"Floating" foundation is a win-win solution for the problem soil. Technology of construction of slab foundations area of 36 and 190 m2

Of course, the foundation is the most important, but almost completely hidden from our eyes part of the house. It also lives his own mysterious life, which is not always given to builders. Experts argue that among the entire modern abundance of structures there is one universal and non-problems during operation. It is called a floating foundation. Our article will tell about the peculiarities of his construction technology.
On the device forged (foundation) neither means
No dependency to regret.
Urgent position
(First Russian Construction
Regulatory document)

Developer's question: "Tell me how to properly pour a solid foundation of a monolithic slab without basement? Ground-pumped loams to a depth to 1m (which is further unknown, presumably the same thing). Water is at a depth of 0.8-1m, the drainage depth is 1 , 8m. Dimensions at home- 1410m. Residential building - two floors, the first floor-brick, the second - wood. If we give phased technology, I will be grateful ... "

| 
| 
| 
|
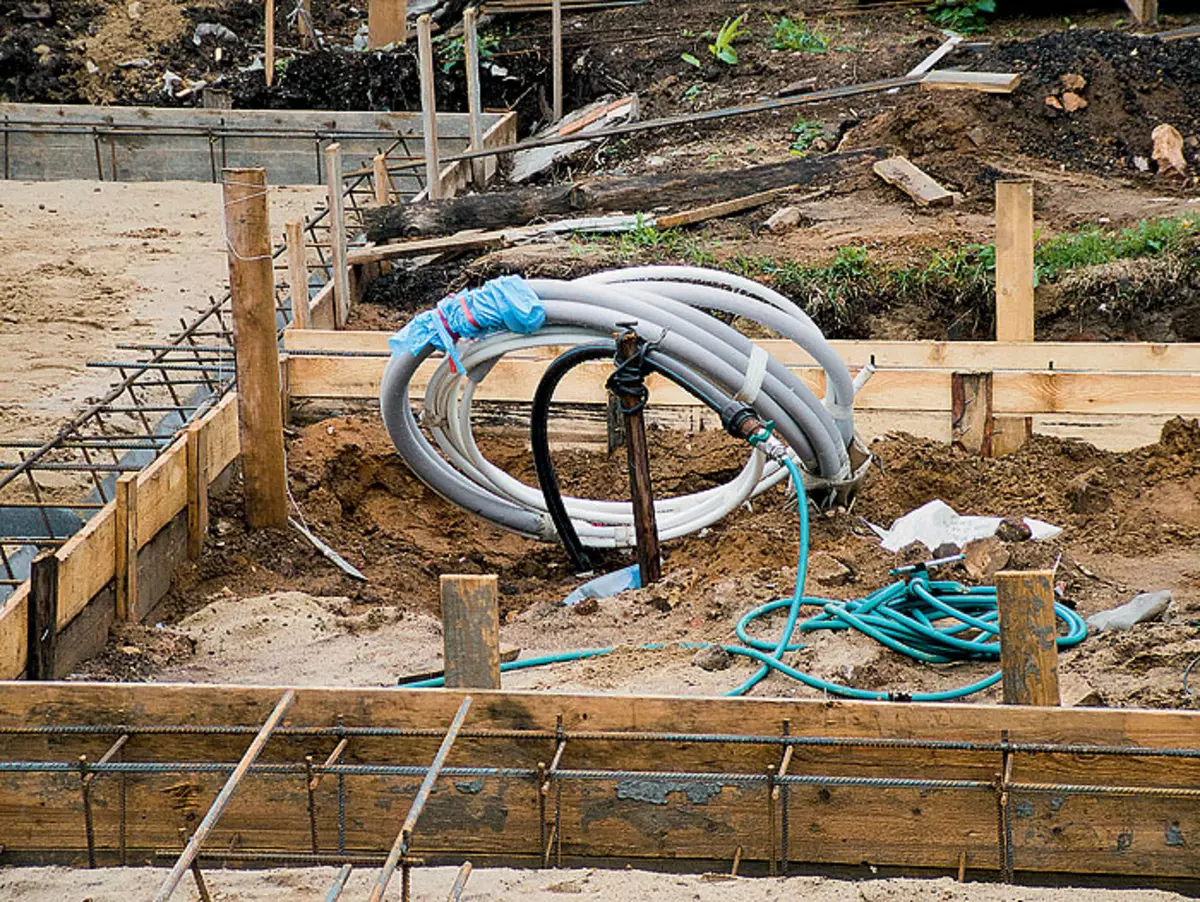
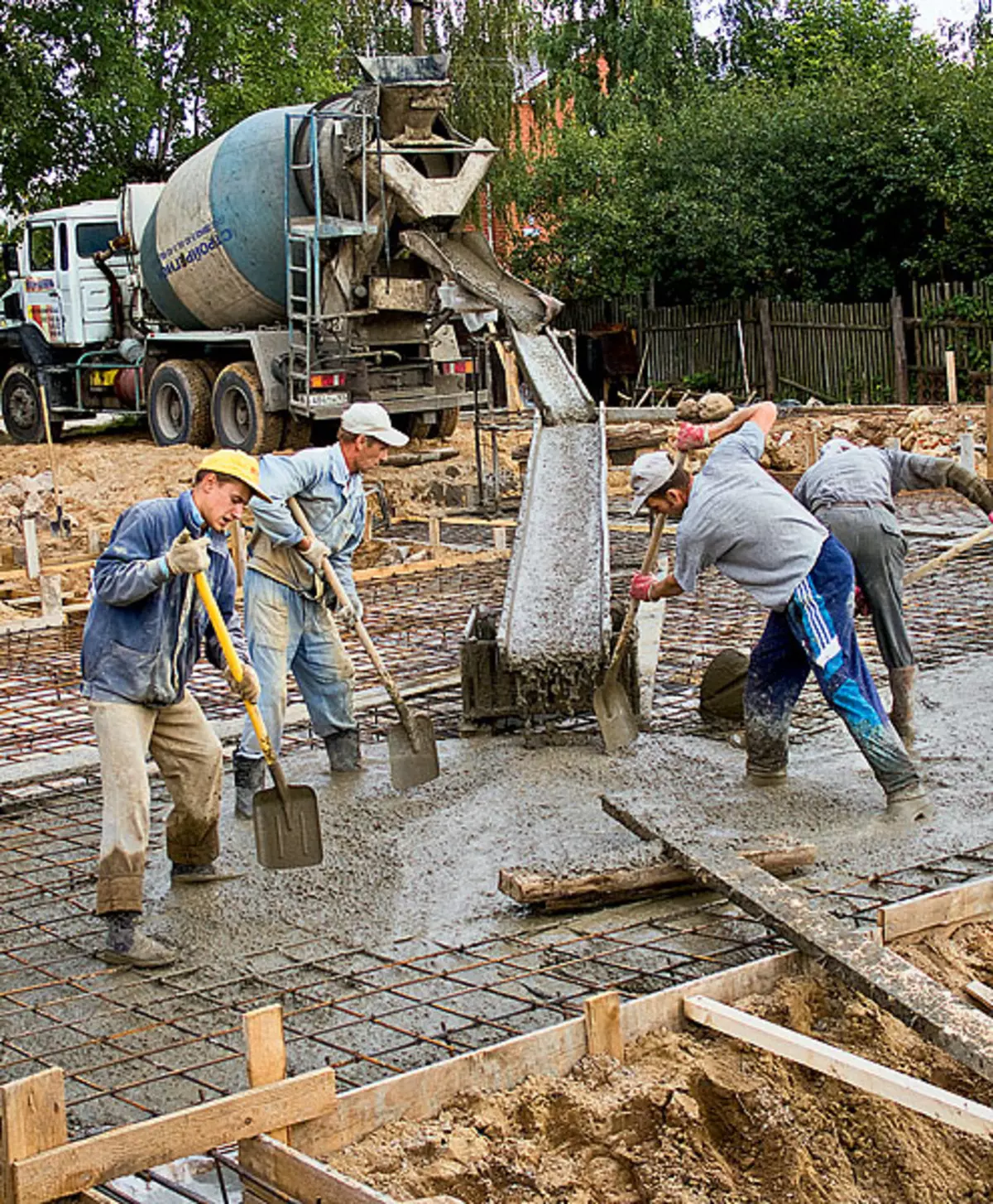
