

Peter Nikolaev
Warming of part of the facade under the window opening extruded polystyrene fiber DOW CHEMICAL (USA)


In second place on heat leakage - the roof and overlapping of the top floor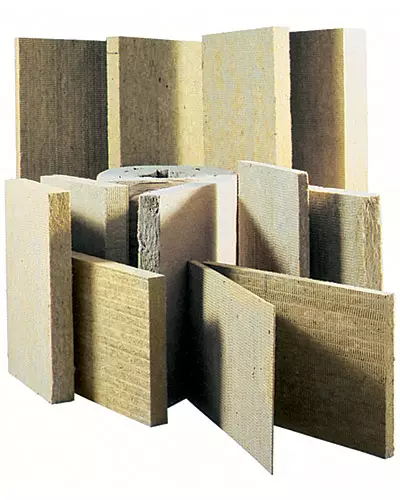



Thermal insulation materials should maintain their initial geometric sizes during the entire period of operation.
This is the insulation of the frame of the frame inkonny partition glass

According to its technical characteristics for the insulation of the foundation and base, the plates of extruded polystyrene foams are best suited.


Cold attic ceiling insulation
Above the heat insulation layer should always be a clearance of at least 1.5-5 cm for free air movement in space between the basis and the final floor
Floor insulation The attic fiberglass material KL-E from Isover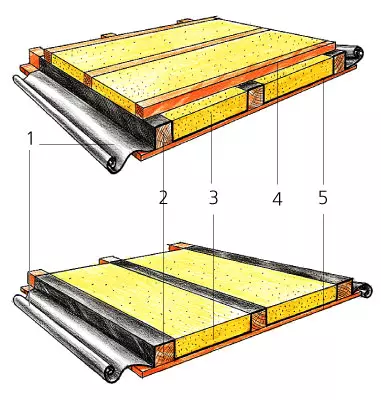
1 warehouse;
2-beam overlap;
3 - insulation;
4- remote bars;
5 - Low room ceiling cover

Warming of the walls of the attic. Rockwool mineral wool plates with a thickness of 10cm laid into the space between the base frames of the wall frame
Metal support for the first row of thermal insulation material. When insulating the house outside his finish ceases to play only aesthetic role. It must necessarily create comfortable conditions inside the building and ensure the protection of the supporting structure and the insulation reinforced on it from the influences of various weather factors, naturally without loss of the external attractiveness of the facade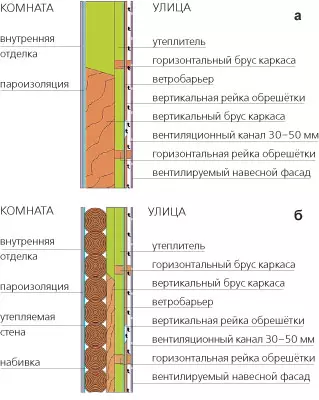
Schemes of layers of insulation materials when insulating wooden structures of frame (a) and log (b) houses

Warming of mansard walls. The heat insulating layer of mineral wool serves as the basis for the heat-reflecting and vaporizing coating "Penofol". Thermal insulation properties of foamed polyethylene enhances the reflective layer of aluminum foil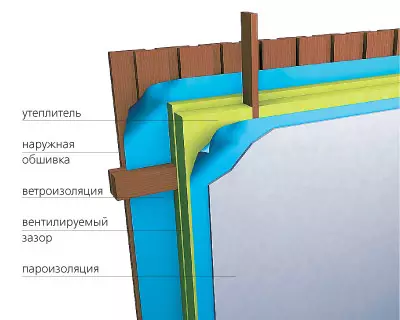
Scheme of the location of the bars of crates and insulating materials when insulating a wooden structure, eliminating the appearance of "cold bridges"
The URSA rolled insulation is easily cut by a knife. With the insulation of the attic usually use heat insulation from glass gambles or basalt wool with a thickness of 150mm
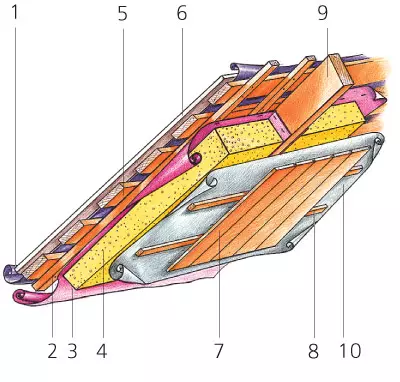
1 - waterproofing;
2 - bars;
3 - Membrane
vapor-permeable;
4 - insulation;
5 - Obesetka
subsecutive;
6 - roofing;
7 - lining;
8 - doom;
9 - a rafter foot;
10 - vaporizolation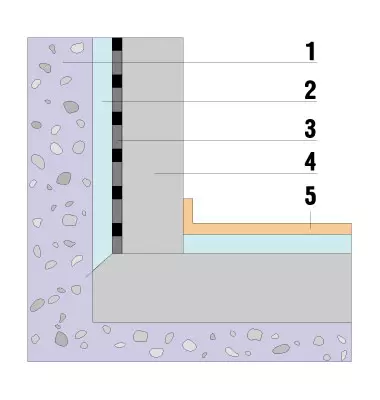
1. Grunt
2. Treatment
3. Hydroesolation
4. The bottom of the foundation, the floor of the basement
5. Polymercement
Naya defense
Even relatively recently, the word "thermal insulation" in many have been associated mainly with glassic domestic production. And the work on the insulation of a private house was carried out in the old manner: any blowed materials were going to move - sawdust with lime, rags, foam rubber. Now the situation has changed: the approach to this problem has become competent, modern technologies and special materials and insulation came to replace the "Dedovsky" methods
According to the regulatory documents adopted recently, the issue of thermal insulation of residential buildings began to pay maximum attention. Yes, and the owners of the suburban real estate have finally learned more carefully to treat their wallet. After all, after the insulation of the house, according to experts, the required power of the heating system, and, accordingly, costs are reduced in two or three times.
