Oblaged eaves and icicles on the drains. Solving the problem - anti-flaking systems for roofs.








1 - shell;
2 - copper braid;
3 - isolation;
4 - wires







Winter in our edges rarely happens equally cold or, on the contrary, warm. More often, the thaw is replaced by frosts, freezing - thaw. The patient of the situation in most country house owners appears a difficult problem - icy cornices and icicles on the drains. You can fight ice using an anti-icing system.
Why ice is bad
Under certain weather conditions, the weight of the icicles only for one day can increase by several tens of kilograms. Thus, the picturesque appearance of an ice cone will be quite a real threat to all residents at home. Well, that, you will think, the probability of falling the icicle is not too high, but if it is possible, it can be knocked down by any gear. Why spend money by setting some systems against ice formation?In fact, the problem of roof icing is much wider than the question, the icicle will fall or not. Not only is the breakdown of sufficiently massive ice masses creates a real danger to the life of people and can damage not only vehicles, but also architectural elements of the house. Due to the accumulation of ice, the mechanical load on the elements of the roof increases, the brackets for fastening the drainage pipes and the gutters, which inevitably leads to a reduction in their service life, and therefore, to an increase in your costs for the appropriate repair work. Since the drains and gutters are clogged with ice, water in the autumn-spring period and in winter during thaws or flows on the facade, or delayed on the surface of the roof. In the early case, leaks are possible. And then they suffer the upper floors of the house and part of the facade near the drain and endands (that is, the lines of the butts of the roof planes). The result of the mechanical cleaning of the roof faces in full growth. This work is very laborious, and the roof itself can incur a considerable damage, because most roofing materials (metal tile, galvanized steel, copper) are very sensitive to mechanical effects.
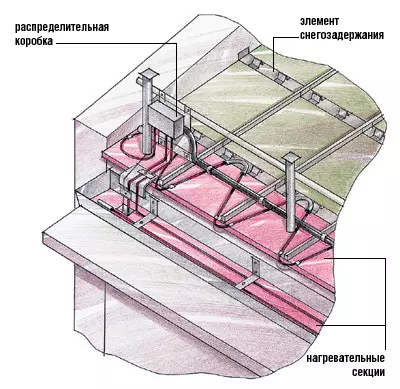
It turns out that it is necessary to fight ice. And here the electrical heating system of those roof sections can come to the rescue, where the likelihood of its formation is the most important. Essentials of this kind as a heated element are used special cables stacked in drains and gutters. Due to this, the lowered snow does not turn into ice, and in the form of a melt water flows to the ground.
All on the ice!
What can be opposed to the Nature on the Nature? Perhaps only modern technologies. When creating anti-icing systems, engineers proceeded from considerations that it is more profitable to heat the melting water, without giving it to frozen than to melt the already formed ice. In case, it will take much less power, which means that electricity consumption will become more economical. So the main task of the system is during the winter and offseason to accompany the water to the roof to the ground level, simply not allowing it to freeze it on the elements of the roof and in the drains, and at the same time eliminate the leaks, damage to the finishing of the facade and fastening the drain pipes. This is a fairly simple idea in its essence in the form of a complex engineering complex. The principle of his work is generalizable to the next.
In the most "unfavorable" places of the roof (gutters, drainters, endowers IT.), where it is most often formed, and on the entire path of the thawing water, a heating cable with power supply from a voltage of 230V is placed. Heated controls a special automatic thermostat that accepts commands from one or more sensors installed on the roof. These can be temperature sensors, air and precipitation humidity, water availability sensor. As soon as they signal that conditions contributing to the formation of ice in the atmosphere (and this happens, as a rule, during precipitation in the cold season or drip melting of snow cover on the main part of the roof during thaw), thermostat (or programmable thermostat, A kind of home meteorological station) "activates" the flow of electricity, and the heating cable begins to highlight heat. The water generated freely and freely flows through the grooves, trays and drainage.