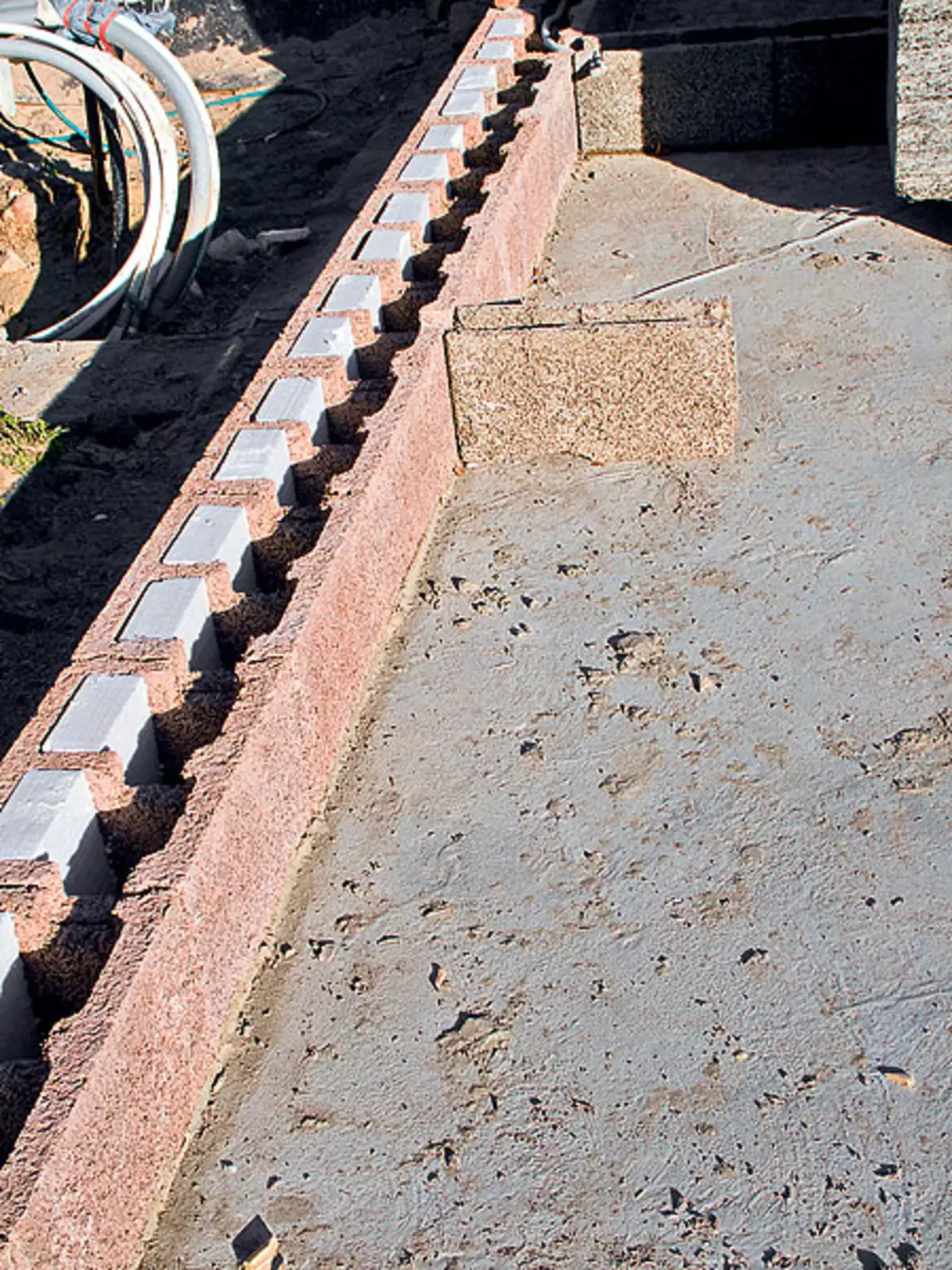
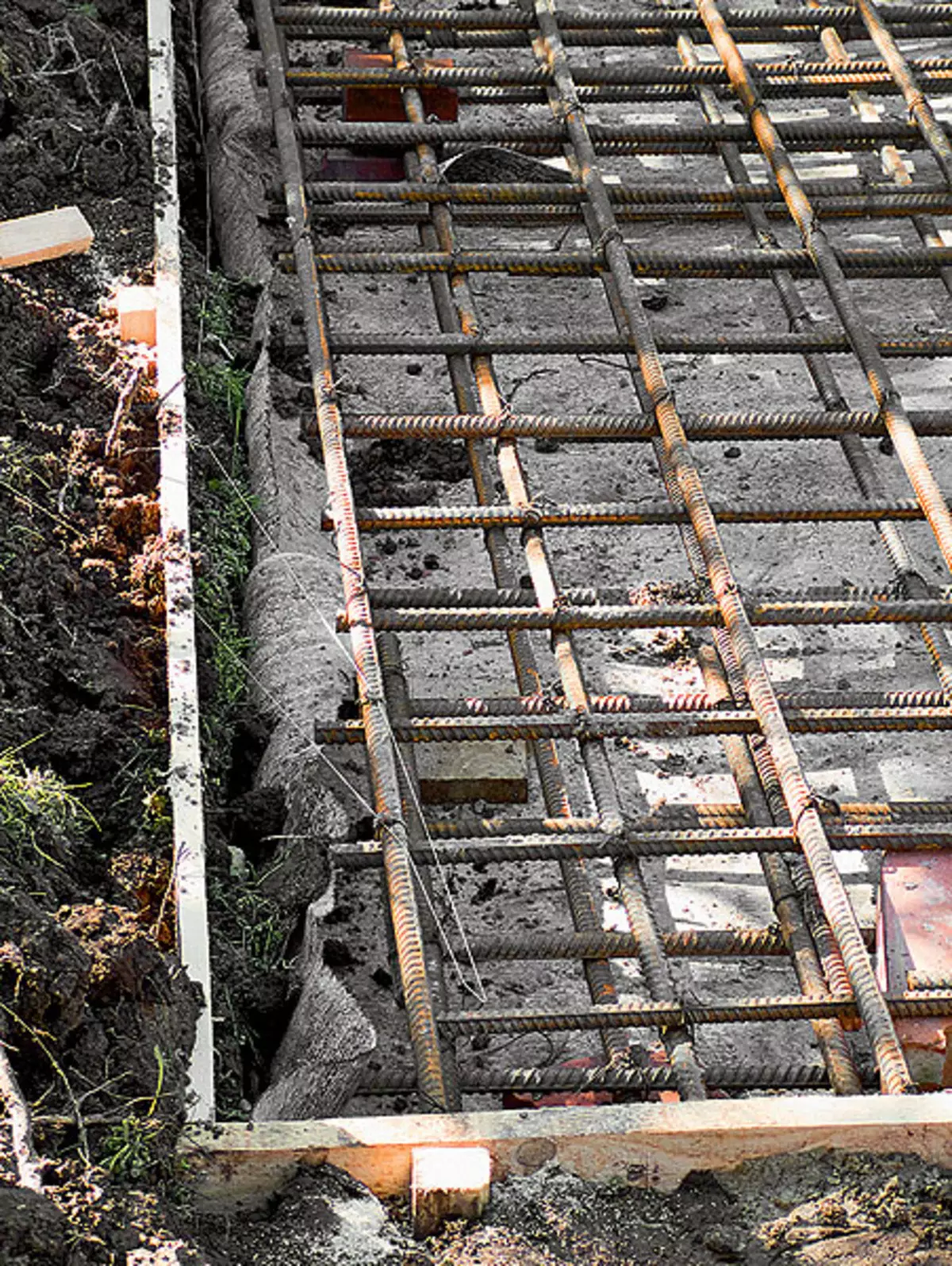
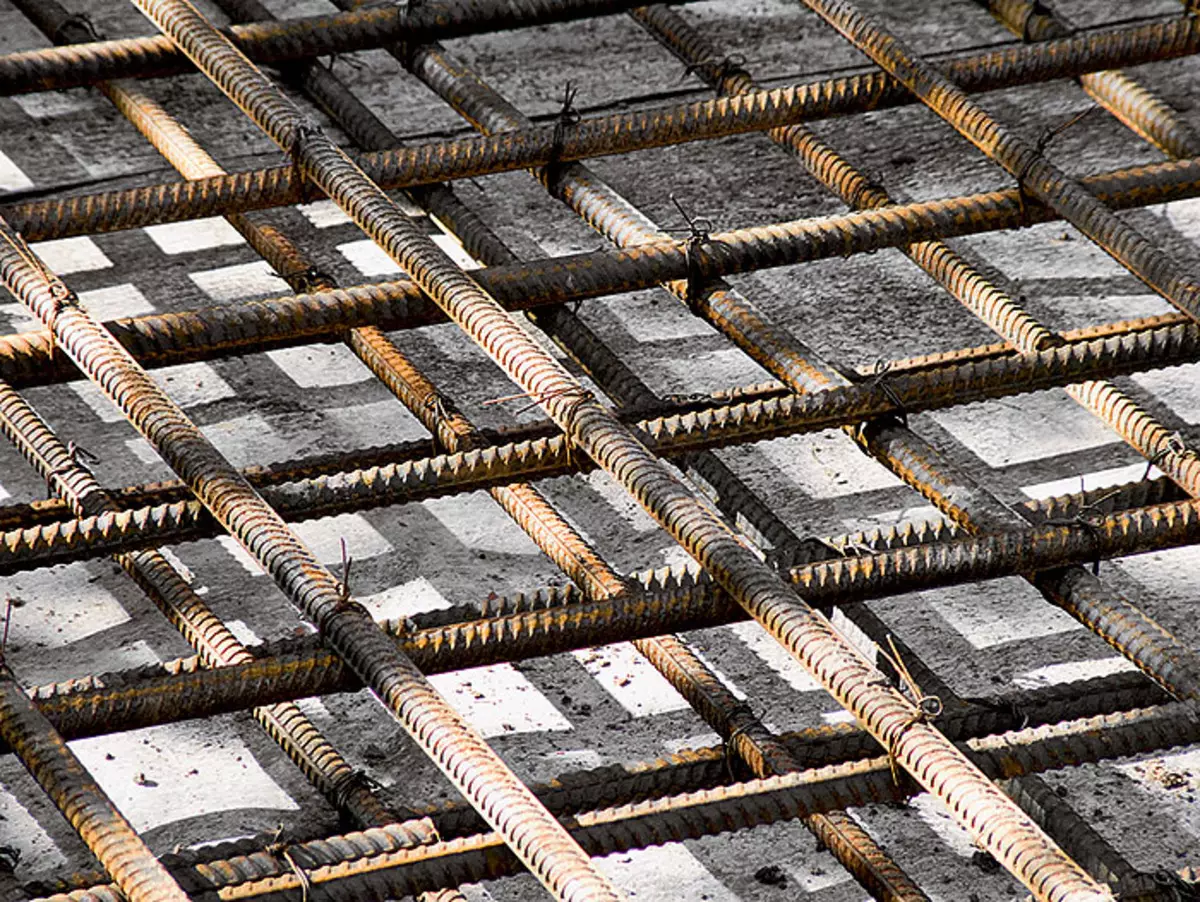
1,2. The test pillow (example 1) was covered with a layer of waterproofing (photo 1). The two-layer reinforcing frame made 16mm from rods, tied with steel wire (photo 2). Frame cell size - about 1515cm
3.4. Betonomy to the place of development (example 1) on the old and rather narrow section, it was not possible to immediately unload at the gate to a special box, and then deliver the wheelbarrow (photo 3). To do this, the agitaturated carcass was put on a boardwalk (photo 4)
Specialist's answer: "Responding to your question, I will say the following: such a foundation under such a building is impossible to perform neither with a constructive, or from an economic point of view. With such an area of base and loads (brick walls of the first floor), the slab will have to pour rather thick, not to mention On the volumetric reinforcement throughout its area. You also did not indicate how the first floor is planned: if reinforced concrete slabs are additional loads on the foundation, which will reflect on the reinforcement and thickness of the plate.
