Basic requirements for walls. Factors affecting the choice of design and building materials. Cocols, cornices, smoke channels.

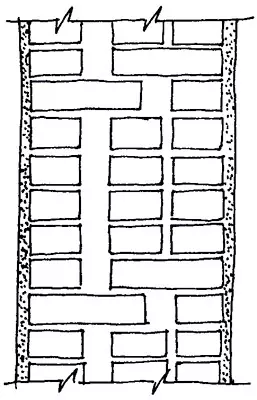
Bearing bricks
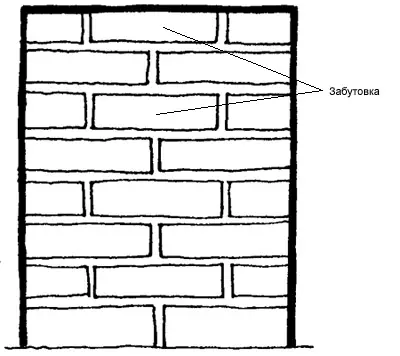
Chain (double row):
A - incision,
B - facade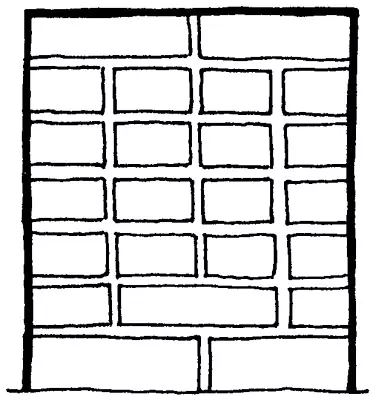
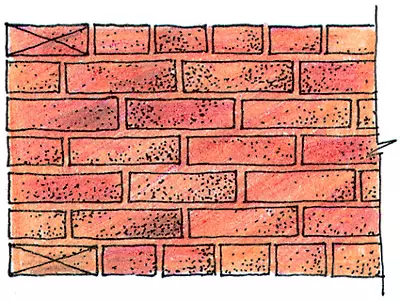
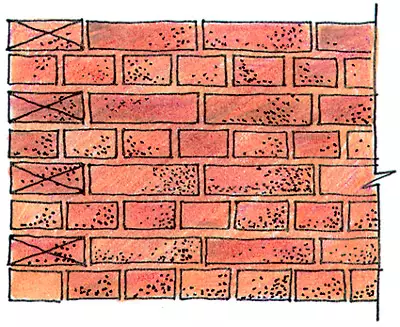
Spoon (multi-row):
A - incision,
B - facade Master schemes
So, the dear reader, the outlines of your home already visibly marked the foundation based on all carriers of vertical designs (walls, columns, partitions). New worries and troubles arise. Forward a queue of houses. What software, constructive solution, sizes are assumed, you already know from the project. But much seems fuzzy. So, let's talk about the walls. The choice of materials and designs of the walls depends on the climatic conditions of the place, from the appointment and temperature and humidity regime of the festable premises, the floors of the building, the presence of local building materials and their technical and economic indicators, taking into account the range of transportation, from the appearance and architectural solution of the facades of the house.
In Russia for a long time, for the construction of civil buildings, churches, monasteries and other structures, we widespread wooden, stone, and later and brick structures. Beautiful choirs, tents and multi-row churches, beautiful and peculiar. It is enough to mention the magnificent temple of Vasily blissful (the correct name of the Pokrovsky Cathedral, which is on the RB, 1555-1560). No less beautiful and amazing achievement is the construction of a 22-chapter of the church (1714) of the Savior of the Transfiguration on the Kizhi graveyard.
Of course, in the old days, when there were no heat engineering calculations, the thickness of the walls was often excessively large. For modern low-rise cottage construction, except for traditional stone, brick and wooden wall solutions, more efficient materials and structural solutions are used: light concrete, ceramic, lightweight, layered brickwork, wooden frame, shield and others with the use of light insulation. These structures make it possible to significantly reduce the weight of the walls, improve their economic indicators, speed up the construction.