Why appear icicles
By itself, the snow that fell on the roof does not represent any danger. The whole trouble is that the snow mass begins to turn into ice under the influence of two factors - technogenic and natural. Daily air temperatures fluctuate with an amplitude reaching 15c. And with oscillations in the range from +3 ... + 5c during the day to -6 ...- 10c at night are created by the most favorable conditions for the formation of a land. Melta water at first partially flows, partially freezes, creating ice floors on drains and grooves. But as soon as the paths are overlapped on the roof for the rapid waste of water, at the occurrence of a negative temperature it freezes. Moreover, with a short impact of heat (for example, the rays of the outstanding sun), ice plugs are not melted, but only increase. As a result, whole icy congestion, corks and icicles are several meters long and weighing up to hundreds of kilograms, threatening the integrity of the waterproof system can be formed.
The main reason for the appearance of the temperature difference between the central part of the roof and the edge, where the drains are located. It can arise for several reasons. The most common is the heat sink through the upper overlaps and the roof, due to which the temperature of the central part of the roof is higher than the temperature of the street air. The temperature difference increases if there are no insidious indoors in the house, if the underpants are rebuilt under residential premises or there is a fuel equipment, such as expansion tanks, heating manifolds, etc. The lower layer of snow cover on a relatively warm roof is imposed, turns into melt water which flows into cold drainage and freezes there, blocking further water removal. Mansards, turrets, all sorts of superstructures, complex roofs with inner angles, horizontal sites and protruding "collars" of roofing windows from fashion do not go out. And, alas, contribute to the formation of snow cover. By the way, from this point of view, the specialists consider the most efficient in the middle of the middle of Russia the pitched roof of the most simple form with an angle of inclination at least 30 is the optimal option for a better snow.
Due to solar radiation at the borders of snow cover, melting is activated. According to meteorologists, on average, about 70 temperature transitions are recorded over 0C. It is these daily fluctuations in the evening lead to rapid cooling of air (and hence the drains), while the mass of snow on the roof, together with the elements of the roof itself, can save heat for some time.
Usually, the system of anti-icing and heating of the roof and drainage consists of several functional subsystems. First, it is the so-called "heating part" - the actual heating cables, which must be electrical safe, mechanically durable, resistant to sunlight and atmospheric precipitation. An important part of the "heating" subsystem is all sorts of fastening elements. They fix heating cables in a predetermined roof location and in drainage structures. And, secondly, the distribution network is a set of power and signaling (information) cables and switchgears for switching wires. This subsystem assigns obligations to provide power to all elements of the warming part and carry out information signals from sensors to the control panel. The "heart" of the anti-icing complex is an automatic control system in which special thermostators are involved, temperature and humidity sensors, a flow-adjusting and protective equipment.
Heat runs on wires
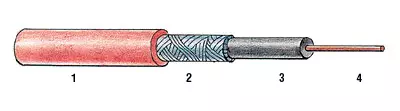
Now is the time to talk about the most important components of the system. Let's start with the most important, with heating elements. The role of the heater in the anti-icing complexes is played by special cables. Their appointment is to convert the electric current to heat flowing on them. Therefore, the power per unit length (specific heat release) is their most important technical parameter. The cable is paved and fixed in places of intended icing, along the edge of the roof and drip, in the endows, around the protruding structures (lights, pipes, mansard windows, etc.), as well as along the entire drainage system. On flat roofs and roofs with a small slope (up to 30), the heating cable is usually mounted either over the entire surface or on receiving drainage funnels and areas adjacent to the drainage.Resistive cables have a constant unchanged resistance along the entire length and consist of a fuel metal core, insulation, copper braid and an outer shell. Today, the Russian market presents resistive cables produced by such firms as "Special Systems and Technologies", or CST (Russia), Thermo, Kima Heating Cable (Sweden), Ceilhit (Spain), Ensto, Tash (Finland), Nexans Norway as (Alcatel, Norway / France), Devi (Denmark).
