



Primary conditions to dig trenches under the laying of the power cable are carried out using a compressor and a jackhammer, as well as manually


The cable is unwinding manually either from the bay, or from the coil on the mobile trailer
Cable passages are sealed with inflatable RDSS type seals (Rychem) covered with sealant. When inflating the sealant makes the penetration of waterproof

When compliance with the installation technology of the coupling of any type, the tightness of the cable connections for a long time is ensured. Installation of the filler clutch is extremely simple


Traditionally, the cable penetration seal is made by a mixture of sand, cement and clay.


Gel clutches are used for connecting, branching and repairing cables with plastic insulation without armor (type VG, AVVG, PVG, N (A) YY, N (A) YBY IDR.). Silicone gel has good adhesion and hydrostability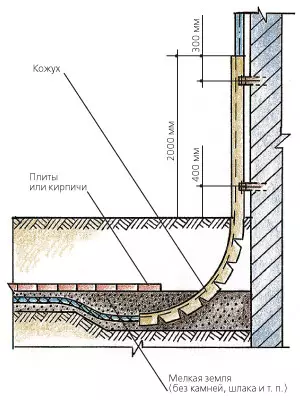
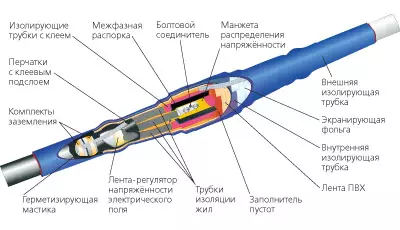
Construction of the cable coupling "Progress"
Electricity consumption in the individual residential sector is growing at from year to year. The latest technical developments comes to the change of moral and technically obsolete brand of cable and cable connections, allowing to significantly increase the efficiency, reliability and safety of electrical networks, extend their service life
Cable. Which one?
Electricity enters the house on the wires of the electric transmission line or by the cable laid in the ground. How to enter electricity in the building- wires or cable, solves the local energy supplying organization in coordination with the owner of the dwelling. Interest for the reader is that the traditionally wide range of modern cables is recently updated with new brands, whose characteristics are beneficial to distinguish them from prototypes. Methods of laying to the house of cables and wires from a complete transformer substation (KTP) or a pilot transformer, receiving cable connections are changed.
The cable entry of electricity in the building allows you to do without wooden or concrete supports that do not always organically fit into the landscape. At the same time, this is more expensive compared to air input method of electrification housing. In addition, until recently, cable entries in reliability were inferior to air. Low and medium voltage cables (1-10 kV) of the traditional design were negatively reacting to the increased acidity and moisture content of soils, the cycles of their freezing and thawing, on the bunched and sedentary soils. Listening to the breakdown and disorders of the tightness cables with paper-impregnated (BP) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) wasolation had to be changed in areas up to 20m long (the moisture time was time to spread along the conductive current veins). The disadvantage of cables with stitched polyethylene insulation (SPE) and with rubber cores for longitudinal sealing of space between conductive cores, the reliability of cable entries has increased significantly. Therefore, consumers show this today to the cables of the new generation as the same interest as the modern self-supporting wire of air input. Almost all profile plants in Russia are engaged in the release of power cables for trench input into the house, a number of industries in Ukraine. Among them are such large enterprises as CJSC "Plant Moskabel", OJSC "Electrocabel" Kolchuginsky Plant, OJSC "Irkutskabel", CJSC "Lyudinovokabel" plant, Sevkabel. High-quality products are supplied to our country from Finland (ENSTO) and France (Nexans).
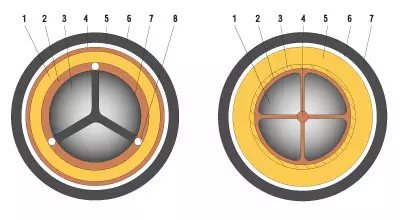
1- shell; 2 - waist isolation; 3- lived;
4- pillow under armor; 5 - armor; 6- outer cover; 7- phase isolation; 8- interfacial filling harnesses;
Construction of plastic insulation cable:
1- conductive veins; 2- phase isolation; 3- polymer shell; 4- filling in the center; 5- pillow under armor; 6 - armor; 7- Outdoor Pokrov
