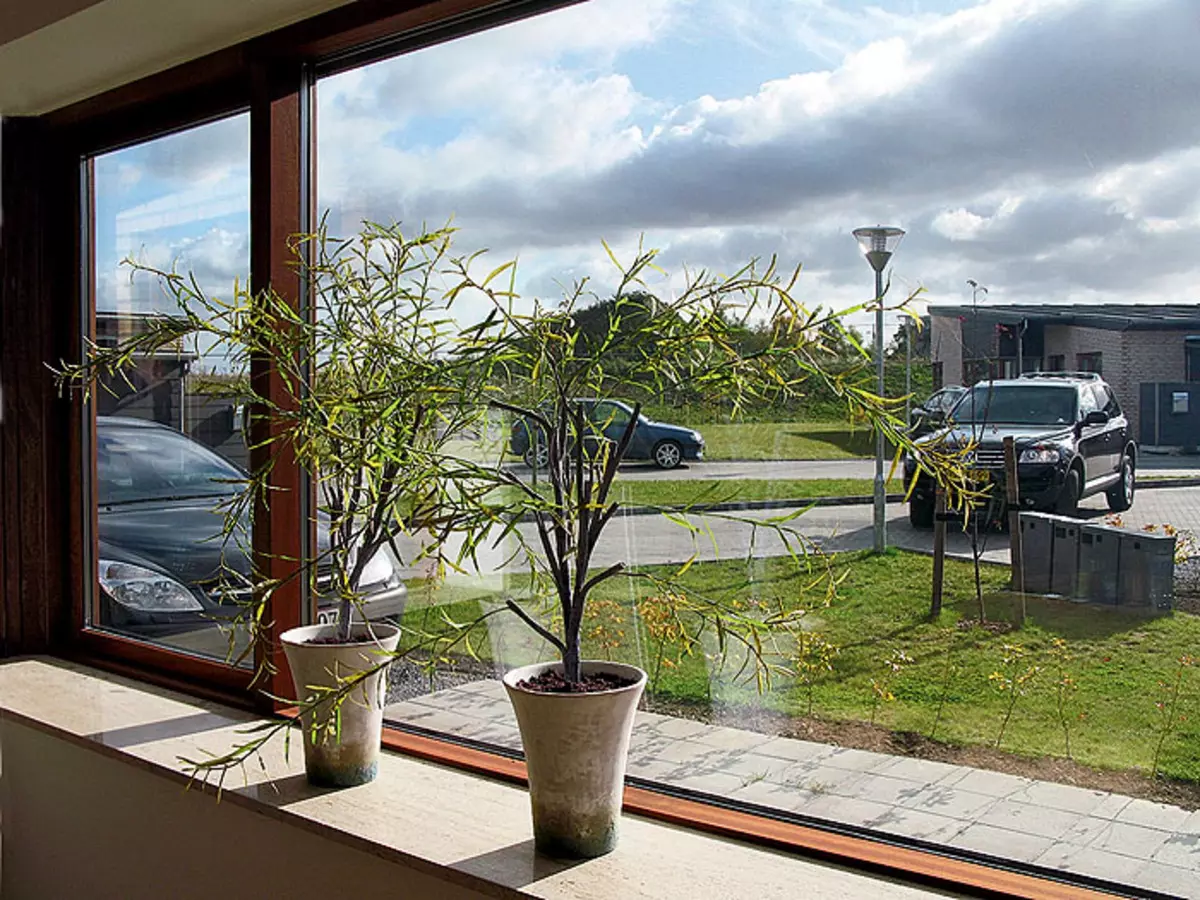

Photo Y. Evdochemova21-22. Draided energy-saving windows: Lammin Ikkuna with separate sash (mounting depth - 130mm); Rudupis with single sash (mounting depth - 104mm).
23-24. Blossy "Warm" windows: from the profile of Trocal Innonova (5Camer, mounting depth - 70mm); From the profile of EXPROF AEROSUPREMA (5Camer, mounting depth - 118mm).