In the case, I recommend you to perform a boron-born foundation. Sulking well with a diameter of 40cm and a depth of 2-2.5m with a pitch of 2.5-3m, install the reinforcement frame in them and fill with concrete by releasing the reinforcement above the fill level for binding to the framework of the woodwok. Then create an anti-pillow under the ribbons of the woodwok, install a macaw formwork, put the reinforcement frame in it and fill the woodwork on the perimeter of the building and under the bearing walls. "
|
|
|
|
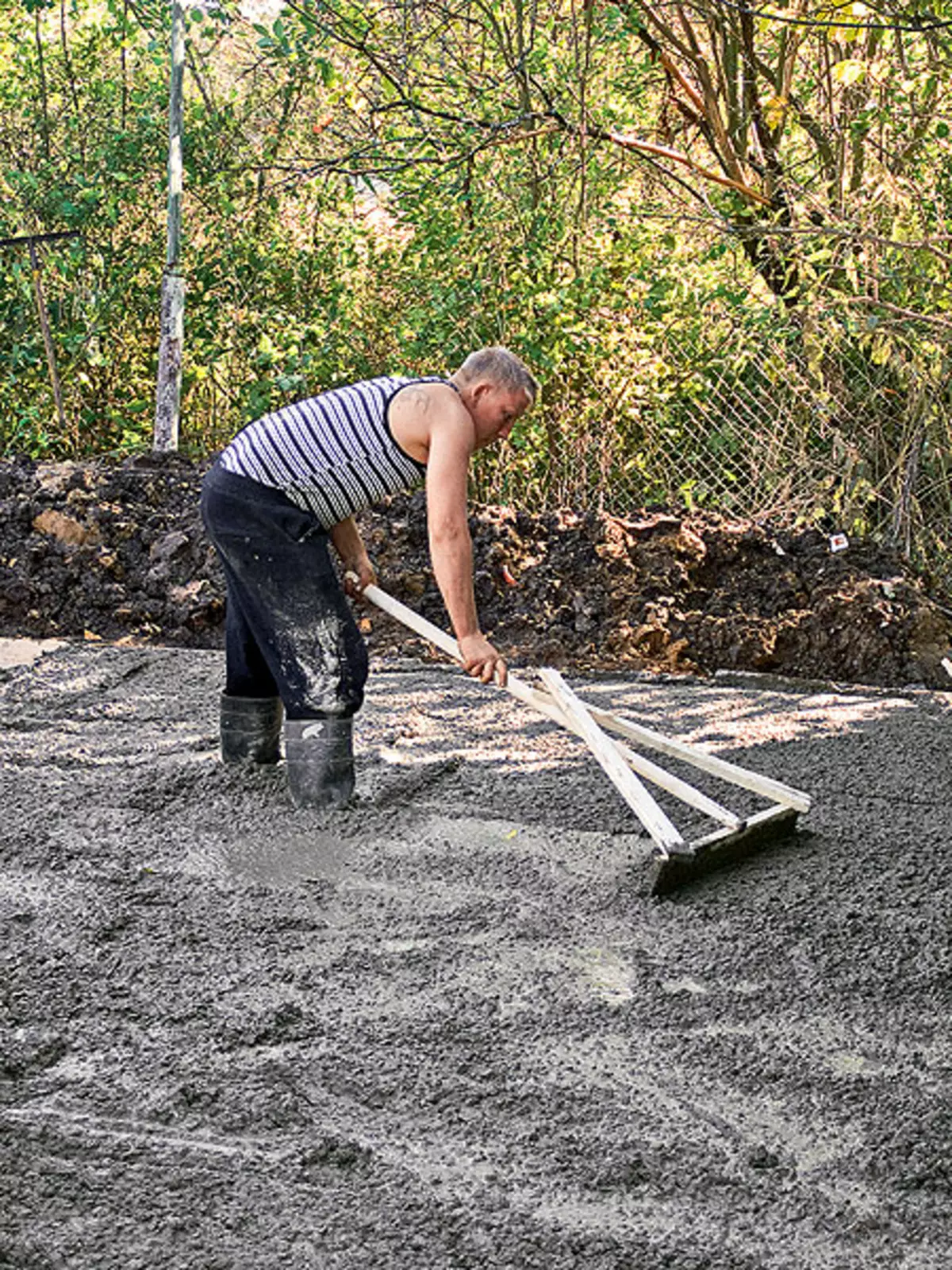
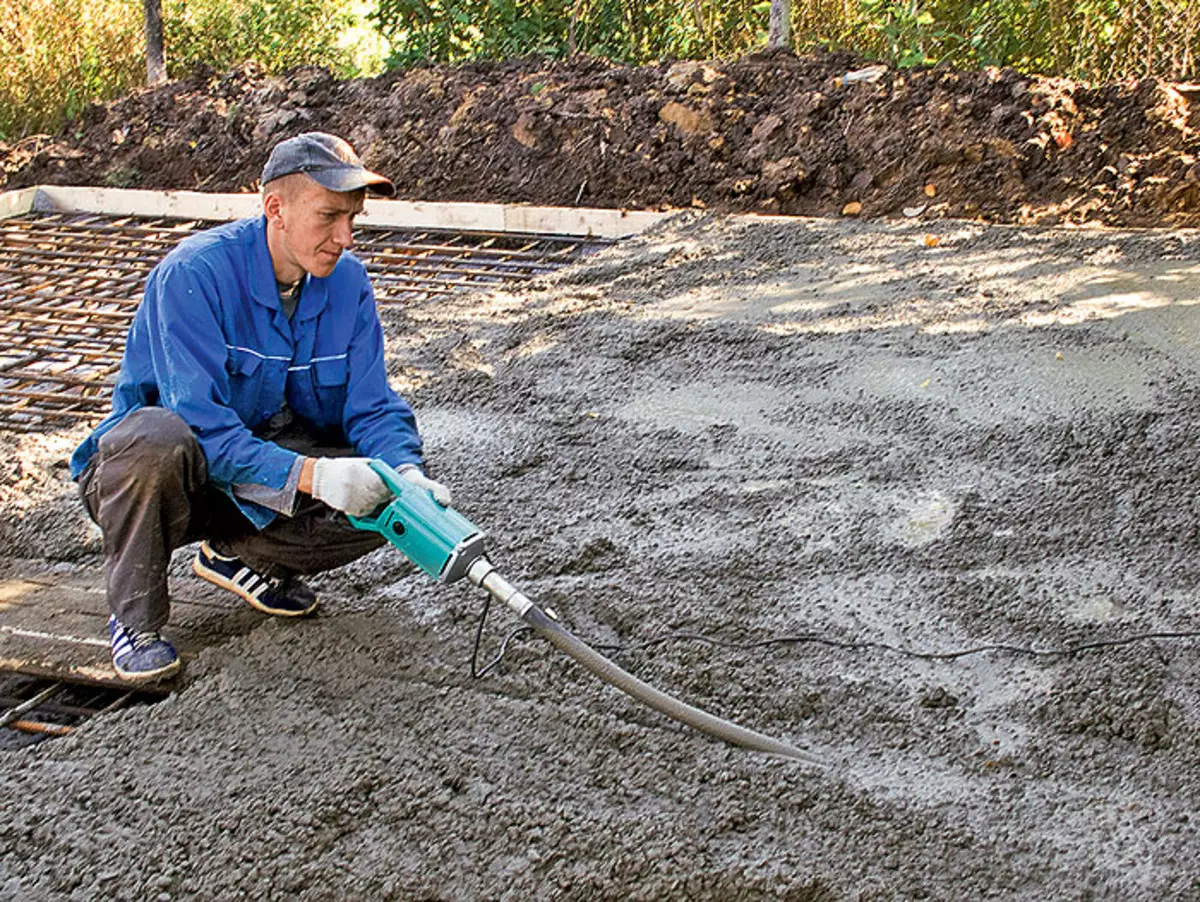
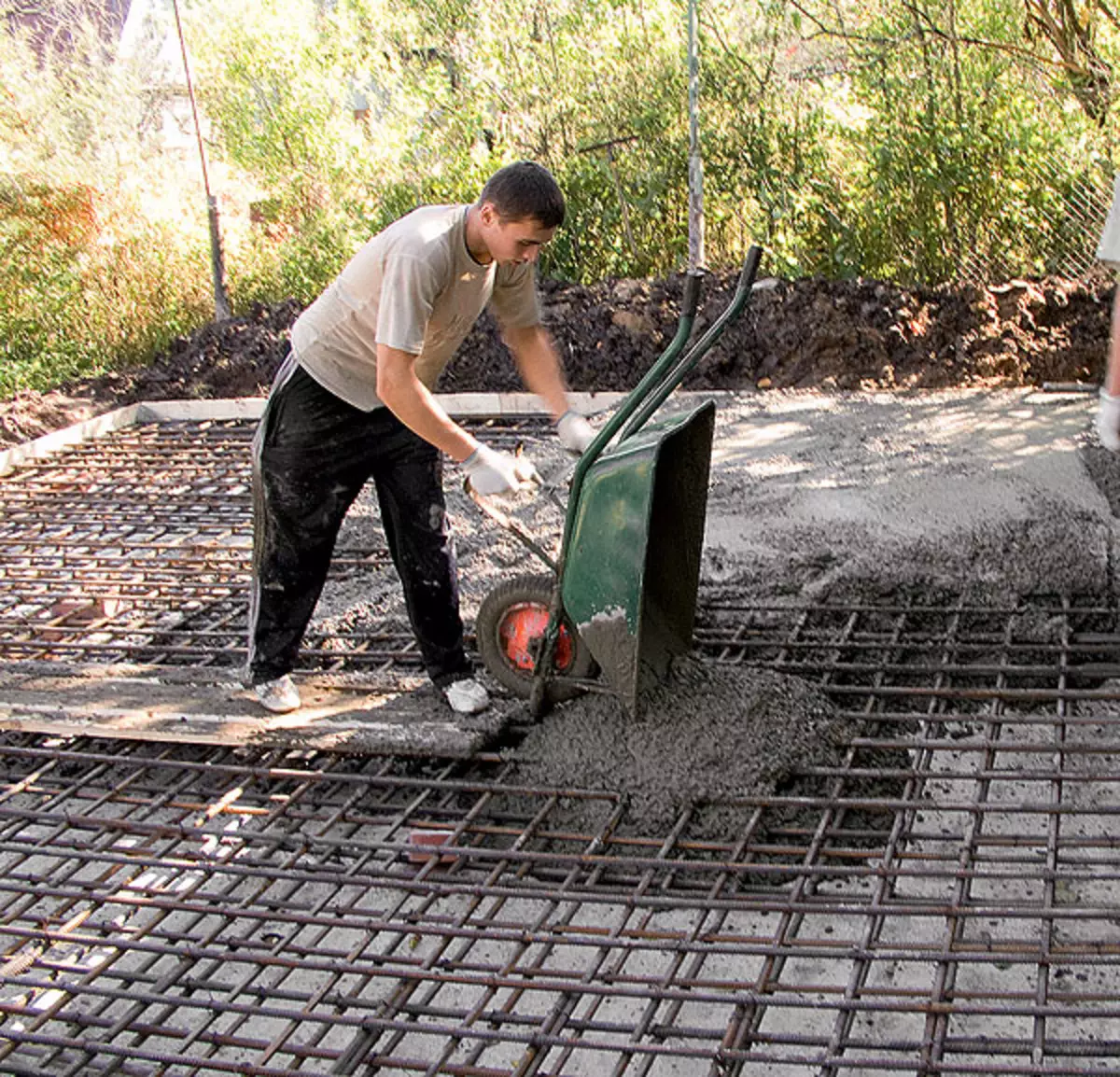
5.6. Increased concrete (example 1) thoroughly leveled into a wooden row (photo 5), and then seal, using a deep vibrator (photo 6)
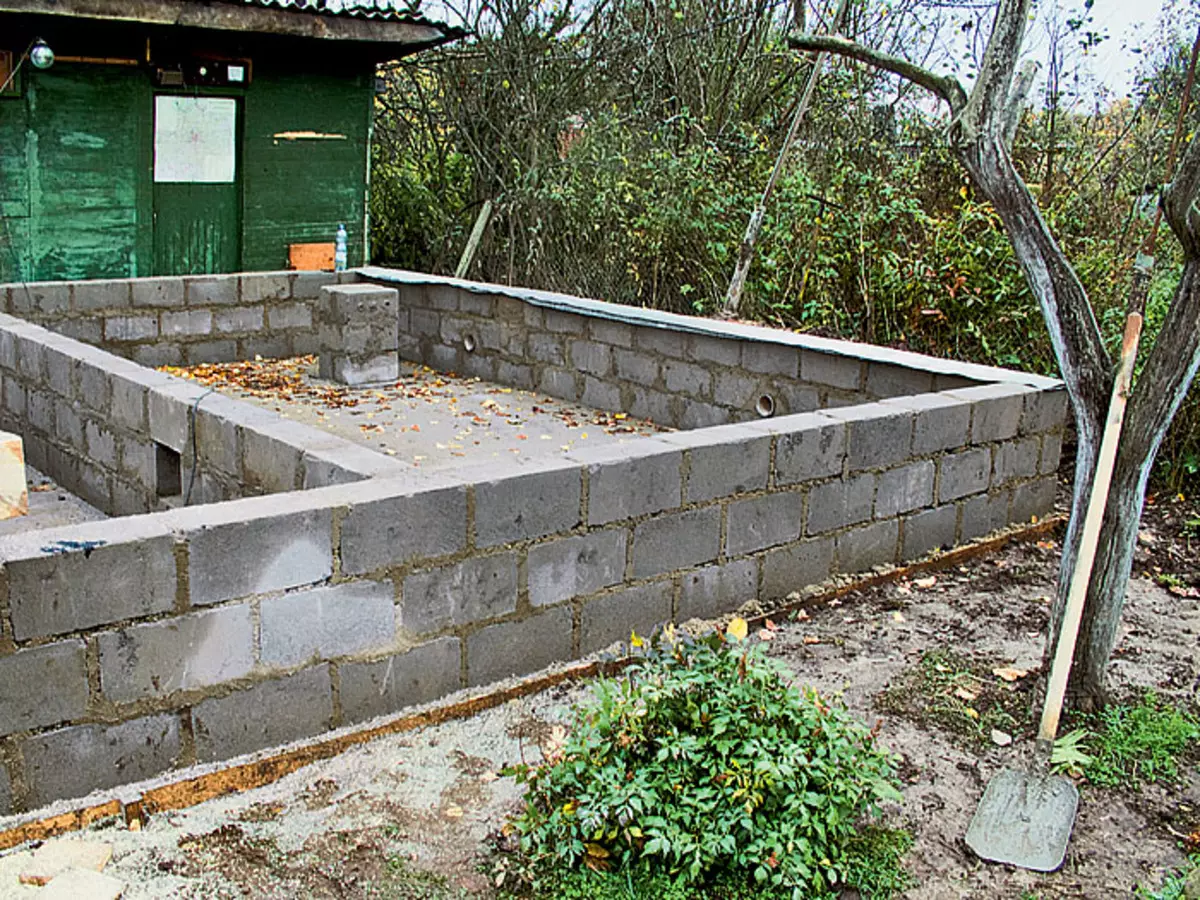
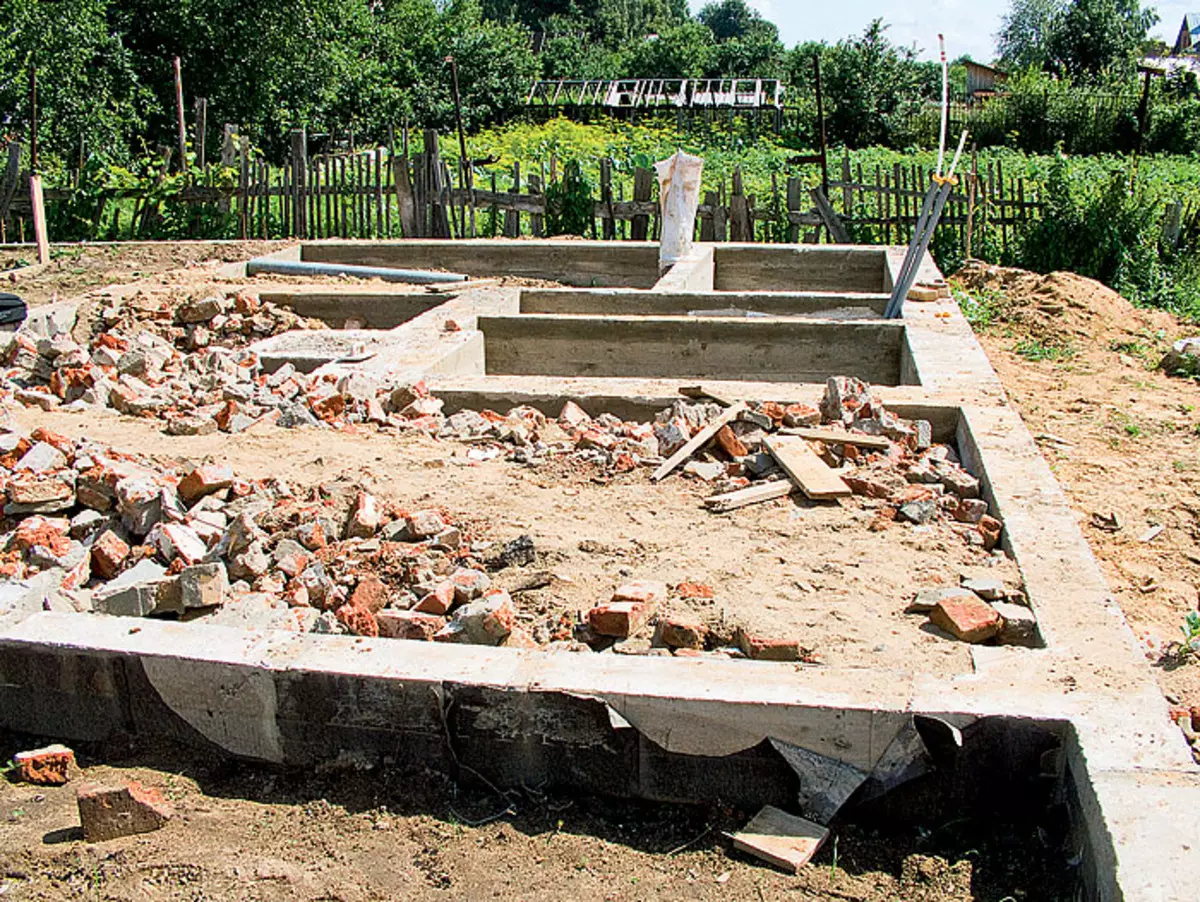
7. When concrete froze (approximately 3 weeks), it was built on the plate from the slag blocks of the base of the future dacha house (example 1) - its tapes are located under the outer and carriage of the inner walls. Together the installation of the heating furnace laid out support column