As a rule, when laying uses either cable sections, or the cable supplied in the bays (drums). Sections are already ready-made products in which a segment of a fixed-length cable with a special clutch at the factory is docked with the so-called "cold end" - a feed wire intended for connecting heating ("hot") cable with an electrical network. The length of the "cold ends" is also fixed and is 0.75-3m. The ends of the feed wires are hardened in the distribution terminal box, where they are docked with other electrical pipelines, for which the power supply from the power shield is supplied. So, in fact, the heating section is the main element of the anti-change system, and the coupling connecting the cold wires with a constantly heating and cooled heating cable is the most critical element of the entire design. The service life of the system depends on the reliability of the system, so manufacturers usually experience the heating section in very harsh environments. Many firms connect cable heating veins with cold wires using mechanically crimped sleeves. Those are placed in a plastic box and then fill with special mastic. This ensures reliability and tightness of the connection. Cut ready-made sections can not.
Another option is to lay the heating cable from bays. Such a cable is cut directly on the place of laying, and connecting heat-sustained couplings are used to connect power wiring or other heating sections.
Most firms produce ready-made heating sections, and cable in bays. Thus, the DSIG series cables from Devi, Thermocable SVK from THERMO, TASSU from Ensto are supplied in sections with a fixed length of heating and power wires. The cables in the bobbins offer Ceilhit, Nexans, Devi, Tash, etc. But to make segments of any length. It is impossible: the cable length is due to such characteristics as resistance, specific power and the voltage used voltage. The heat generation power depends on the size of the segment. KRYMERA, to obtain the required power of 30W / m. For cable with a resistance of 70m / m. We need a length of 15.5m. If it is less, the cable will overheat if it does not reach the nominal routing power.
The problem of the formation of a land is most relevant not cold in winter, but during periods of thaws, when the air temperature passes through zero and water from the lowered snow almost immediately freezes. Sometimes at +3 ... + 4c is a sleet with rain, and heat the drainage is simply necessary. The lower boundary temperature at which the melting of snow on the roof is stopped. Direction This process stops at 0s. But since the building loses part of the heat through the roof, water can drip out of the grooves and at -10s. Often the roof does not have due insulation; Many homes, especially reconstructed, have attic floors through which the most intense heat loss, and, accordingly, ice formation on the roof occurs more intensively.
The operation of the anti-icing systems at temperatures below -15С, as a rule, is not needed. Firstly, in this case, it is usually not formed to find and sharply decreases the amount of moisture due to the heat loss of the roof itself. Secondly, under such conditions, the number of drop-down precipitation in the form of snow is reduced.
It is not scary if the snow falls during frosty weather. To melt it, you will have to, in theory, put 3 or 4 cable threads. But this is an increase in the cost of the system 2 or 3 times. Therefore, it makes sense to wait, when warming and snow will begin to lift. That is why the working mode of the systems is limited to the bottom -6 temperature ...- 15c.
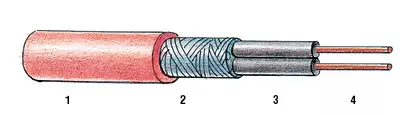
To date, manufacturers produce resistive cables or a single-core (with one heating residential), or a two-pot design (one vein-warming, second-connecting). The section with a single-core heating wire is connected to the supply network at both ends, and the two-core cable only from one end (on the opposite there is a plug, inside which heating and connecting veins are connected). The use of two-housing heating cables is somewhat easier when installing, but they are a bit more expensive than one-core. Heating veins are protected by insulation of high molecular weight polyethylene, on top of which another layer of insulation is applied, and then the copper shielding braid. Outside, the cable is protected by a high-strength shell of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or from fluoropolymer compositions.
Of course, each manufacturer takes care that his cable serve as long as possible and was most reliable. For example, the thermocable SVK resistive cables from THERMO current-handed veins are protected by an embedded braid from the muddy copper. Internal insulation, the veins is made of silicone rubber, resistant to temperature drops. Additional insulation is a high-strength polyester film. The cable itself is reinforced with fiberglass, and the outer shell is made of PVC. In the Russian market, cables from Ceilhit with teflon coating of the veins appeared, which makes it possible not only to increase the maximum operating temperature of the heating element (up to 50-60 ° C), but also improve the uniformity of the heat sink.