We will get acquainted with the basic requirements for the walls. The selected wall design should have the same durability as the house as a whole, and perform two main functions: protective from the adverse effects of the external environment (rain, snow, wind, sun, overheating) and carrying up the load (weight) transmitted on them (weight) Challenge structures, equipment, furniture.
Depending on the location in the building wall there are two types: external and internal. The latter also perform partition functions.
The outer walls must have sufficient (comprehensive standards) heat-shield quality: the calculated heat transfer resistance (frost resistance in winter, protection against overheating in summer), vapor-permealing and air permeal, that is, they should provide in rooms the necessary temperature and humidity mode at any time of the year. Depending on the required degree of fire resistance at home, the walls should have a group of ignition and the limit of fire resistance not lower than the fire standards established by fire standards. Both external and interior walls should have sufficient (passing standards) soundproofing properties.
These and some other requirements for which you need to pay attention to when choosing a project and coordinate the structures of different elements of the house, sometimes contradictory. It is necessary to choose materials and structures that satisfy all the technical requirements and most economical solutions. According to a structural solution, the wall can be divided into solid, consisting of homogeneous material and solid, consisting of various materials. The first is performed simultaneously both protective, and carrier functions, and the second or carrying, or a protective function.
Consider first the structures of the stone walls, the most frequently used in the cottage construction, iskrpich, concrete, ceramics, as well as from sandstone, limestone, and a seven. Baby low-rise buildings own weights of walls together with foundations is 50-70% of the total weight of the building, and the cost of walls is up to 30% (sinted architectural details) of the value of the entire building. It can be seen how important it is to skillfully choose the type of walls, especially outdoor.
Brick walls
They are laid out of artificial stone-sized 25012065mm, without taking into account the tolerances of 3-5mm. Bricks are laid by a long side (25mm) along the facade (along the wall) and are called spoons, or short-across the wall - and nimble. The gaps between the bricks filled with the solution are called seams. The normal thickness of the horizontal seam (between rows) is 2mm, vertical (between bricks) - 10mm. Often, builders use significantly thicker seams, which is extremely undesirable, because it reduces the thermal quality and strength of the wall and violates the modularity of the sizes.In the cottage construction, a full-time brick is used or clay red, burned over a volume weight of 1700-1900kg / m3 and less expensive silicate or white (volume weight - 1800-2000kg / m3). For convenience, the weight of one (full) brick from 3.2 to 4kg. The thickness of homogeneous (solid) brick walls is always painted half of the brick and is built in 1/2; one; 11/2; 2; 21/2 bricks, etc. Supporting the thickness of vertical seams is 10mm, brick walls have a thickness of 120, 250, 380, 510, 640 mm and more. It depends primarily from winter calculated outdoor air temperatures.
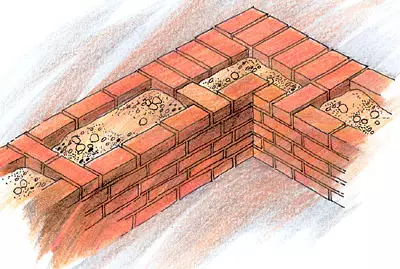
The placement of bricks in the wall masonry is made with a certain alternation of spoonful and tonch rows to get a dressing of vertical seams.
The greatest distribution received a double row (chain and Russian) and multi-row (spoonful) masonry system. Twitched spoonful rows alternate with choke, forming on the facade as two repetitive series circuits.
In the multi-row system, three-five spoonful rows alternate with one pumping. The outer and inner parts of the walls are made from the whole brick by a qualified bricklayer, and the middle of the slaughter (forge) is filled with broken bricks and is poured with a liquid solution. This method of masonry is easier chain, therefore labor productivity is higher, and a larger amount of chasing reduces the cost. Before laying a brick, it is necessary to make it necessary to wet, for example, the perch of it in a bucket with water. After all, otherwise, especially on hot days, water from the solution will be absorbed into bricks, poorly tying them between themselves, creating conditions for the destruction of the wall.