8.Grunt waters on the site (example 2) are located very highly accumulated 1,5m depth immediately filled with water
When you read this advice, it is waved to ask the specialist who answered the question: "Dear, did you read the letter carefully?" After all, there is all the key information: "Suglink to 1 m", "water is at a depth of 0.8-1m", "what is further unknown." A turning point to the usual language means that it will fail all attempts to develop a trench or dried a well with a depth of more than 1m: they will instantly fill with water, and then tightened. To use the recommended pile-screened foundation, in this case it will be necessary to carry out geo-spoke, which will allow you to understand whether there is a solid layer of soil under the construction site and at what depth it is located (after all, piles should rely on it). But that's not all. I will buy a bored well. It is necessary to immediately install a casing, for example asbetic, which, firstly, will prevent the wellness of the well soil, and secondly, it will later eliminate the access of water from the soil to the concrete filled into the well (water from the well immediately before the fill pump up the pump) . When piles will be filled, you can start the manufacture of writing. (About such a foundation was written in detail in the "IVD", 2008, №3.) In the case under consideration, the developer based on the existing construction experience (own or neighbor) or not wanting to do it, it seems to be right, deciding to pour a monolithic plate. . After all, such a foundation, according to experts, the win-win behaves on any soil. I asked about it knew, but he simply did not hear his specialist. Let's try to fix the flaw and tell about the construction of slab foundations with an area of 36 and 190m2.
|
|
|
|
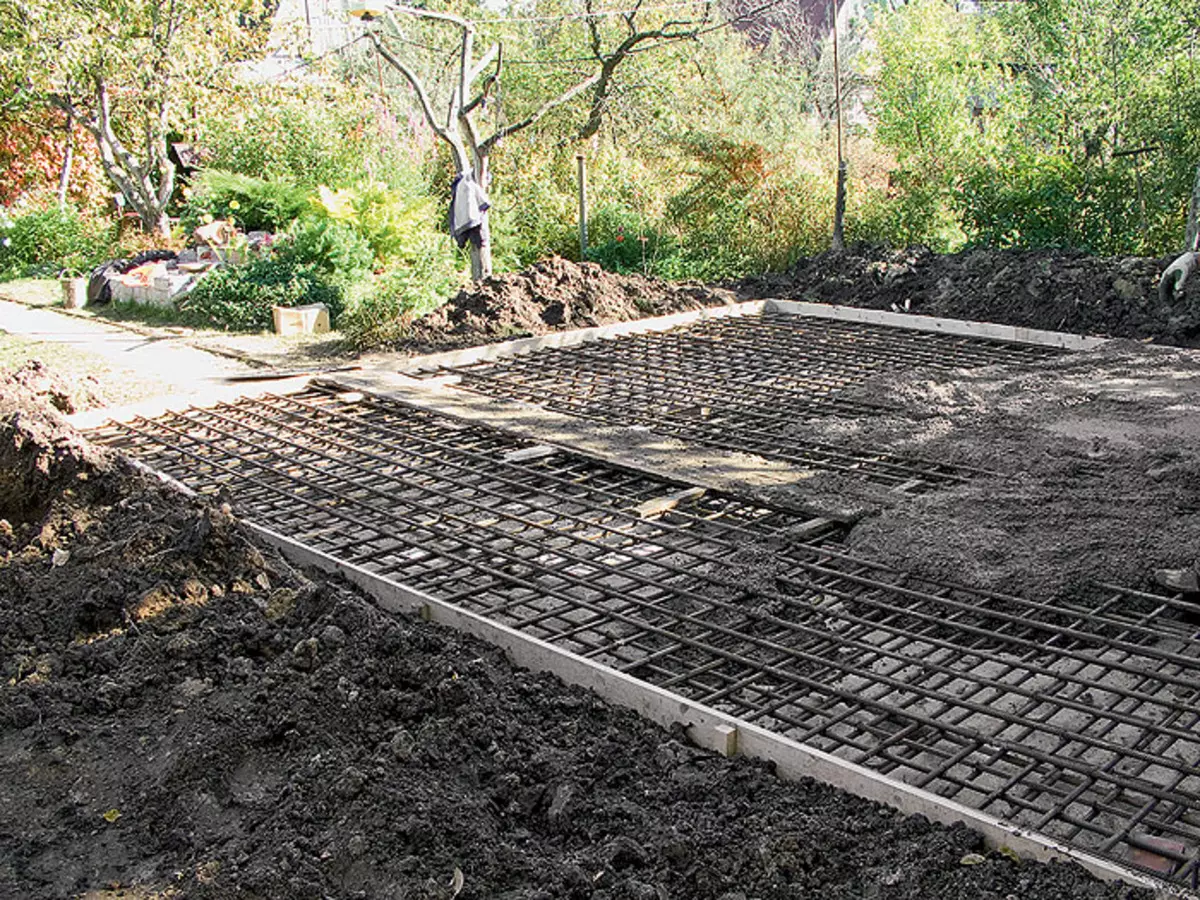
9. Before the creation of the foundation (example 2), the house was summed up to the house, and insulated "heating mains" stretched to the bath and garage.