Assortment of goods
The domestic market presents a wide range of heat-insulating materials, characterized by technical specifications and spheres of application.Thermal insulation materials are divided into several groups:
- mineral wool;
- glass and fiberglass;
- gas-filled polymers (foam):
polystyrene and expanded polystyrene, polyurethane and polyurethane foam, polyethylene, polyester, from phenol foam;
- thermal insulation from natural materials and products of their processing (plug, peat blocks, paper, etc.);
- heat insulating panels and structures;
- Modified concrete: cellular concrete (foam concrete), polystyrene concrete;
- products based on synthetic rubber;
- Products from silicon production waste.
Today, the main type of insulation used in Russia is mineral wool, whose share in the total production and consumption is 65-70%. About 20% falls on foams, and 6-8% - on glass materials.
General classification of thermal insulation materials
| According to the type of raw materials | Organic and mineral |
|---|---|
| In shape and appearance | Piece products (plates, blocks, brick, cylinders, half-cylinders, shells, segments), rolled and cylinder (mats, cords) |
| Middle density | The brands of thermal insulation materials: 15, 25, 35, 50,75, 100, 125, 150, 175, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500 (in contrast to many other building materials, the brand of insulating material is determined not by the indicator Strength, and by the magnitude of the average density, which is expressed in kilograms per cubic meter) |
| By hardness | Soft, semi-rigid, hard, as well as products of increased rigidity and hardness, well-resisting external loads |
| According to the method of poroid formation | Running, foamed, with porous aggregate, with burning additives, with spatial frame |
| By thermal conductivity | Class A- Low thermal conductivity (0.06W / (M C), Class B - average thermal conductivity (0.06-1.115W / (m m c), The class is increased thermal conductivity (0.1-0,175W / (M C) |
With proper laying of thermal insulation materials, it is possible to reduce the cost of heating houses by 3-4 times.
Mineral wool insulation
Mineral wool is thin and flexible fibers obtained by cooling the pre-crushed and elongated mineral melt. In addition to the type of raw material, it is divided into stone and slag. Raw materials for the production of stone wool serve rocks: diabases, basalt, limestone, dolomite IDR. Slag cotton wool is obtained from waste black and non-ferrous metallurgy. Leading world companies are used as raw materials exclusively rock rocks, which allows producing high quality products with a long service life.The indisputable advantages of thermal insulation materials made of mineral wool are a wide temperature range of applications (up to +1000 seconds), high heat and soundproofing ability, hydrophobicity, chemical and biological resistance, environmental friendliness and simplicity of installation (the plates are easily cut by a knife). Mineral wool products refers to the class of non-combustible materials, effectively prevents the spread of the flame and is even used as fire prevention and flame retardants. An important property of mineral wool insulation is negligible shrinkage and preservation of geometric sizes during the entire period of operation of the building. This ensures the absence of "cold bridges", which otherwise inevitably arose at the joints of the insulating plates.