Some types of bricks, ceramic and light concrete stones, small concrete blocks (solid or vertical voids) have several large sizes than ordinary brick. For example, their height can be 88, 140, 188mm, in order to link the individual coinciding horizontal rows and seams when laying together with a facing of an ordinary red brick.
When laying the walls of stones with slick-like emptiness, it is necessary to lay out the stones so that the slots are located in parallel with the wall, that is, perpendicular to the heat flow. The laying of walls from natural stone, which give the right, larger than brick, shape (sawing or ottoman), is carried out on a chain system, mainly for unwanted buildings in areas where this stone is a local building material.
Bricks are durable are durable, but in their heat-shielding qualities is significantly inferior to effective multi-stroke and trendal, more porous (volume weight - 1100-1300kg / m3). Applied brands of bricks 50-150; Marks of solutions (binding substance) from 10 (lime) to 25 (cement) for different types of masonry and structural elements. The laying is carried out on heavy bulk weight more than 1500kg / m3), so-called cold (cement-lime, sandy) or light (slag), warm solutions. Solid brickwork of walls of full-scale bricks with a thickness of more than 380mm is considered inappropriate, for such a brick size, its large volumetric weight (mass) makes a solid laying of non-economic. The thickness of the outer wall of cottages, which is assigned to heat engineering calculations, under the conditions of strength is excessive. It is used sometimes only 15-20% of its carrier ability. Therefore, in cottage houses, an easier, efficient brick is used, inhomogeneous (layered or lightweight) wall masonry systems, as well as ceramic and light concrete stones.
The laying of silicate bricks having a smoother surface than clay is usually carried out without outer plaster and with a latch of seams. The same solution can be recommended for masonry from red bricks using a special facial clay brick.
The combination of masonry from clay red and silicate white brick can give an interesting artistic solution of facades. However, apply silicate brick in places exposed to enhanced moisturizing, such as cornice, base, should not be. Wet agencies (bathrooms, pools) laying of walls and partitions should be solid from a full-scale clay plastic pressing brick.
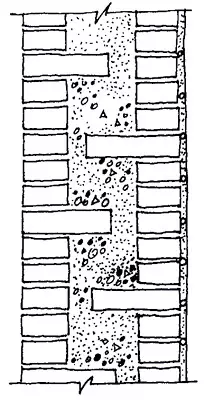
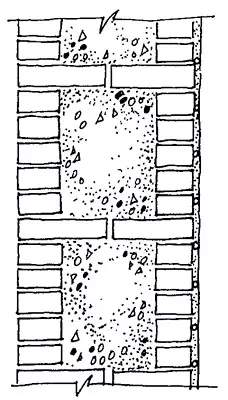
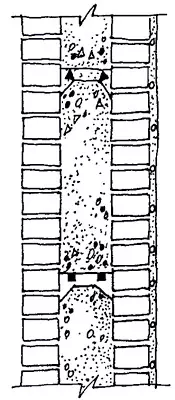
The common and economical design of the outer walls is the so-called wellwork, in which the wall is laid out of two independent walls with a thickness in the Polkirpich (outer, versta and internal), interconnected by vertical brick bridges through 0.6-1.2m, forming closed wells. The wells for masonry are filled with insulation: slag, claying, light concrete with a seal. So that the insulation does not appear over time, the versts are combined with horizontal jumpers through 3-4 rows: tiley rows, mortar diaphragms in height of 0.5 m, band-view anchors (1.520 mm) or round (diameter 6-8mm) steel coated with anti-corrosion compositions ( Cement milk, bitumen).
Mastering systems are more industrial and accelerating work, in which the wall insulation is replaced by less microscopic thermal vehicles from slag concrete, foam concrete, phenosilicate. The width of the thermal lady on 40-50 mm is less than the distance between the versts to form clearances that are filled with a solution.