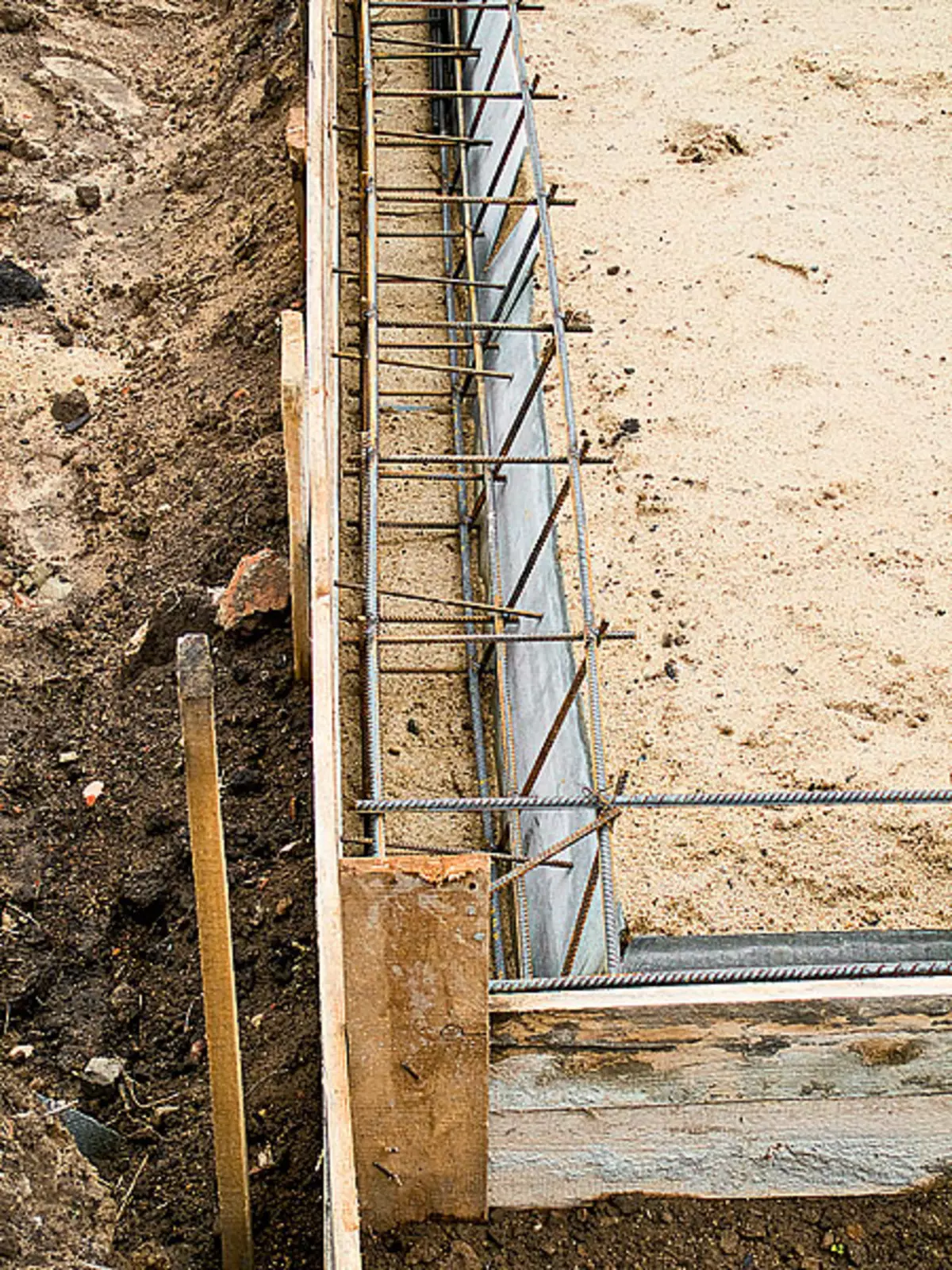
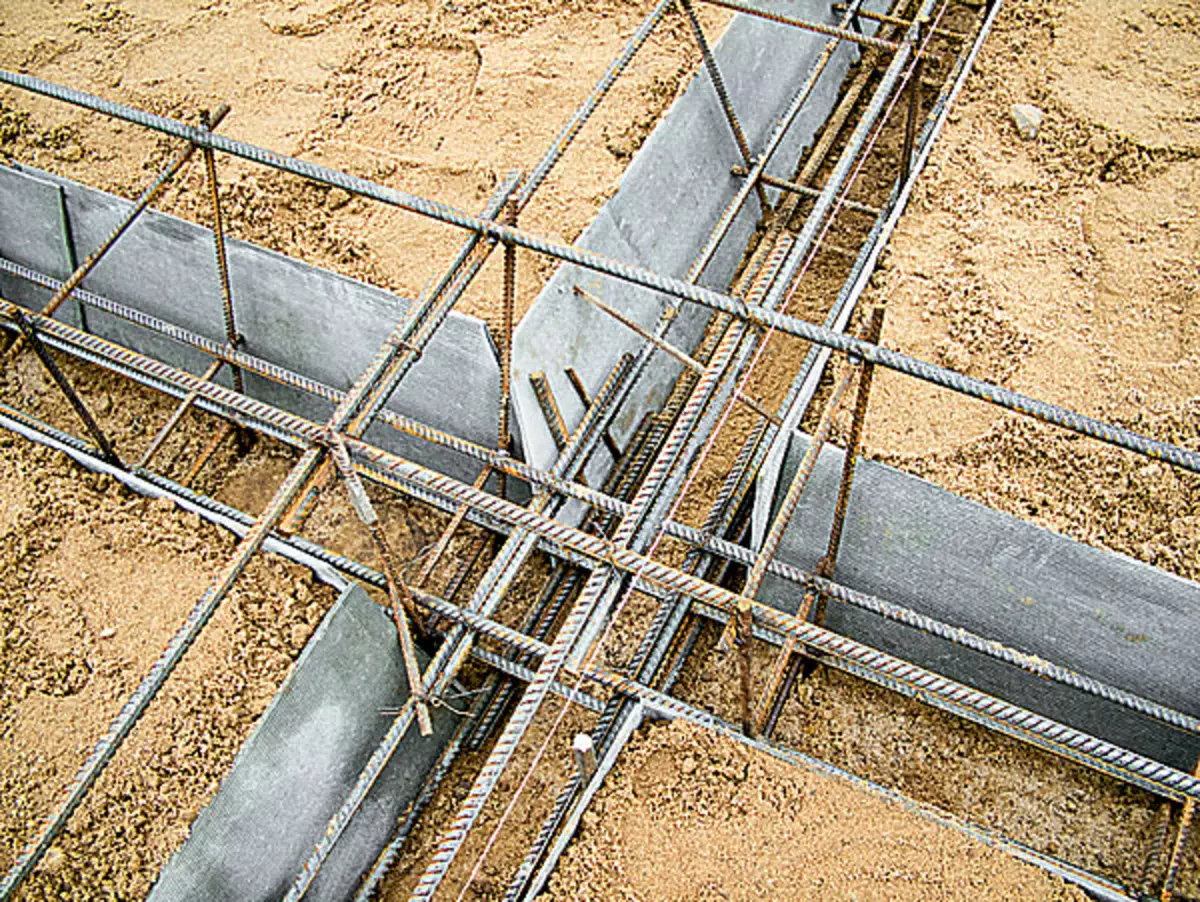
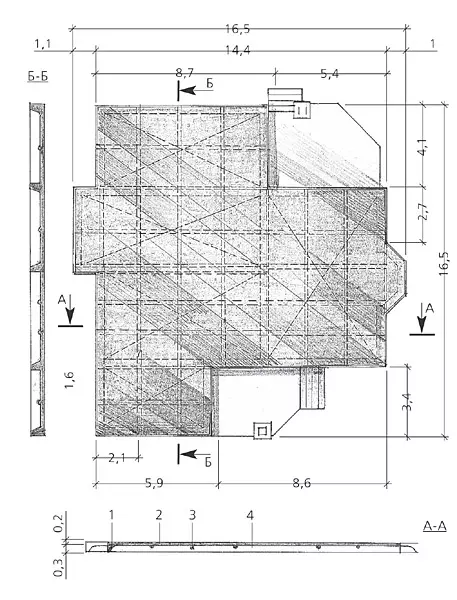
10,11. The rher around the perimeter of the plate (example 2) had a section of a rectangular trapezium height of 325mm (photo 10), intermediate ribs-chained trapezium height 200mm (photo 11). So that the walls of the grooves do not appear, they have strengthened with sheet slate
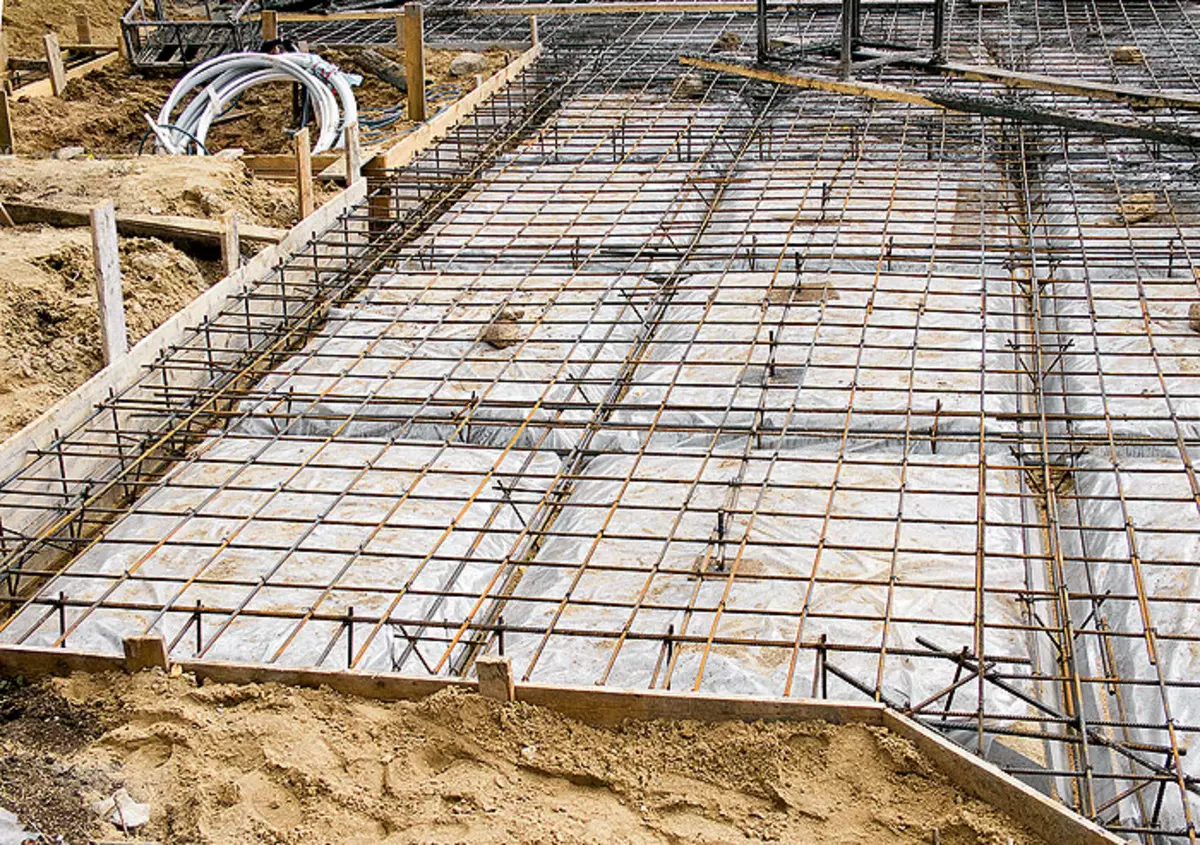
12. After a preliminary assembly of rebar rebar (example 2), they were taken out of the grooves and covered the sand pillow with a polyethylene film so that moisture from concrete did not immediately go into the sand. Then put the frames of the ribs in place and the frame of the plate was created from the rod with a diameter of 12 mm, whose thickness according to the project was 175mm.