The Russian thermal insulation market from mineral fiber is currently quite extensive. Products of OJSC "Aksi" (Chelyabinsk), ZAO "Izorok" (MAKOV), Nazarovskaya factory of thermal insulation and structures (Krasnoyarsk Territory), OJSC "Tizol" (Volgograd), Sverdlovsk region.). We also have imported mineral wool products such companies like Rockwool (Denmark), Paroc (Finland), Izomat (Slovakia). Some firms opened their plants for the production of thermal insulation from mineral fiber in Russia, which affected the price of materials. The cost of domestic products is $ 38-150 for 1m3, imported- $ 40-160 per 1m3.
The products of Western manufacturers differ from the domestic broader nomenclature, which sometimes has several dozen names. Such an assortment allows you to cover almost the entire sphere of the use of thermal insulation: insulation of roofing, attic, overlap, wall facades, floors, foundations, grounds, fireplaces and furnaces. Combining private houses mainly use plates made by pressing mineral wool. They are almost not subject to shrinkage, thanks to which the thermal insulation of the building does not deteriorate over time.
Areas of the use of thermal insulation materials
| Types of insulating materials | Walls | Roof | Floor | Ceiling | Foundation, Ground Floor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Facades | Outside | From the inside | Masonry (medium layer) | |||||
| Fiberglass | +. | +. | - | +. | +. | +. | +. | - |
| Mineralovate | +. | +. | - | +. | +. | +. | +. | - |
| Prestlest polystyrene foam (foam) | - | +. | - | +. | - | +. | - | - |
| Extruded expanded polystyrene foam | - | - | +. | +. | - | +. | - | +. |
Fiberglass-based products
Fiberglass is a mineral fiber, which, according to the production technology and properties, has a lot in common with mineral wool. Fiberglass materials are made from silicate melt with a high silica content. The main components of the charge (raw materials for the blast furnace) - quartz sand, dolomite and alumina are environmentally friendly in all respects, including radioactivity.Products based on fiberglass practically do not contain non-binding inclusions and have high vibration resistance, heat and soundproofing capacity, as well as increased elasticity and durability.
The main difference is the glass gamblets from the stone wool consists in the length of the fibers: the average length of fiberglass is 5cm, while the length of the stone fiber is 1.5 cm. Compared with mineral wool, fiberglass materials have greater strength and increased elasticity, which allows to transport insulating mats in the form of rolls.
Due to the low density and the large content of air, these insulation have a low thermal conductivity coefficient and for a long time retain their thermal insulation qualities. Fiberglass materials are so light, soft and elastic, which are suitable for skinning uneven surfaces, as well as for use in the structures of any configuration. Products have the stability of the shape, withstand aging, without exposed to deformation. However, due to the significant proportion of the binder component (for example, in high density glass), heat-insulation based on fiberglass belongs to weakly thorough materials. A streak of time is also a significant shrinkage of glassware.
The manufacturers of the ISOVER trademark (Saint-Gobain Concern, Finland), as well as URSA (Uralita, Spain Concern, are actively promoted on the Russian market. These companies and in our country opened plants for the production of thermal insulation based on fiberglass. From domestic manufacturers, Tisma enterprises (Tyumen), Novgorod fiberglass plant, glass insulation plant (G. Makhachkala), Khabarovskoye Fiberglass, "Ivotteklo" (Bryansk region) should be noted from domestic manufacturers. The cost of Russian products is $ 25-60 for 1m3, imported- $ 40-120 per 1M3.
OPINION OF SPECIALISTS OF ROCKWOOL RUSSIA

Promotable low-rise construction was quite widespread by three-layer enclosing structures with the arrangement of the insulation between the two carrier layers. They are made using a variety of materials - from wood panels to reinforced concrete and brickwork. The inner and outer walls connected by flexible bonds in the form of reinforcement rods or frames ensure the strength of the structure, and the insulation of the inserts, the required heat shield parameters. Here they find the use of mineral wool slabs, as well as panels of polystyrene foam.
