
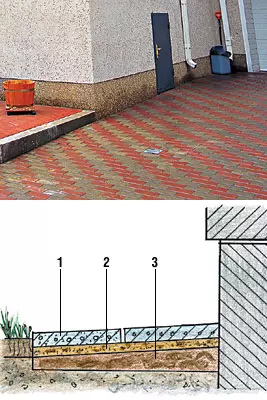
1- Plates;
2 sand;
3- clay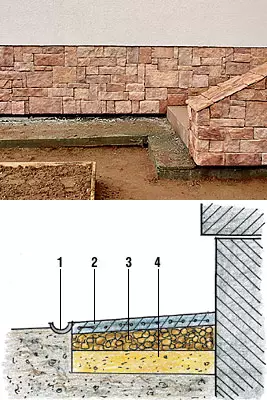
1- drainage chute;
2-reinforced concrete;
3-crushed;
4- sand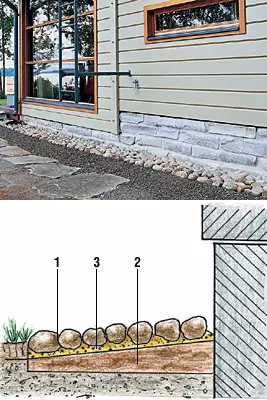
1- cobblestones;
2 sand;
3- clay
Separating a horizontal waterproof strip of materials along the perimeter of the exterior walls of the house designed to protect its foundation from rain and flood waters. Return of the scene includes a delay and removal of water into a storm sewage sewer or "on the relief" (eddy-road ditch) through the gutter. It not only warns the deformations of the foundations due to the frosty powder of the soil, but also is a kind of decorative element of the facade of the building, playing the role of "sidewalk" around the house.
The scene consists of two layers: underlying (sand and crushed stone) and upper protective (concrete, asphalt, cobblestone). Material for the base is selected depending on the type of final coating, however, in all cases, the constructive solution of the scene must provide its waterproofability. If there is a warm basement in the building (as in the house in question) or the basement, it is advisable to arrange a break with the insulation to reduce the calculated impairment depth. It protects the basement from sharp temperature fluctuations; At the same time, the swelling of the soil near the foundation does not occur.
The construction of the scene began with removal of the surface layer of the soil to a depth of at least 15 cm and removing the remnants of the roots. (Otherwise, the germ can then destroy the coating.)
The width and depth of the trench under the device depends on the type of soil and removal of the roof of the roof. On the bunched soils, it should be wider than the carnis, but not less than 1m and have a depth of at least 30 cm. The scene must be adjusted close to the base of the house and to be continuous throughout its perimeter - otherwise the water will fall into the gap between the scene and the wall.
Let us dwell on the device of the gallery from the monolithic concrete, as the most common and practically only acceptable for bunching soils.
The bottom-dilated trench with a depth of 30cm was covered with a layer of sand with a thickness of 10-15 cm with a mandatory traam, and then with a fracture, to bring down the backfill level "on zero". After that, along the edge of the future, the formwork was set up a height of about 10 cm.
The base was flooded with a 7-centimeter layer of concrete M 250 and, without giving it to grab, spread over the reinforcement grid, placing it closer to the lower edge. (The armature works better on bending and, accordingly, enhances the concrete, only being laid in the lower or in the upper part of the fill layer. Without reinforcement, the monolithic gossip will be collapsed from the cracks formed under the influence of natural conditions.) The top layer of concrete (3 cm) was filled. For a natural drain of water, this coating was performed with a slope of the houses of the house within 5 cm per 1 width, the layer thickness along the edge of the scene was at least 10 cm. The wet surface of the frozen concrete was covered with cement (2-3mm) with simultaneous smoothing by a trowel to improve waterproofing, that is, they conducted the so-called ironing, thanks to which water is less absorbed into the concrete.
On the concrete break, transverse gaps are needed every 2m (temperature seams) in order for after seasonal deformations of the soil it is not crackdown. To do this, we used flexible vinyl tapes with a thickness of 10mm, which, bending under the load, warn the formation of cracks: during the frosty bearing of the soil, concrete will not break, and will "play" on the arranged seams.
At the external perimeter, the scene was installed gutter for removing water with a slope toward the natural drainage. The usual groove for these purposes is not suitable, as it will constantly overgrow herbs.
The flow of water from the roof directly to the slate is not recommended, the flow of water will gradually destroy it. So that this does not happen, the chute strengthened on the karnis, and now the water collected from the roof will be discharged into the storm sewer or dick.
In addition to the described design of the scene, there are other applied in less flooded soils. They are usually less depth and width, and no such time-consuming materials can be used for the upper layer as concrete with reinforcement. The protective coating in such cases is performed from concrete slabs, asphalt, laid by a cobblestone.
Those who during the construction and arrangement of the house and the plot are choosing exclusively natural materials, can build a break from the turf (if the type of soil allows).
On dry non-emergency soils, the breakfast is usually not done, but in places of the rain and melt water from the roof to prevent the sweeping of the sub-undermined soil are arranged by the discharge gutters.