Impact on support
The foundation-supported part of the building intended for transmitting the load from the supervised designs to the soil under the house. The device, the material and depth of the foundations depend on the magnitude and nature of the loads on them, from the "capital capacity" and the design features of the building (the presence of the basement IT.P.), as well as from the natural conditions of the construction site (the depths of the fruit of the soils, the nature of their location, presence Groundwater Idr.).For a prominent form, we can assume that two types of loads are affected by the foundation in directly opposite to each other: from top to load, created by the structure of the house, from the bottom of the upload acting on the foundation from the ground.
Loads created by the house design are divided into permanent and temporary. Cutting include the weight of building structures (the foundation, walls, floors, roofs of IT.P.) and operational loads (weight of furniture, equipment, people). Knophen- weight of snow cover and wind load. The magnitude of the temporary depends on the region and the slope of the roofing rods. For example, for the suburbs with a flat roof, a snow load is taken into account 180kgs / m2, and at the angle of inclination 60 this value is reduced almost to zero. The wind load is made in calculations only when the roof is biased over 30, choosing it on the table, depending on the location of the object: in the city feature, in the forest array, in the open area of IT.D. So, the maximum value of this load for the suburbs - 35kgs / m2.
Loads acting on the foundation from the ground are also divided into permanent and temporary. Proponent is primarily the power of the resistance of the soil (depends mainly on its composition, the nature of the occurrence and bearing ability). The quirhosno-forces of the so-called frosty transition that should be told in more detail.
Groundwater in minus temperature turn into ice, increasing in the amount of about 10%. This is the main cause of frosty radiation (swelling) of the soil, which is maximally exposed clay and loam. When the foundation on the wall begged on both sides, the efforts are not only compressive, but also acting on the tangent, seeking to push it up. The magnitude of these forces is directly proportional to the depth of the freezing and can reach 12 kN per 1m2. When the soil is freezing below the bottom depth of the basement of the foundation, it is added also to the sole of the lift force, the value of which is an order of magnitude greater than the sum of the lateral poverty forces.
It is clear that the foundation (and therefore the house built on it) can be in a state of rest only if the strength acting on it in the oncoming directions is balancing each other. But if the forces created by the beagon are too high, the rise of the foundation is inevitably begins. Well, after thawing the soil, the foundation can either return to the previous place, or not return, and, more dangerous, - return unevenly. It is in the latter case that the deformation is most likely, as the foundation and the structure standing on it.
Not less danger than bunched, represent for the structure and highly compressed under load soil, for example peat.
How to protect yourself from attack?
To avoid the sad consequences of the impact on the foundation of frosty powder forces, these constructive measures are taken. First, the sole is placed below the level of primerization of the soil (in this case, it does not experience the actions of the lift forces from the bottom). Secondly, the walls of the foundation of the reinforced concrete are cast. Thirdly, expand the foundation base (it acts as a kind of anchor). Fourth, they do the walls not vertical, but narrowing upwards (then as a result of squeezing the walls with a bunched soil, not only the force raising it, but also to her opposite). Fifth, cover the walls with a sliding material (for example, rubberoid), working as a lubricant. It is clear that the implementation of each of the listed measures requires additional capital investments. Inini is one of them not applicable for highly compressing soils.
But there is another way: the creation of a solid slab that allows you to easily distribute the loads acting on the foundation both from the structure of the structure and on the side of the soil. The jewelry of this slab at such a depth, where the forces of the radiation either will not act at all, or equaline the load from the structure. Achetoba additionally reduce the action of powered forces on such a slab, replace the soil under it sand (create a sandy pillow, which is designed to extinguish the effect of any forces from the ground). Such a foundation, even if it is susceptible to seasonal movements, will perceive them (and they will forgive us specialists for unscientific terminology) just like durable flat-bottomed barge on lung waves. That is, it will rise and go down together with the soil not deforming, and therefore, without causing deformations of the buildings erected on it.
Such foundations are called floating. It is possible to use them for the construction of houses on all types of soils (including peatlands, heavy bunched, bulk, sediments and weakness) and with any depth of groundwater, including very small. Their design is a solid or lattice plate made of monolithic reinforced concrete (concrete must be a class not lower and frost-resistant brand). It is rigid spatial reinforcement throughout the carrier plane that allows such foundations without local deformation to perceive alternate loads arising from uneven movement of the soil. The largest support area makes it possible to reduce the pressure on the soil to 10kpa (0.1kgs / cm2). Communaries of continuous plates include the simplicity of their structure and a slightly smaller cost compared to the familiar foundations suitable for use in the previously difficult geological conditions listed.
When should the solid slab be used, and when the lattice? For houses of a large area or complex in terms of shape, a solid plate is recommended with a thickness of 150-180mm, with contour and cross-ribbies of rigidity (edge-approximately 2m). For smaller houses, a smooth monolithic plate (250-300mm) is suitable for houses, and for compact buildings (garages, baths) - a lattice plate with a cell size of about 1.51.5m. Let us turn to specific examples.
|
|
|
|
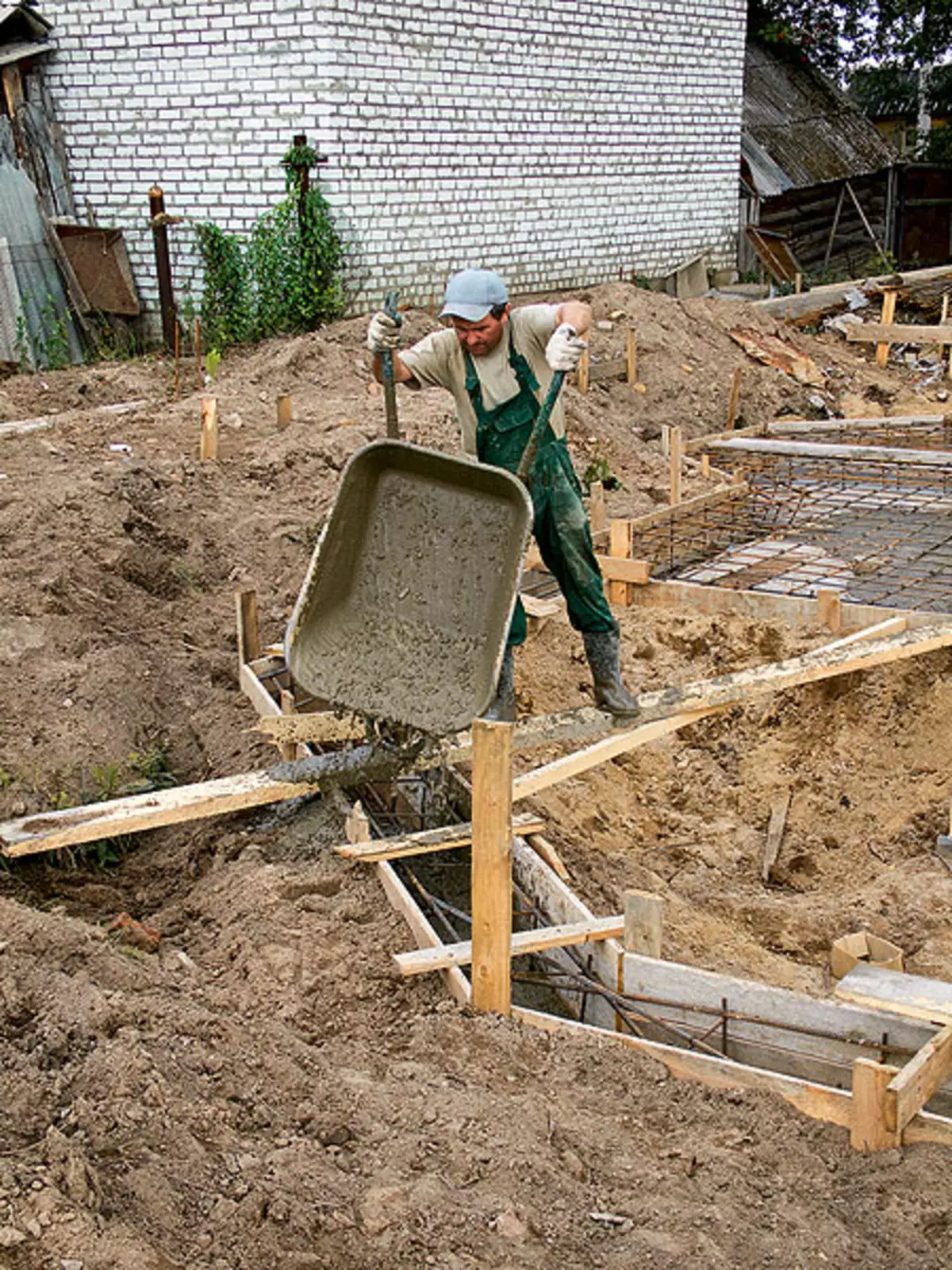
13. Button when pouring the plate (example 2) was supplied along a wooden tray, the inner surface of which was abandoned by tin
14.Poda, the open veranda, adjacent to the house (example 2) poured a ribbon foundation, the reinforcement frame of which is firmly tied with a frame of "floating" plates. Concrete for casting tapes had to bring a wheelbarrow - the distance for transportation along the tray turned out to be too large
15.Shem is a fundamental monolithic plate: 1-rigid rigidity around the ceiling; 2-reinforced concrete plate; 3-intermediate rigidity edge; 4- sand pillow with a thickness of 400mm
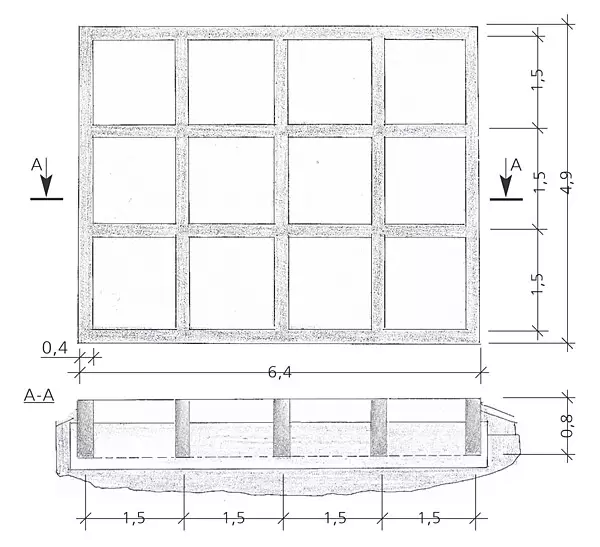