Gas-filled polymers (foam)
Gas-filled polymers (polystyrene and polystyrene foam, polyurethane and polyurethane foam, polyethylene, polyester, from phenol foam) are organic high-art materials obtained from synthetic resins. Due to the low average density, excellent thermal and sound insulation characteristics, increased specific strength, as well as a number of valuable technological and operational properties, foam plastics have analogues among traditional building materials. However, most gas-filled plastics are inherent in certain disadvantages, significantly limit the possibility of their use (reduced fire, heat and temperature resistance). In addition, the biostostility during the long-term use and processes of destruction ("aging") of these materials were not fully studied.The most popular type of gas-filled polymer-extruded polystyrene foam. Along with zero capillary and extremely low water absorption (less than 0.2% in volume), it has an unusually high compression strength, as well as stable thermal insulation characteristics, significantly exceeding the average values of most other insulating materials (thermal conductivity - 0.03W / (M C) . It is frosty, durable, resistant to chemicals (with the exception of organic solvents, anhydrous acids and gasoline) and is not subject to rotting. The closed cellular structure of extruded polystyrene foaming provides a slight change in thermal conductivity in wet conditions (in the range of 0.001-0.002W / (m ), which allows you to successfully apply it as the outer thermal insulation of basements without additional waterproofing. The tests were shown that the material retains its thermal insulation properties after 1000 cycles of discharge, while the change in thermal resistance does not exceed 5%. Not so long ago, new different The privacy of polystyrene foam, in which it was possible to thoroughly reduce the combustibility due to the introduction of more efficient flames. The obtained samples relate to the group of employment materials.
Products of this sector of the thermal insulation market are represented by enterprises of OJSC ISOTEK (Leningrad region), LLC Penopelex Holding LLC (St. Petersburg), Mosstroy-31 CJSC (Moscow), OONPP "Expole" (G. Moscow) IDR. In addition, Russian consumers are well-known styrodur polystyrene foam manufactured by Basf AG (Germany), Styrofoam Concern Dow Chemical (USA) and URSA XPS Concern Uralita (Spain). The cost of domestic products is $ 40-170 per 1m3, imported- $ 140-200 per 1M3.
Comparative characteristics of some grades of extruded polystyrene foam used for the insulation of the foundation and floor of the basement
| Manufacturer | Mark. | Typical Sizes plates (length Width, thickness), mm | Average density, kg / m3 | Heat- the wire- BT / (M C) | Water absolutely Sent (28 days),%, volume | Compressive strength, N / mm2 | Rose 1m3, $ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BASF AG, Germany | Styrodur 2800. | 1265615 30-120 | 25-45 | 0.025-0.033 | 0.1-0.5 | 0.15-0.7 | 195. |
| Dow Chemical, USA | Floormate 200. | 1200600 20-100 | 25. | 0,028 | 0,2 | 0,2 | 165. |
| URSA, Russia | URSA XPS N-III | - | 35. | 0.031 | 0,3. | 0.32. | 172. |
| "Penopeleks", Russia | "Penopeleks 35" | 1200600 23-100 | 29.5-38.5 | 0,028 | 0.4. | 0.25. | 168. |
| Penopelex 45 | 1200600 23-100 | 38.6-50.0 | 0.030 | 0.4. | 0.5 | 182. | |
| Mosstroy-31, Russia | PSB-C 25F | 2000, 10001000 20-100 | 16.2-25 | 0.038 | * | 0.1. | 53. |
| * Manufacturer does not stipulate. |
What will we warm?