25. Draid window in the ecode.
Without loss!
The third most important condition for the preservation of the thermal contour of the building is the presence of supply-exhaust ventilation with heat recuperator (heat exchanger). The principle of its action lies in the fact that the outer cold air enters the countercurrent heat exchanger, in which moves along the pipes, washed outside with warm air, which comes from the house in the opposite direction. As a result of the outlet of the heat exchanger, street air tends to purchase the temperature of the room, and the latter, on the contrary, before leaving the heat exchanger, tends to street temperatures. So the task of a fairly intense air exchange in the house without heat loss is solved.
Opinion of a specialist
It is necessary to warm your home in strict accordance with the construction standards to save on heating. Effective thermal insulation retains heat in winter and cool in summer, it is environmentally friendly, non-combustible and non-hygroscopic. So, through the walls take up to 40% of heat. They are more efficient to insulate outside. Modern facade systems, such as the non-combustible Rockwool Rockfacade system (it is mounted on the facade with complex architectural elements), allow you to simultaneously warm the walls and arrange the facade.
Tatyana Smirnova, Technical Specialist of Rockwool
There are more severe climate than, for example, in European countries, the primer should also be added to the main recuperator. Its feasibility is proved by the fact that in some Western Ecodomas, the use of the ground recuperator made it possible to abandon air conditioning. The soil temperature at a depth of 8m is more permanent and is about 8-12c. Therefore, it is necessary to plunge the recuperator on this magnitude to the street air, passing in the ground, regardless of the season, it sought to take the appropriate temperature. On either the July heat can stand on the street, or the January frost, but the house will always come to the house, the temperature of which is optimal about 17c.

Mossinepartners. |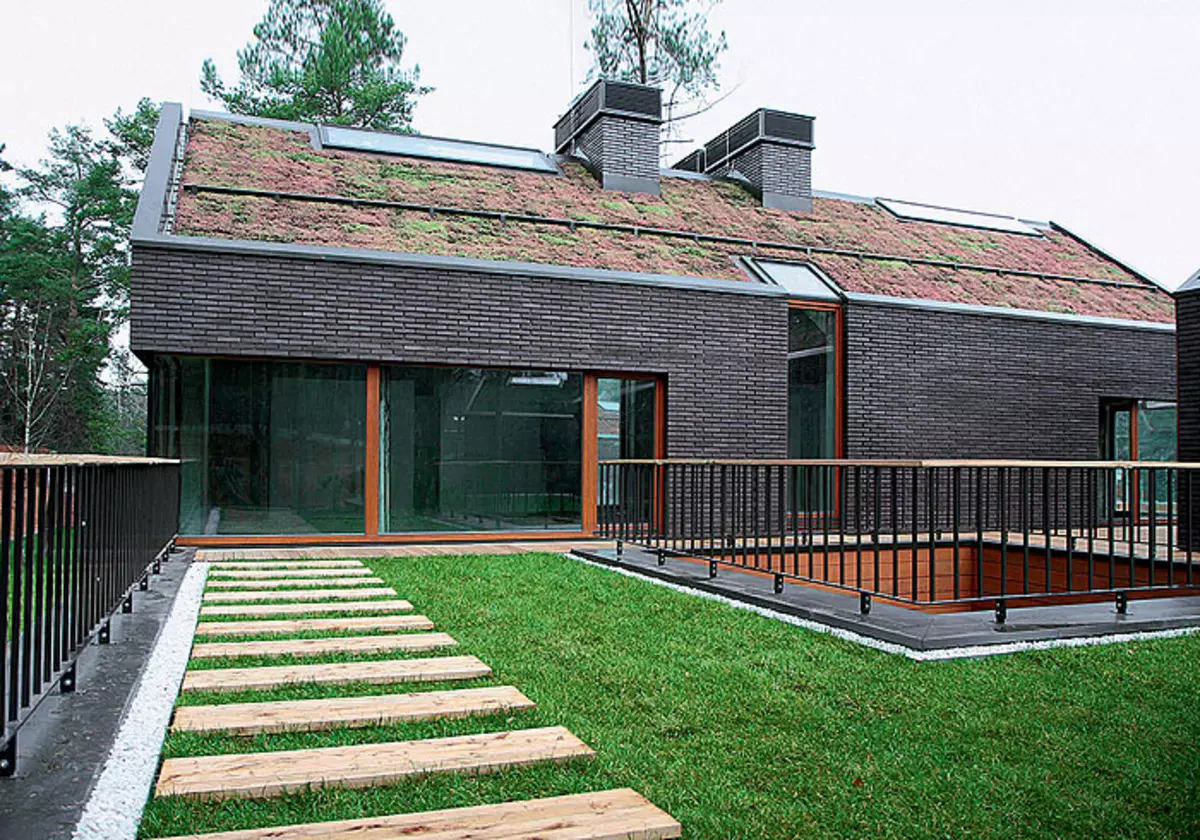 
Mossinepartners. | 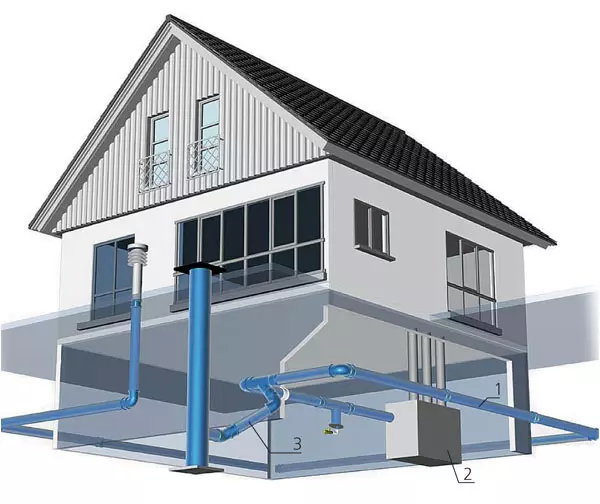
Rehau. | 
Rehau. |
26-27. The vessels already have villages, at home in which they meet the principles of maintaining a healthy microclimate: in summer, the "green" roof does not heat up, and in winter it does not allow the premises to cool.
28.The device of the device of the ground recovery (heat exchanger) in the country house (REHAU): 1-ground heatollector AWADUKT THERMO; 2-heat recuperator; 3-drainage condensate.
29. Right with the house there is an air intake tube of a soil heat exchanger.
Proszia is possible to acquire the supply and exhaust installations of various foreign companies (to order) with a recuperator with a capacity of up to 1000m3 / h and even more. The cost of the system is quite high enough - from 225 thousand rubles. Some companies, such as Rehau and others, produce a special set of details for mounting a soil heat exchanger, significantly increasing the cost of the latter.