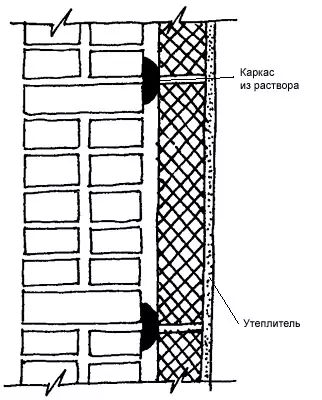
Pretty economical are masonry from full-scale bricks consisting of two walls with closed air layers with a width of 40-70mm. At the same time, the consumption of brick is reduced by 10-15%; The outer wall consists of spoonful rows of half of the brick, and internal depending on the required heat shocks in 250 or 380mm. The walls are connected to the methods specified above, the outside is plastered to reduce air infiltration. When filled with air cavities with mineral felt, the thermal efficiency of the wall increases by 30-40%.
To increase the thermal insulation qualities of the walls, it is possible to use heat-insulating plates (drywall, foam concrete, wood-chip), installed on wooden (necessarily antiseptic) bars, mortar beacons and other ways from the inside. For thermal insulation and airtightness, the inner side of the plates facing the masonry is recommended, to crack the aluminum foil, kraft paper, etc. An in the same way is made by the walls of the walls from the inside boards. Tile insulation can be attached to the wall directly on the solution. The outer surfaces of the walls, warmed on the inside, also need to be placed.
Important remark, dear reader. The internal bearing walls and carrier partitions (on which the beams or ceiling plates are based on) should be layered out of a full-skinned clay or silicate brick, with a minimal enough (!) Thickness of the walls of 250mm (sometimes 120mm). The pillars cross section should be at least 380380mm. With large loads (clarifying on the place), the carrier poles and a simpleness should be reinforced by a wire mesh with a diameter of 3-6mm through 3-5 rows of masonry in height. Partitions are laying out a thickness of 120mm and 65mm (Brick "Maparo"). With the length of such partitions, more than 1.5 m, they should also be reinforced after 3-5 rows.
Bearing partitions can be arranged (except for rooms with wet processes) from light-concrete, gypsum concrete and other plates of thickness usually 80mm, from boards and other materials suitable on local conditions using appropriate finish.
For facing facades, which is carried out simultaneously with the masonry walls, it is best to use a facial ceramic brick, which is somewhat more expensive, but in appearance, texture, coloring and permissible deviations in size is the highest quality. At the same time, there is no need for painting for three or four.