What are attractive for a private developer cables with isolation from SPE? First of all, the term "stitched polyethylene" should be explained. The "stitching" of polyethylene is its physical and chemical treatment at the molecular level, which increases the electrical and mechanical characteristics of insulation, which reduces its hygroscopicity, expanding the range of operating temperatures. The design of modern low and medium voltage cables, along with an isolation from PTE, provides for the presence of copper or aluminum insulated conductive veins made from one or more, twisted wires of the round or sectoral section. The insulation of zero lived is made in blue, grounding veins are painted into a combination of green and yellow colors. Cables make three-, four and five-housing. They have all the veins of the same cross section or one living of a smaller cross section (zero or grounding) in four-core cables. The insulated veins are twisted into the core around the PVC plastic harness or non-carcanized rubber, which takes the necessary form during the cable twist and seals it in length. Over the twisted veins, there are waist insulation from polyethylene, PVC plastic or a minor-filled non-buckled rubber mixture with the filling of the gaps between the conductors. Sometimes the belt isolation is a two-layer: the inner layer of non-carcanized rubber mixture, outer polyethylene or PVC plastic. The following should be a protective cover from two steel galvanized tapes imposed so that the top overlap the gaps between the tips of the bottom. The finish coating is a protective hose, discharged from polyethylene.
The table below confirms that low and medium voltage cables in an isolation from the EST in comparison with cables in BP isolation have a number of distinctive properties. This is a large (15-30%) throughput by increasing the permissible temperature of the vein, the best electrical and mechanical characteristics of isolation, minimal dielectric losses, increased moisture resistance, less bending radius, the possibility of laying on the tracks with an unlimited level difference and at temperatures below -20 With without preheating, smaller mass and cable dimensions in general.
Characteristics of power cables with insulation from SPE and cables with BP and PVC insulation on a voltage of 1 kV
| Parameters | SPE | Bp | PVC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durable heating temperature lived, with | 90. | 80. | 70. |
| Permissible temperature when working in emergency mode (6h), with | 130. | 105. | 80. |
| Maximum allowable temperature lived with a short circuit, with | 250. | 200. | 160. |
| Permissible current loads depending on the cross section of the vein,% | 120-125 | 105-110 | 100 |
| Relative dielectric constant | 2,3. | 4.0 | 4.5 |
| Specific volume resistance, OM. cm | 1016. | 1013. | 1013. |
| Tangent Angle of dielectric losses | 0.001. | 0.008. | 0,01 |
| The minimum allowable gasket temperature without preheating lived, with | -20 (for APVBSP) -15 (for other cables) | 0 | -fifteen |
| Minimum bend radius (DH- outer cable diameter) | 7.5.dh. | 15.dh (for cables in the lead shell) 25.dh (for the remaining cables) | 7.5.dh. |
| The difference in the level on the track of the gasket, m | With no restrictions | fifteen | With no restrictions |
What kind of cable stamps should be used for trench input of electricity into individual houses? PVP cables, APP, PVP and APPP can be stretched under the ground regardless of the degree of corrosion activity of soils. If products have additional indices "g" and "2g", they are suitable for laying both in the ground and in water, subject to the measures that exclude mechanical damage to the electric line. PVV brands cables, ATV, PVVNG-LS *, APC-LS are designed to accommodate in dry soils (in sand, sand-clay and normal soil with humidity of less than 14%). In the absence of danger of mechanical damage to the ground, cables are placed in plastic isolation AVVG, VG, as well as APBBSH, APBBB, PVBBSH, PVBBSP, if the soils are non-repurient and non-emergency. For any soils without restrictions, the WBBSH cable is suitable. The listed brands of cables are mounted without taking into account the difference in levels of terrain. For underground gasket, power cables with paper insulation, impregnated with the unscrewing composition still use. Cammake with medium and high corrosion activity stretch three-core cables CAASHV, CAAB2L, TsASBL, ZASB2L, TsASBB, low and medium corrosion activity - Caçabl, TsAB, CSB, TSSBL. Analogs of the production of foreign firms have their own labeling, correlated with the classification of cables adopted in Russia.
Cables intended for transmission and distribution of electricity that can be laid in the ground