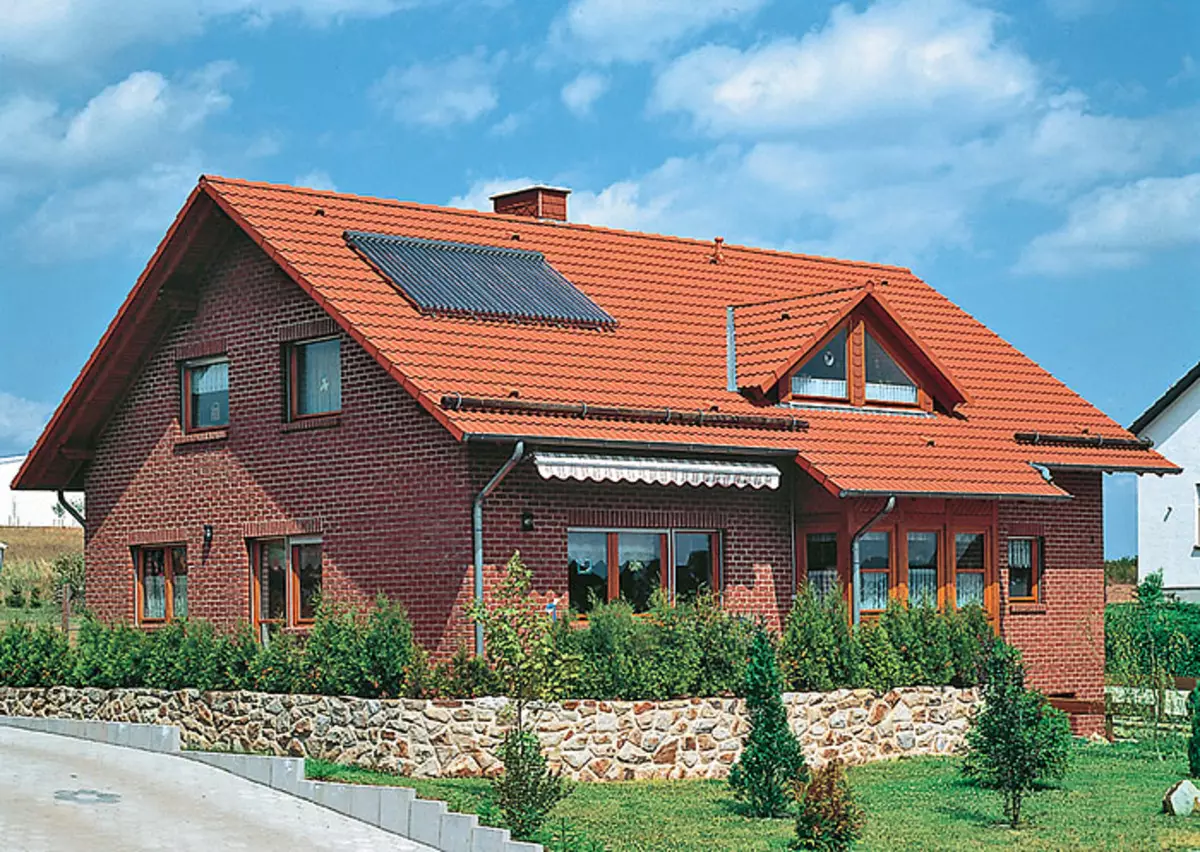
Heliosystems
Solar collectors (or batteries) - Heliosystems - the fourth condition of the existence of an ecodom. The operation of the solar collector is based on the greenhouse effect: the absorbable thermal radiation of the Sun significantly exceeds the reverse thermal radiation of the collector. There are two types of solar collectors: flat and vacuum. The greenhouse effect is reinforced by the fact that the reverse thermal radiation of the collector cannot pass through the vacuum, as in the vacuum flask of the household thermos. The result is a vacuum collector, unlike flat, heats the coolant to a high temperature even in the frost, which is a decisive factor in favor of its choice for our country. But in winter, with a short light day and clouds, the amount of heat generated by a solar collector is significantly reduced. The Russian Federation of Russia is beneficial for the solar system of DHW, having a spare heat source, because for collecting poor winter heat you need a lot of expensive collectors. The concepts of Ecodoma as such a source of thermal energy corresponds to a gas generator, schoblined with a Cumulative GVS tank and working on wood-renewable fuel.
Features of the operation of heliosystems
You can heat the accumulative tank only solar energy up to 10 months a year. With very strong clouds and frost, as well as for washing and washed, it is easy to heat the water in a cumulative tank to the desired temperature, running the gas generator, because the cost of fuel for the gas generator is significantly lower than when using only the boiler (saving of funds can reach 90%). At the same time, during periods of operation of the gas generator, the underground gas storage facility is intensively replenished with gaseous fuels.
It is possible to damn the greenhouse all year round, the year-round functioning of the biological waste disposal system is ensured.