The laying of outdoor walls should be started with the corners of the building. Underwear. For better compliance with the rectinity of walls and evenness, the horizontal of the rows of masonry must be used to use a plumb, stretched pitch cord and a vertical co-order with a markup on it of each row of bricks and a seam in height.
Elements of walls
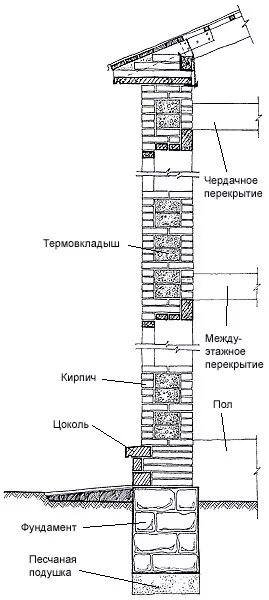
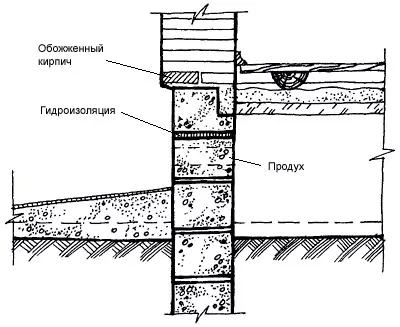
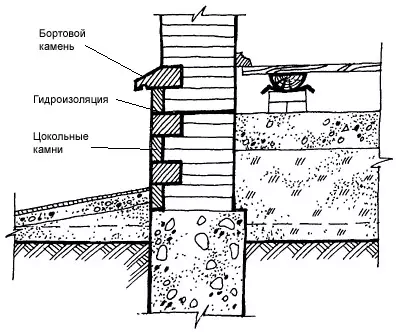
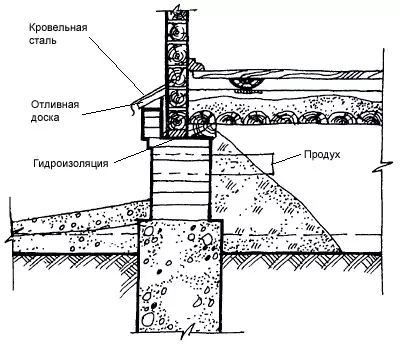
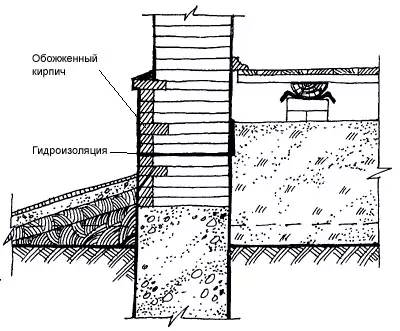
Cocol - The bottom of the wall from the ground level to the floor level, a height of at least 500mm, which enhances the underground space of the house. The base is subjected to moisturizing atmospheric and soil moisture, snow, mechanical effects, therefore, when it is applied to apply strong, water and frost-resistant materials (stone, concrete, red brick-iron).
The outer surfaces of the base may have different textures and trim; Smooth and relief, including from a thick layer of cement plaster with cutting into rusts, imitating stones masonry, lined with natural stone, solid rocks, ceramic tiles on cement mortar, composition is one part of cement to three sand parts. At the level of about 150 mm above the adjoining breakdown, it is necessary to organize the entire perimeter of the base layer of anti-indexing horizontal waterproofing, consisting of two layers of roofing, rubberoid or cement screed.
Socities of layered walls should be carried out from solid brickwork or other durable, frost and moisture-resistant materials.
Baby - Lightweight base. The thin wall between the pillars of the foundation, at the bottom of the walls of the veranda, insulates under the complete space that protects against moisture, snow, etc. It is performed from the same materials as the main wall, for example, in one or pollipich; It is plunged into the soil at 300-500mm. On clay, bunched soils, a sandy pillow with a thickness of 150-300mm is arranged under the burning.
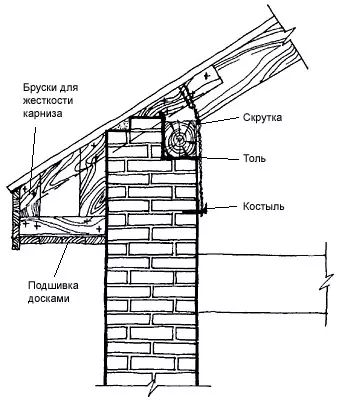
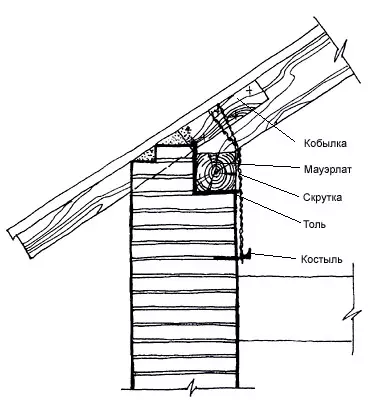
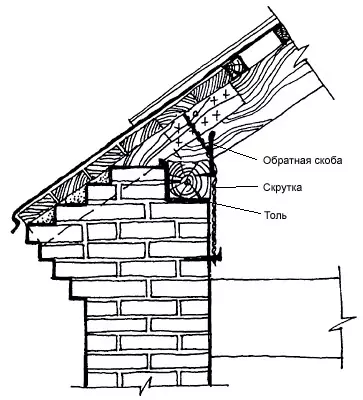
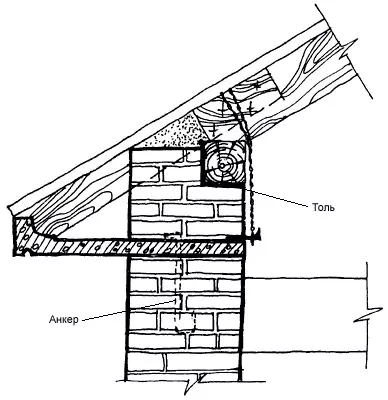
The corze ends the top of the wall and is called crown. It is designed to protect the wall from oblique rain, excessive heating by the Sun, as well as for removing water flowing from the roof. In addition, the eaves usually decorate the buildings, giving the composition a finished look. Therefore, its shape, height, departure and color are largely determined by the general architectural solution of the facade.