16. The funding scheme of the foundation-lattice plate under the construction of 6.44.9m. The stove such design is only conditionally called, since a solid horizontal "membrane" is missing in it
Example of the first
In this case, a small two-storey skeleton country house (6.56m) was erected on the site already used for 30 years. The long-term experience of its operation and suggested to the owners, which may have to be a foundation for a new structure, and therefore they courageously went on his rise in prices, refusing the proposed work of a small-maleed foundation. Ipozhuya, correctly arrived: the primer, the groundwater is already in a half-meter from the ground level.Under the future house, the fertile layer of soil was removed and digging the "pit" with a depth 50cm (later the outlined soil was scattered over the site, thus lifting its overall level). At the bottom of the pit, a sandy pillow was created with a thickness of 20cm, on top of which a two-layer reinforcing frame was laid (the lower layer of fittings, using concrete beacons, lifted over the level of the sand pillow on 10 cm, the distance between the layers of fittings is also 10cm), after which the M300 brand was cast from the M300 concrete 30cm. The order of work is shown in detail in the photos and in the comments, perhaps does not need.
An example of the second
Here, the developers decided not just a house, but a complex of buildings, which includes a bath, garage and a fence around the plot. To squeeze all this they were going on a non-removable formwork technology for our country, which is called Durisol (Durisol-Werke, Austria).
The construction site was very old and therefore, they learned about the problems with the soil from the neighbors almost immediately: the strongest, groundwater is at a depth of about 1m. In addition, the site was repeatedly erected and demolished at home, so under the place of development there were multi-layer deposits of construction trash. The designers proposed to be used as a foundation under the house a monolithic slab with ribbies, and under the garage and baths, lattice plates.
Works began with the fact that the "centuries-old" layer of construction garbage from the site was plundered, replacing it with coarse-grained sand (the thickness of the layer is about 40 cm). The sand was shed with water and constructed using vibrotem. Along with the sand, the ground was taken to the site, with which they subsequently aligned the soil level (the height difference along the length of the site was about 80cm).
|
|
|
17.The technologies of creating lattice plates under the garage and bath (example 2) as a whole was similar to the technology of the construction of a low-breed belt basement. The difference is that in the low-boiled basements of the tape are located strictly under the bearing walls, in the lattice plates - with a step of 1.5 m (the plate has a cell size of 1.51.5 m). Cross section of reinforced belts- 8040cm
18.Fundament fence-cutting-solid (example 2). The base of piles with a diameter of 160 mm is at a depth of 1.2m. Cross-section ribbons painted - 5025cm. Investments left the releases of the reinforcement necessary for further work
19. When the concrete of an ordinary monolithic plate (example 2) hardened, builders, as in the first example, began to build a base on it. It was created from insulated blocks of non-removable formwork Durisol. The material from which the blocks themselves are made are somewhat resembled opilk concrete: at 80-90% it consists of the past processing of flaky-protected compositions of large chips of coniferous trees bonded by Portland cement
Simultaneously with the planning of the territory, communications laid. The gas and plumbing pipes (eyeliner already had) extended and brought upstairs under the future boiler room. Then from the boiler room stretched water and heating highways to the garage and bath-metal-polymer pipes in the tubular insulation were laid in PVC pipes used for laying sewage. The order of work on the creation of the slab itself is quite detailed in photos. Well, about Durisol technology, we will tell you in detail in the next issue of the magazine.
Enlarged Calculation of the cost * Devices with a smooth "floating" plate under the size of 6.56m (Example 1)
| Name of works | Number of | price, rub. | Cost, rub. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handling axes and marks, layout | Kombl | - | 590. |
| Manual soil development and removal | 27m3. | 600. | 16 200. |
| Sand base device | 16m3 | 380. | 6080. |
| The device of foundation plates of reinforced concrete flat (with fittings and formwork) | 12m3 | 4000. | 48,000 |
| Waterproofing horizontal and lateral | 46m2. | 420. | 19 320. |
| Reverse fusion, layout of the area remaining soil | Kombl | - | 3900. |
| Applied materials on the section | |||
| Concrete M300 | 12m3 | 3900. | 46 800. |
| Cement | 350kg | 6. | 2100. |
| Sand | 16m3 | 450. | 7200. |
| Sawn timber | 5m3 | 5900. | 29 500. |
| Steel fittings | 1.6 T. | 34,000 | 54 400. |
| Wire knitting | 100kg | 65. | 6500. |
| Polyethylene film | 1 roll | 3000. | 3000. |
| Hydrosteclozol, Bituminous Mastic | 46m2. | - | 13 300. |
| Hardware, nails and other materials | Kombl | - | 1700. |
| TOTAL | 258 600. | ||
| * - the calculation is made without accounting of overhead, transport and other expenses |
Enlarged calculation of the cost * Devices of an ordinary "floating" plate under the house of a complex shape with the first floor area of about 190m2 (example 2)
| Name of works | Number of | price, rub. | Cost, rub. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handling axes and marks, layout | Kombl | - | 830. |
| Removing vegetable soil | 190m2. | 70. | 13 300. |
| Collection and removal of construction trash | 10 T. | - | 14 500. |
| Development, recess and refinement of soil | 137m3 | 551. | 75 500. |
| Underflow of the soil, the layout of the section manually | Kombl | - | 9200. |
| The device of a sand base with a seal of pneumatic traaming and watering water | 76m3 | 380. | 28 880. |
| The device of foundation plates of reinforced concrete finned (with installation of fittings and formwork) | 48m3. | 4700. | 225 600. |
| Waterproofing horizontal and lateral | 210m2. | 420. | 88 200. |
| Reverse Freshness, Planning Site | Kombl | - | 4700. |
| Applied materials on the section | |||
| Concrete M300 | 48m3. | 3900. | 187 200. |
| Cement | 500kg | 6. | 3000. |
| Priming | 20m3 | 950. | 19 000 |
| Sand | 76m3 | 450. | 34 200. |
| Flat slate | 200m2 | 153. | 30 600. |
| Sawn timber | 8m3 | 5900. | 47 200. |
| Steel fittings | 8 T. | 34,000 | 272,000 |
| Wire knitting | 400kg | 65. | 26 000 |
| Polyethylene film | 6 Rules | 3000. | 18 000 |
| Hydrosteclozol, Bituminous Mastic | 210m2. | - | 60 700. |
| Hardware, nails and other materials | Kombl | - | 3200. |
| TOTAL | 1 161 800. | ||
| * - the calculation is made without accounting of overhead, transport and other expenses |
The editors thanks the company "Archvizhen Group" and personally Alexander Kharkov for help in the preparation of the material.