According to the calculations of the heat loss specialists through the walls of the house, there are 30-40% of the total heat loss, through the windows - 30-35, basements and attic floors - 30-45, the entrance doors are 5-8%. To significantly reduce heat loss, you should perform a full range of measures for the thermal insulation of all enclosing structures (outer walls, base (lower) and an attic (top) overlap, basement floors, roofing). The insulation must effectively work on the plot where it is laid taking into account the effects of the external environment. For most structural elements (walls, roofing, foundation), moisture penetration is the most dangerous factor. Achetoba Thermal insulation did not lead to serious losses of the indoor space of the house, it is necessary to take into account the thermal efficiency of materials. What types of products to apply in each case? Briefly the problem of choice can be solved so. Where there is no load on the insulation (sceneling insulation, floors on lags, partitions, attics, three-layer walls), use small density materials. For heat insulation of floors on the cement screed, facades, flat roofs - high.Comparative characteristics of some of the materials most commonly used for insulation Roofing
| Manufacturer | Type of heat Isolation | Mark. | Typical sizes of plates (length, width, thickness), mm | Heat- Helping, W / (M C) | Steam permeability bridge, mg / (m | Rose 1m3, $ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isover, Finland | Fiberglass | KL | 870, 91061050-150 | 0.036 | 0.55 | 41.5 |
| KL-E. | 122056550-100 | 0.036 | 0.55 | 33. | ||
| Rockwool, Denmark | Mineral wool | Light Batts | 100060050-200 | 0.036 | 0,3. | 55,3. |
| URSA, Russia | Fiberglass | M-15. | 18000120050. | 0.041 | * | 35. |
| P-15. | 125060050. | 0.041 | * | 37. | ||
| P-20 | 125060050. | 0.038. | * | 45.6. | ||
| Paroc, Finland | Mineral wool | WAS 35/45 | 120060030-180 | 0.032-0.034 | 0,3. | 85.8-110.7 |
| "Thermostepse MTL », Russia | Mineral wool | "Thermo" | 1200400, 60030-200 | 0.035 | * | 38-48. |
| * Manufacturer does not stipulate. |
Warming of the foundation and floor of the ground floor
The insulation of the foundation should simultaneously ensure the direct heat insulation of the foundation and the basement and the protection of the waterproofing coating from mechanical damage. Therefore, the materials used for the thermal insulation of the foundations are presented by compressive strength and water resistance, which is best complied with extruded polystyrene foam.The scheme of the foundation insulation is very simple. After laying a layer of waterproofing, the plates from extruded polystyrene foam are glued to mastic or only pressed and fall asleep. It is not necessary to protect them in such cases - on the contrary, they will carry a protective function, preventing waterproofing from possible mechanical damage and effects of negative temperatures. In the presence of pressure generated by groundwater, thermal insulation from extruded polystyrene foam can be placed both above and under the reinforced concrete plates laid on the crushed. As foreign experience shows, extruded polystyrenes are reliable at a depth of more than 7m and with prolonged contact with water under pressure.
Comparative characteristics of some of the materials most often used for insulation of walls
| Manu- Dutyer | Type of heat isolate tion | Mark. | Walls | Typical sizes of plates (length, width, thickness), mm | Heat- the wire- VT / (M C) | Steam penetrate Cance bridge, mg / (m | Read to the separation of layers, kPa | Rose negli- Naya Price 1 m3, $ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Of- Nutri. | Sleep Rui | Layers a flock of bricks putting masonry | ||||||||
| Isover, Fin- Lydia | Glass- fiber | OL-E. | - | +. | - | 1200600 50-150 | 0.035 | 0.50 | 3. | 122. |
| KL-A. | - | - | +. | 1200600 50-150 | 0.036 | 0.50 | * | 45.6. | ||
| Rock- Wool, Denmark | Mine Solid Wat. | Facade Batts. | - | +. | - | 1200500 40-500 | 0.039 | 0,3. | fifteen | 135. |
| Kaviti Batts | - | - | +. | 1000600 50-200 | 0.035 | 0.58. | * | 56. | ||
| URSA, Russia | Glass- fiber | P-30 | - | +. | +. | 1250600 40-100 | 0.033 | * | * | 42. |
| Paroc, Fin Lydia | Mine Solid Wat. | UNS 35. | - | +. | +. | 1320565 30-175; 1170610 30-175 | 0,0335 | 0,3. | * | 68.9 |
| UNS 37. | - | +. | +. | 1320565 50-200; 1170610 50-200. | 0,0365 | 0,3. | * | 55.9 | ||
| Izomat, Slovakia. | Mine Solid Wat. | Nobasil TF. | - | +. | +. | 1000500, 600 x 40-160 | 0.037 | 0.32. | fifteen | 138. |
| Nobasil TF Lamella | - | +. | +. | 1000180, 200 40-200 | 0,040. | 0.38. | 100 | 130. | ||
| * Manufacturer does not stipulate. |
Modern materials for thermal insulation of walls