Cornis The stone walls of a simple form can be laid out by a gradual intake of each row by no more than 1/3 of the length of the brick (80mm). The total removal should not exceed half the thickness of the wall. With a large removal of the cornice of a complex configuration, special precast concrete slabs, beams, cantyled on the wall and enchanted by anchors should be applied with brackets. Correspondures are often used on the releases of the rafter feet or the mare; They are open and stitched.
Undoubtedly, improve the aesthetic type of cottages can be introduced into the plane solution of the facades, various architectural details, belt, intermediate and crown eaves. Lathed from brick or other, such as concrete elements, but uncomplicated in drawing.
Smoke and ventilation channels For low-rise buildings, they are arranged, as a rule, in the interior walls with a thickness of 380 mm, laid out of a red smooth solid brick. The cross section of these vertical channels for furnaces is taken 140270mm, and the ventilation, from kitchens, restrooms, bathrooms - 140140mm.
Carrying residential rooms through the velocity. Each furnace (or fireplace) must have a separate smoke channel. The internal surfaces of the channels for the best thrust must be clean and smooth, lighted (it is important not to forget about it) clay (non-cemental) solution. The alignment and grout of the walls are carried out with a clean wet cloth when laying channels through five or six rows of bricks.
Smoke channels from different furnaces in the attic are combined into smoke pipes, which are displayed above the roof level. If a combustable design is adjacent to the wall at the location of the flue channels, for example, the wooden beams of overlapping is adjacent, then in this place to height (thickness) overlapping the chimney wall (120 mm) thicken according to fireproof rules up to 380mm.
Ventilation channels (spare room have a channel) are also combined into ventilation pipes that are removed above the roof.
Other design elements of walls, such as lintels, horizontal, arched, inhibitory over door and window openings, we will look at later, together with the floors of buildings.
Wooden walls
Wooden walls are traditional in the construction of low-rise buildings in Russia, they have excellent sanitary and hygienic properties, have low fire resistance and briefness, amenable to rotting.
Wooden log house, requiring a large number of primitive forest, about 30-40 years, as a rule, is thrown and comes in disrepair. The construction of cottages with wooden solid walls in modern practice is rare. However, the device of the second floor with wooden walls and the first bricks-gives good results.
Types of wooden walls: logged chopped, paving, frame and panel, as well as frame-shields. Frame and shield walls are used in uncomplicated factory manufacturers and garden houses. Chopped exterior walls of houses, constructed average climate zone should be of logs diameter of at least 220mm, have a thorough pripazovku (width of the upper longitudinal oval groove timber into which the "hump" nizhnego- approximately 2/3 log diameter).