You can use the outdoor pool from March to October (water in the pool is heated by the energy of the Sun). For heating Ecodom, there are 8-10 collectors with a total area of 32-40m2. Ito, taking into account heating with their help of water for a family of four, as well as their use for heating the greenhouse and the operation of the system of biological waste disposal. True, the accumulative tank (or two tanks) is needed for hot water with a volume of 1.5-2 thousand.

Viessmann. |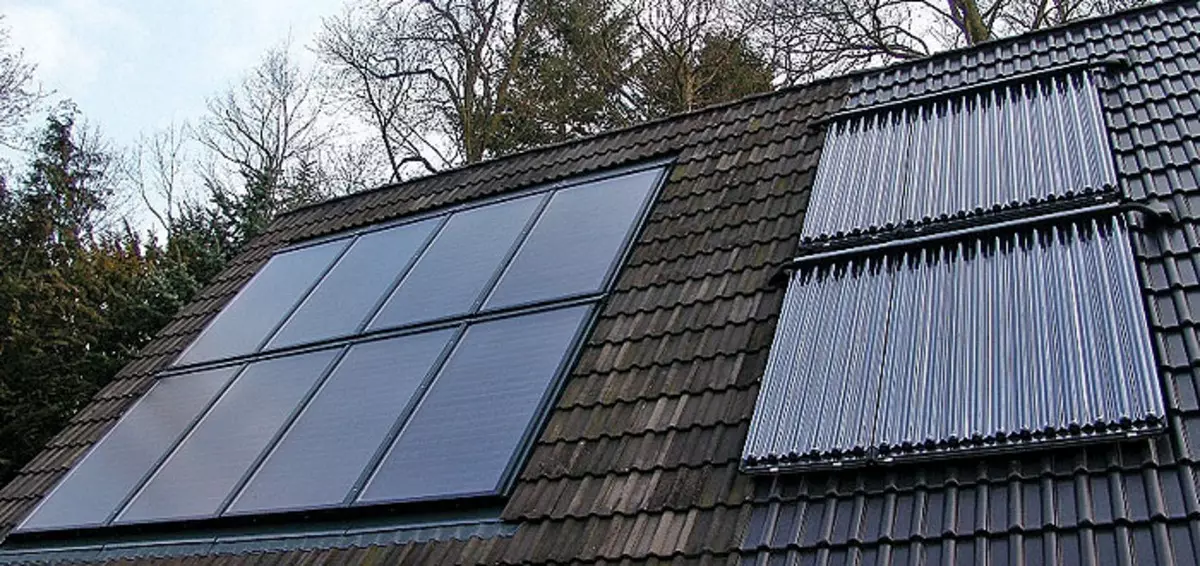 
Viessmann. | 
Photo by D.Minkina |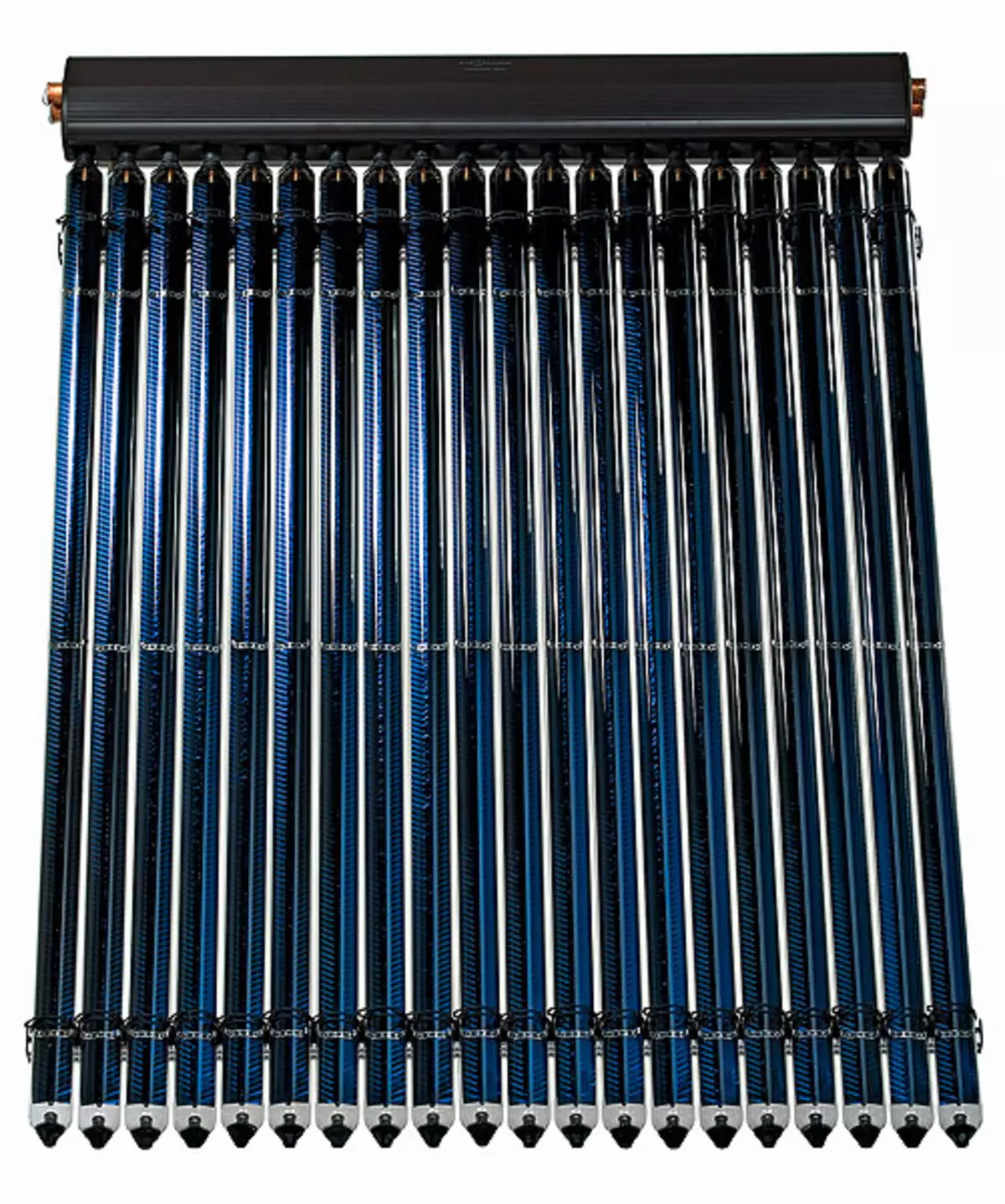 
Viessmann. |
30-31.Vacuum solar collectors mounted on the roof.
32. Phoelectric panels that produce alternative electricity are an element of the roof design.
33.The set vacuum tubes collector Vitosol 300-T (Viessmann).
Instead of imprisonment
The house with the properties described is not accidentally called the thermal fortress. At the soft climate, it does not need a heating system, nor air conditioners, no drafts, does not feel cold, since the difference in room air temperature and the inner surfaces of the enclosing structures are negligiously small. The house heats the heat secreted by household appliances, bodies of residents and domestic animals, as well as solar energy. Since there is no drying heating devices in the building, the microclimate can be compared with a gracious summer weather somewhere at the resorts of the Mining Switzerland. This is favorable, for example, on those who suffer from allergies.
Invisions built in Russia, with its short winter days, when solar collectors cannot give enough heat, you have to mount additional heating systems. To minimize their influence on the microclimate of the house, it is advisable to give preference to warm floors. We will tell the water from the following numbers of the magazine about the equipment for the closed system "Energy Saving House Plot".
The editors thanks Rockwool and personally Polina Kuleshov, as well as Viessmann and Rehau for help in preparing the material.