As a separate variety in the class of resistive "heater wires", you can mention the so-called zonal cables. They are presented, for example, the products of HEATTRACE (United Kingdom) and CST. The fuel element here is slices of wire from high resistance alloy, superimposed on a two insulated conductive conductors. Moreover, the "spiral" compound step with these housing is not more than 1M. Thus, heat dissipation zones are formed, connected in parallel. The cable has many heating zones and can be used by pieces. Slowing them, you do not risk breaking the work of the entire chain. Zonal cables are sometimes called "quasis-correlating", because during the installation process they can be cut "on the place" to pieces, multiple in length of the warming zone, directly at the facility. Thereby decreases cable overrun.
Zonal wires have a specific heat dissipation from 15 to 200W / m (depending on the cross section of the spiral) and are powered from one end. They are recommended to be placed on the roofs, in long and long-domed drainage (40m and more), as well as in systems where the absolute lack of land is necessary. Vitoga It turns out that at the same time the rigid characteristic of the zonal cable develops from a lack of dignity.
A separate type of resistive cables can be considered their armored versions with an additional single or double braid from steel galvanized wires - for reliable protection against mechanical damage. The main area of application of such cables is laying in a concrete screed with arrangement of systems of heating open areas, ramps, steps, as well as concrete drainage trays.
| Type of cable | Main appointment | Power Range, W / M | Section length | Applicability on the roof | Price, $ / m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistive | Heated pipelines, trays, drains | 5-30; Fixed power | Fixed, 10-200 m | Limited | 2.5-5 |
| Self-regulating | Heated pipelines, trays, drains | 5-60; Variable power | Anyone up to 150 m, cutting at the place | Full | 13-25 |
| Zone | Heated pipelines, trays | 10-80; Fixed power with the possibility of insignificant correction | Anyone up to 150 m, cutting at the place | Heated long drainage | 3-10. |
| Armored | Heated open space, drainage | 20-60; Fixed power | Fixed, with the possibility of climbing at the place of 1-2 m | Heated drains, drippers, concrete trays | 2-4 |
In Russia, resistive cables with "armor" are presented mainly by the company of the company. It produces, in particular, a resistive two-housing cable of TSB of high power (up to 30W / m) for heating the roof, drainage and outdoor sites. The product has high mechanical strength and resistance to short-term overloads. If necessary, you can choose a cable and with high specific heat generation, for example, armored EM2-XR from Raychem with a capacity of up to 130W / m. The "Leggalized" dial should include PSV cables (dwelling, with a coaxial copper-steel metal braid) from Ceilhit, Kima Armor D from KIMA, as well as a MBC armored cable manufactured by the CST in a polymer shell.
Russian resistive cables are cheapest. As for imported products, 1pog.m of the cable of any brand costs $ 1.5-5. Two-room options are more expensive than one-liner approximately $ 0.05-0.1. At the same time, the quality of products from different manufacturers is on the same high level. The resistive cable of domestic production for the anti-icing system "Teploskat" from the CST costs about $ 2.5-3 for 1Pog.m.
In contrast to resistive, self-regulating cables automatically change their heat dissipation depending on the temperature of the external environment. Moreover, the amount of heat released varies, so to speak, locally: each section of the cable "adapts" to the surrounding conditions. How does this happen? The so-called matrix made of polymer with the addition of conductive carbon material and located between two current-time conductors is served as a heating element in self-regulating cables. When the cable site is in low ambient temperature, the material of the heating element is compressed, the resistance decreases, the current passes through the matrix, and that intensively distinguishes thermal energy. That is, on a cold piece of cable, the current flows not along the lived, but across, from one vein to another. When the temperature is raised, the electrical resistance of the matrix becomes very high, which leads to a sharp decrease in heat generation capacity. The power generation of cables changes and depending on which physical environment is the cable, say, in melt water or in air. For the efficient operation of systems in Russian climatic conditions, according to specialists, there is enough cable with a specific heat generation at 0С-36W / m in melt water and 18W / m in air.
In our market, self-regulating cables are represented by various modifications (from 13 to 66W / m). It is enough to name D3 from Raychem-Isopad (Germany), GM-2X from Raychem (USA), KIMA K-3 from Kima, a series of G-trace from Nexans, FSR and FSRE from CST, RGS-2 from Thermon et al. Prices for They, at least 4 times higher than the resistive. This is explained by higher consumer characteristics and labor-intensity of manufacturing. As a rule, a good self-regulating cable can be found at a price of at least $ 11 for 1Pog.m. Products from Europe costs $ 10-30 for 1Pog.m. Several cheaper Russian products (CST) - from $ 11.2 to $ 12.4.