There are three ways of heat insulation of the walls: from the inside, outside and inside the design itself. For a cottage, the most relevant outdoor insulation. In terms of exploitation itself, a system with insulation, located on the inside of the facade wall, is considered to be the most capricious. First, the useful area of the house is reduced; Secondly, the thermal inertia of the enclusive design is noticeably reduced, as a result of which the microclimate in the premises deteriorates. Thirdly, additional costs for the installation of vaporizolation are required. The temperature of the facade wall per layer of the insulation is significantly reduced, and the walls from the inside are constantly exposed to a thermal and humid effect as a result of the vital activity of people. Therefore, in the winter, water vapor, formed in the room, is inevitably condensed by layer of insulation on the inner surface of the wall. Increased humidity leads to a deterioration in the heat engineering characteristics, a decrease in frost resistance. Mushrooms begin to actively develop, mold, and ultimately the enclosing structure is destroyed. Alsa one drawback. Partitions and overlaps, tied to the carrier wall, as a rule, do not have thermal insulating liners. Thus, all over the perimeter of the room there are numerous "cold bridges", by which heat freely goes outside. As a result, the entire system of internal isolation is reduced to zero. If you still need to use the insulation from the inside of the structure, give preference to extruded polystyrene foam.Hearth roofing
Russian climatic conditions require high heat resistance roofing materials (in summer the roof is often heated to 80-95 c), low-temperature resistance (up to -50 C and below), frequent transitions through 0 C and ultraviolet radiation. The design of the insulated roof includes internal facing (from the inside of the room), vapor barrier, insulation, windproof, ventilated air gap and external cladding (or roofing). Thermal insulation should remain dry at any time of the year and under all weather conditions. Only partially for the insulation of the pitched roofs and the attic suited polystyrene foam, the most appropriate to use mineral wool slabs.
Market news
The thermal insulation market is constantly evolving, offering consumers more and more perfect products. Vgzhecksk (Tver region) developed peat-free blocks "Geokar" (0.51x 0.250.88m). Located in the outer wall, they are able to withstand the load of 8-12 t per 1m2. And, of course, the unconditional dignity of this material is environmental purity.Newly new insulation - plates and rolls from pressed cork. They are used for internal insulation and decorative decoration of walls and floors. The thermal insulation corkboard shields of the Portuguese Wicanders line can be used for the insulation of facades.
Specialists of the Danish company Rockwool Russia have developed the Facade Lamella heat-insulating material. It is produced in the form of bands, cut from mineral wool slabs of the corresponding density (90kg / m3), in size 120020040-240mm. Facade Lamella is used as a heat insulating layer in systems of insulation of external walls of buildings and structures, followed by surface plastering. Also, the material is used in the insulation of curvilinear or broken sections of the walls (erkers, pilasters).
OPINION OF SPECIALISTS OF THE COMPANY CJSC SAN-GOBEN Eau
"Choosing thermal insulation material, it is necessary to make a calculation showing whether it is beneficial to purchase one or another brand or type of insulation. KRYMERA, you are going to buy heat-insulation based on fiberglass with a thickness of 100mm and thermal conductivity 0.042W / (M C). Calculate: for this you need a thickness Insulation in meters (in our case 0.1 m) divided into thermal conductivity. The resulting digit is 2,38W / (M C) - denotes the thermal resistance of the material. The higher the better the house is protected from heat loss.
Now we calculate the cost of insulating ability. Price 1M2 of this material - 116 rub. We divide it on an insulating ability: 116rub. / 2.38 = 48,801. Uopmal version of the insulation This figure will be the smallest. We do the same calculations for the foamed polymer covered with one side by aluminum.
Thermal conductivity material - 0.037m C, thickness - 10mm (0.010m), price 1m2- 78 rub. Thermal resistance: 0.010 / 0.037 = 0.27W / (M C). Cost: 78 rub. / 0.27 = 288 rub., Much more expensive than in the first version. It is also very important to take into account, in which the region is being built a house, since, for example, for the heat insulation of the cottage in Moscow, the insulation of one thickness will be needed, in St. Petersburg, and in Novosibirsk third. It is difficult to cope with these calculations, so it's better to seek help to manufacturers' companies. "
The editors are grateful to the companies "San Goben Iravey" and URSA for help in preparing the material