Laying cables
How is the laying of power cables? In most cases, they are tested to the house with a trench manner, in pipes or without them, in accordance with the "rules of electrical installations" and technical operating conditions. The cable shoulder stretch is made using a cable stocking or wedge gripping for conductive core. The permissible force of the cable tension during the strip is not higher than 30 H / mm2 for aluminum veins and 50 N / mm2 for copper. At the same time, the minimum radius of the bending of the cable should be at least 15 DH (7.5, when installing using a special template), the number of bends is no more than eight on the construction length of the cable. Without prior heating, the cables are mounted at temperatures up to -20 C for PVP brands, an APP, PVPU, APPE and up to -15 C for PVV brands, ATMs, PVVNG-LS and APVG-Ls. At lower temperatures, the cable must be withstanding in a warm room at a temperature of +20 with at least a day or warm on the drum by blowing hot air from a special installation.How is the connection of cables between themselves, how and what protects the places of compounds underground? To ensure uninterrupted power supply at home, this problem is very important. You can connect and branch cables of various types and stamps, as well as cables and wires of air input, if there is a need. Cable connections and branches are sealed with couplings. Were wide widespread clutches. This method is good, but it is quite time consuming; For mounting, gas burner and tools are needed. Cold shrinkage clutches are usually used in field conditions, in the absence of the desired equipment. Gel and fuel couplings are extremely easy to use and reliable, but quite the road, besides, their storage is limited. For sealing cables connections with various types of insulation, the corresponding couplings are chosen.
In all cases, the ends of the connected current-carrying livers are securely attracted to the steel connector with two bolts with disruptive heads. According to the technology of thermal shrinkage, every place of articulation lived isolate with a plastic tube containing glue melt: when heating the burner it makes a mixer with hermetic. For the correct arrangement of compounds relative to each other between them, plastic interfacial spacers coated with mastic-dielectric. Metal cable screens are associated with a metal ground ribbon by soldering or mechanically. To protect against electrical interference, the connection site is shielded by foil. In addition, installers carry out a set of measures to competently distribute the electrical field strength of the conductors, to isolate the mating cores from the effects of the internal impregnation composition of the cable (if oil and rosin) are used), fill the emptiness between the conductors and eliminate the possibility of moisture and gases to the connection node. To do this, use insulating tapes, sealing mastic and adhesives.
According to the cold shrinkage technology, the coupling are sealed on the cable due to the "molecular memory", which has plastic material. After operating condition, the coupling nozzles are held from the inside from the shrinkage with metal or plastic spirals. After the head of the coupling on the insulated ends of the cables and the fulfillment of the necessary silent, the spirals are removed, and the clutch is hermetically seated. This technology has been widely used in low-voltage devices such as insulating tubes, couplings, adapter couplings and an end sealing of the cable.
For a long time permissible current loads of cables with an insulation from SPE in networks with a voltage of 1.3 and 6 kV
| Nominal cross section lived, mm | Long permissible current loads of cables, and | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With copper housing | with aluminum housings | |||||||
| In the ground | On air | In the ground | On air | |||||
| one; 3 kV. | 6 kV. | one; 3 kV. | 6 kV. | one; 3 kV. | 6 kV. | one; 3 kV. | 6 kV. | |
| 10 | 87. | 79. | 76. | 75. | 67. | 62. | 58. | 58. |
| sixteen | 113. | 104. | 101. | 99. | 87. | 79. | 78. | 75. |
| 25. | 147. | 138. | 133. | 128. | 113. | 102. | 102. | 99. |
| 35. | 178. | 166. | 164. | 157. | 137. | 124. | 126. | 122. |
| fifty | 217. | 198. | 205. | 191. | 166. | 147. | 158. | 145. |
| 70. | 268. | 243. | 262. | 244. | 201. | 181. | 194. | 180. |
| 95. | 316. | 294. | 318. | 296. | 240. | 220. | 237. | 220. |
| 120. | 363. | 333. | 372. | 348. | 272. | 249. | 274. | 255. |
| 150. | 410. | 378. | 429. | 389. | 310. | 282. | 317. | 290. |
| 185. | 459. | 429. | 488. | 447. | 384. | 322. | 363. | 336. |
| 240. | 529. | 503. | 579. | 534. | 401. | 278. | 428. | 400. |
Technology using compound Pouring (filling couplings). Rychem (Germany), "3m" (CSH), Ensto (Finland) have developed a cable connection method with a coupling filled with gel or compound. The company "3M" produces a wide range of connecting and branching (for example, to enter cables in the building, outdoor lighting, etc.) of the filler couplings with a transparent housing for low-voltage cable networks. The coupling housing is fixed at the scene of the connection / branch cable. Immediately before the fill, the components of the compound are mixed in a two-section, hermetically closed bag. Through a special neck, the finished composition is poured into the coupling housing, where it harvested as a result of a chemical reaction. The connection is enough to fall asleep with soil, and the cable is ready for operation. Bay devices with a transparent body allow you to visually monitor the process of filling the compound. When they are installed, it is practically no isocyanate, harmful gas formed during the thermal shrinkage of couplings. Compound compound compound is characterized by extremely high resistance to chemicals, mechanical strength and heat resistance contained in the soil. The filler clutches are used to merge all types of cables, including paper-impregnated and polyethylene insulation.
For a combination of three-, four- and five-housing power cables with plastic insulation, with armor and without it, a voltage of 1 kV (AVVG, APVG, AVBBSH, etc.) It is recommended to use heat-resistant PSTT3 / 4/5 couplings. To connect three- and four-cores with paper insulation in a common shell, heat-suite Couplings STP3 / 4 are intended, as well as other structural products certified for these purposes.
The cable from under the ground is connected to the terminals of the transformer and the introductory and distribution device. To ensure the electrical safety, the connected current veins, including the end of the insulation of the veins and the area of the tip, isolate the terminal clutches. To do this, we use thermal and other clutches in the form of gloves and tubes, designed for termination of lived with different types of insulation. So, to rub the three-, four or five-tier cables with plastic insulation, with or without armor, with a voltage of 1 k-AVVG, APVG, AUBBSHV, VBBSHV, IDR. - Manufacturers recommend using heat-suite CKPP3 / 4/5 couplings, UPP3 / 4/5, certified products of trustworthy foreign manufacturers. For cables of the same voltage with paper insulation in a common shell, you should choose the terminal thermal coatable coupling of kV (H) TP3 / 4 or certified products of foreign companies.
In Japan, France, Finland and Sweden in low and medium voltage distribution networks today, only the cable is used in Isolation from the PTE. Russia is once again catching up the West.
* The "NG" index indicates that this type of cable does not support burning, the LS index (Low Smoke) - that in a fire, the cable has little smoke and does not release toxic substances. These cables are more expensive than usual, and, as a rule, they are used for special purposes.
The editorial board thanks Tyco Electronics, 3m, Ensto, OJSC Electrocabel Kolchuginsky Plant, Transherenergo and CJSC Moskabel for help in preparing the material.