At first glance it seems that you can save, finding in the store the product cheaper. In fact, the actual cable system without the development of the project and the implementation of installation work is meaningless. As a rule, large installer firms work with certain suppliers of materials and equipment. We have a sense, because the company accumulates experience in designing and optimal adaptation of the system for Russian conditions. Speaking, the KPD Group of Companies Mounts Anti-icing Systems based on devi cables, the company SAMRIS uses self-regulating cables from Raychem and ISOPAD, as well as resistive from Tash, SIM Ross applies products from Nexans, Teploscat-based products based on cables of its own production .
What type of cable is better to choose? Resistive cables provide increased impact power and, if necessary, can be laid in a few threads (for example, cables from Tash with a rapid power of 25-30W / m are usually mounted in waterproofs and chutes in two or three threads). The use of high impact power allows you to reduce the required cable length and reduce the number of fasteners. The abolit line of the cable stream resistance provides the possibility of heating almost any elements of the roof. Resistive cables are the elastic, have a small permissible bend radius (order 100mm) and well fall along the place on the roofs of almost any complexity.
Of course, cables of this type are cheaper, but they have several serious flaws. One of them is the need for permanent care and maintenance. Accurately, periodic removal from the roof of garbage, at least before the onset of the winter season, which is not easy if it is a roof with a soft roof or with steep slides. Large lack of resistive cable-fixed resistance over the entire length of the section. That is, under different conditions of operation of individual sections of the cable, the heat dissipation remains the same. Imagine: one section of the section lies on a clean roof, the second - under the pile of fallen foliage, and the third-under thick layer of snow. Sensors, reacting to moisture under the snow cover, include the system, but only that segment is effectively working, which is under the snow, the remaining simply warm the air, spending the electricity is wasted. Breast-foliage is the cable and can overdo the cable.
Self-regulating cables change their heat dissipation depending on the surrounding conditions and temperature. For example, the GM-2X models from Raychem, FSR 31 from the CST, this indicator changes from about 10 to 40W / m. Close-in power The resistive cable constantly highlights its 30W / m, but in the winter of such power there may be little, and in the spring, too much. Aesley take into account the most important parameter of the system - electricity consumption, here is a self-regulating cable out of competition. He "feels" where and how much power to give power. If weave water to the drainage system, it is advisable to lay in pipes not resistive, but self-regulating cables. They are placed there, where there is a danger of clogging roofs and drains of the fallen cheese, seeds and leaves of trees.
Self-regulating road cable, but it can be chopped into pieces of almost any length (from 20cm). The resistive is stolen by sections of a fixed length, usually not coinciding with the length of the drain. It is necessary to "round" up to the nearest section, and therefore the cable consumption increases. The more the cable is stacked, the greater the scope of work, that is, the cost of installation increases. Solid side, the resistive cable is more suitable in the case when you have to deal with a plurality of single-type nodes (for example, 10 drain pipes with a height of 10m). Featuring the section of the desired length, cable overrun can be reduced to a reasonable minimum.
According to the meteorological service ...
There are boundaries of the installed capacity of the heating part of the systems defined on the basis of practice. Their non-compliance leads to the inoperability of the system in the specified temperature range, and a significant excess of the overflow of electrical power without any improvement in work.
On horizontal parts of the roof, the total specific power per unit of surface area of the heated part (tray, chute etc.) should be at least 180-250W / m2. The linear power of heating cables in the drains should be at least 20-30W to 1M length and grow as the waterproof length increases to 60-70W / m. The calculated power of the entire system for the country house depends not so much from the area of the roof, how much from its configuration, the length of the drain pipes and trays, the height (floors) of the building. We will have 3-4kW. On a simple row, the roof is 2 times less power than the complex - with turrets, attic, ideologies, closed by IT.D. What is characteristic, the type of cable does not affect the calculated power being laid in the project. After all, the main task is to be enough for the effective functioning of the entire system.
Heating cables- Although the main, but not the only component of the anti-pop system. Many believe that the system must be included when it is snow, someone else is that it should act all winter. Latest - I don't care what to heat the assignments. In fact, the anti-icing complex works on a given algorithm, then activating the heating, then turning it off and translating the system into the standby mode.
The control function is assigned to special thermostat controllers manufactured by Devi, Ensto, Raychem, Danish OJ Elektronik, German Eberle. For small uncomplicated roofs, the simplest option is based on the basis of the temperature and thermostat sensor, which includes the system only in a given temperature range (usually from -10 to + 3-4C). Say, the thermostat ETR-1447 ($ 137) from OJ Elektronik reacts to the air temperature from -10 to + 10c, and the DTR-3102 ($ 110) from Eberle can be installed to trigger in the range from -15 to + 15. To control the anti-icing system on complex roofs, it is recommended to install a programmable thermostat, often referred to as a meteorological station. At the same time, in addition to the temperature sensors, the sensors of the presence of moisture and precipitation sensors are included. The "meteorological" collect and analyze information about temperature and humidity, after which the thermostator operation is automatically selected. In addition, violations in the operation of the system are monitored, as reported by the beep and text information on the liquid crystal display of the thermostat. The EM 524 87 control unit with the temperature and humidity sensors from Eberle costs about $ 490, and the similar Kit DevireG 810 from DeVI with a built-in diagnostic system will cost $ 430.
The temperature range at which there is a threat to the occurrence of the land and, therefore, it is necessary to use cable heating, "set" on the thermostat panel. The system works on a more complex algorithm than a simple thermostat. If the temperature on the street corresponds to the specified range and the sensors recorded the appearance of moisture or precipitation, the thermostat automatically turns on the system. As soon as warmer, and the sensors are "referred" that there is no precipitation and ice, the system will switch to the "standby mode".
For example, the HEAT 200E controller ($ 186, along with automation- $ 230), to which a digital temperature sensor, water sensor and precipitation sensor are connected to the CCT system. The controller monitors not only a given temperature range, but also the presence of precipitation in the form of snow. The precipitation sensor, made in the form of a "cup" heated and two pins, which are closed when snow enters them, gives a signal to turn on the system during the snow. Cables are warmed up, snow and ice in chutes and trays begin to melt, melt water flows. If the snow stops, the precipitation sensor transmits the corresponding signal to the control cabinet. But at the same time, the system still acts on the water sensor, which is installed in the lowest place (somewhere near the drain pipe) to control, whether the moisture of the glass is. After all, it can happen that a strong snow will go briefly. It will cease to go, but thawed water will still need some time so that in all inclined planes will be easily destroyed down. It turns out that the main work is performed on three sensors. There may be a situation when there are no snow, but with 0s there was a thaw. The snow, located on the roof, starts to melt. If moisture appears on the water sensor, the system is automatically activated.
The temperature sensor is set in the shade, in a produced place, away from heat sources, air conditioners, chimneys so that the measurements are carried out the most objective nature. The precipitation sensor is best located in an open place so that nothing hung over. It is desirable to choose the installation site so that with a strong wind, the falling snow has not blown from the sensor. Finally, the water sensor is placed in the lowest place of the drainage system. Do not be discounted from the accounts and "orientation" of devices on the parties of light. It is desirable to put the water sensor on the south, because it is there when the water starts to temper the water. On a country house, as a rule, one set of automation.
Installation and cost
You can order the design and installation of the cable system in a specialized firm. They are in principle not so much. If you decide to fight icicles, it is better to call a specialist in place. Departure, measurements and calculation are usually free (but a number of companies take $ 50 for this). To find out the phone's approximate cost of the system, you need to know at least the total length of trays and drainage pipes and in a nutshell to tell you that you have for the roof. If the roof is simple (two or four-tight), the length of trays and pipes is known, you are most likely to say quite definitely, how much work, materials and equipment will cost. If the roof is complicated, without departure to the object and measure it difficult to talk about anything.
But the specialist will perform a measurement of individual heated areas of the roof, will try to identify zones dangerous from the point of view of snow accumulation and ice formation. The height of the building is also defined; Length, height and width of the roof; bias of the roof; Length and diameter of drain pipes; Length and size of trays, gutters. Swami will discuss the location of heated roof zones, appreciate the specific heating capacities for all system nodes, the number of threads and the type of heating cable, and, if necessary, consolidate the system's operation algorithm.
The question of fastening the heating cable in the flow channels is very important, since it is not enough to throw a cable in the tray, it must lie in the place where water flows. Some installers offer "branded" plastic fasteners from cable manufacturers. Installation In this case, it happens quickly, and you will take less money for work. But if plastic fastenings of unknown origin, they will serve one, maximum two seasons. Other companies use galvanized sheet strips from which special clamps bend. They are attached in such a way as not to leave damage in the trays (at the top of the pipe).
The higher the level of qualification of installers, the less holes in the roof. Thinks and pipes are not made, the wires are fixed with fastening elements at the top. Avt If the cable is stacked on the roof, it makes sense to establish snowstand (the latter is "attracted" to the roof crate using self-tapping screws or anchor bolts).
Mounting technology depends on the roof material. Let's say on the natural tiled cables are usually not unfastened, since it is almost not formed on its surface to sleep. Due to the fragility of the material to walk on the roof and drill holes in it quite difficult, so heating only trays and pipes are performed.
If the roof is covered with metal tile, make sure that the number of holes in the root turns out to be minimal. Many companies (samris, efficiency, ceilhit) In this case, first glue the rubberized fabric to the roof, to which heating cables are fixed. Soft roofs are good with thick roofing pie, the role of additional protection here plays a solid layer of moisture-resistant plywood. If, as a supplement to the heating of drainage, it is necessary to strengthen on such a roof of the synchtercing device, the conscientious installer will take care so that all the holes are carefully embedded with sealant.
When it comes to talking about the comparative cost of anti-icing systems for roofs based on resistive and self-regulating cables, the four-time difference in price does not mean that the total cost of systems will also be varied several times. After all, many components (control cabinet, power supply system, fasteners) are the same for all types of heating elements. So the difference is not so big: a system with self-regulating cables is more expensive by 30-40%.
Push-adjusting equipment from different installers is represented by different stamps, but in any case these are products of authoritative manufacturers: ABV, Legrand, Siemens, General Electric IT.D. The introductory machine controlling the controller system, the starter relay (through which the activation of the system is switched on), the UDO (device of the protective shutdown with a leakage current 30mA) and group machines are mounted in a single control cabinet, which looks like an electrical shield.
How much is it all together? For example, the synthetic system and anti-plating system based on the Nexans cables (Norway) provides styling in standard 55-40W / M cable gutters and drainage cable, and along the roof edge (band 50-60 cm) of the cable with a specific power of 300-350W / m2. Thus, let's say, for the roof with a perimeter of 60m (the area of one floor is 200m2), the 12m with four drain vehicles will need a system with a 12.2kW installation power. Considering that in the year about 35-40 days, when meteo conditions contribute to the formation of a land and snow, it is possible to determine the consumption of electricity for the season. When used as a management system, "meteorological station", this indicator will not exceed 6-10 thousand cmounts. The cost of the materials and equipment for the roof with the specified parameters will be about 2200.
The basic value of the installation of different installer firms ranges from 30-35 to 50% of the value of materials and equipment (for single and two-storey country houses). If high-altitude works are needed related to the construction of scaffolding, installation of steps or auto-tesys, then these services are paid separately.
Service is required in the amount of about $ 100-250 per year. When regulatory work, a company specialist inspects the external state of heating sections, pulls up contacts in terminal boxes, tests the control cabinet and the operation of the entire automation. Power work is carried out in summer or in the offseason, before bringing the system to "combat readiness".
But be sure, with the arrival of cold weather you do not have to independently lead a hopeless flavor with ice on the roof. Modern technique has achieved much more successful success.
The editors thanks the representative offices of Raychem, Devi, Ceilhit, as well as the company Samris, "Special Systems and Technologies", efficiency for assistance in the preparation of material