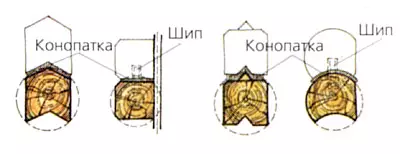
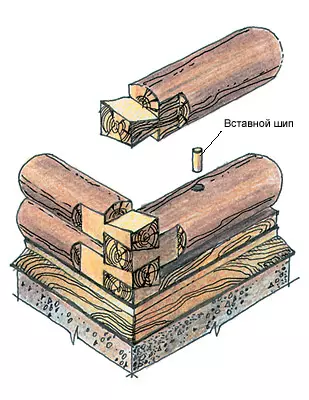
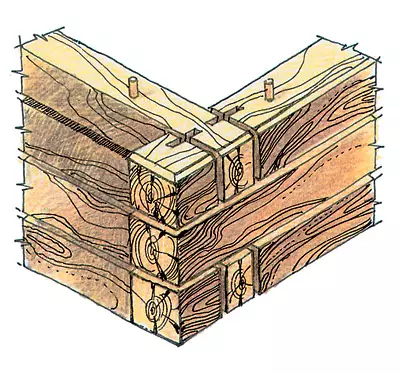
The logging (assembly) of log walls produce "dry" without packles, then the logs are labeled, the log houses are disassembled and already on the prepared foundation are collected on the package. Konopath should be carried out twice: the first time when assembling. The second is 1-1.5 years after the cessation of drying and shrinkage logs. A row of logs laid around the perimeter of the house is called a crown. The crowns mate with each other with the help of plug-in wooden spikes of a rectangular or large cross section located along the length of the log at a distance of 150-2000mm in a checker order. Nests for spikes due to drying logs about 3-5% should be made by 20-30 mm deeper than spike height (120-150mm).
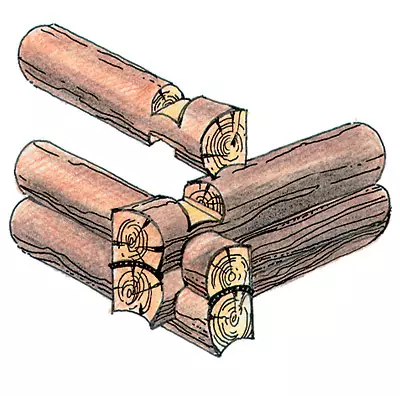
The compound (pairing) of the longitudinal and transverse walls is made using a different kind of wrist-"wishhu", "Woblo", "Munta", "Frying", etc., insteading then some of them boards, nailed outside.
The walls of wooden bars are asking with less labor costs, since all the words, the swords, braided already made on house-building factories and combines. Therefore, the individual developer can buy and build such walls on their own.
The thickness of the bars depending on the climatic area, that is, from the winter calculation temperature, it is accepted for the outer walls 150 (t = -30c) or 180 mm (T = -40 C), for the internal 100mm, with a height of the bars, the same for external and internal walls 150 or 180mm.
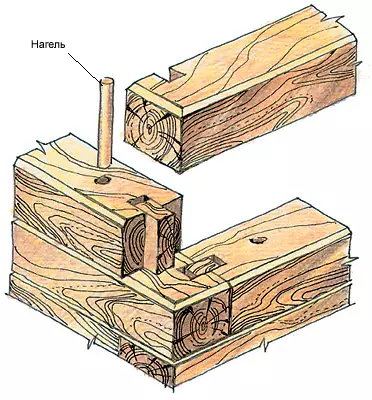
Between the crowns of BRUSIV lay the heat-insulating material - caispacat from the pacular or felt. For a better removal of water from the horizontal seam between the bars from the upper ribs of each bar, 20-30mm width is removed. Stripes of felt should be chopped by 20mm already widths of BRUSEV. To reduce the conductivity between the bars, you can arrange grooves, cords, to fill the triangular form rails. To fasten the crowns (bars) in height in advance, drilled holes are inserted and skaps (similarly discussed above for log walls). Similarly, the compounds (intersections) of the outer walls in the corners and with the inner walls are constructed.
Unlike log, paving walls are collected in a log house immediately on the prepared foundations of the usual type. To improve the protection of broken walls from the biological destruction of wood and from atmospheric exposure, the walls can be seen outside the boards (diameter 25-40mm) or facing brick (diameter88,12mm). It will make the walls warmer, and with brick facing and more fire-resistant. Moody trim is better to do horizontal, which makes it easier for laying insulation. Fastening with wooden bars and metal beammers.
The trimming and lining of the brushed and log walls should be made after their complete precipitation, not earlier than 1-1.5 years after their construction.
The variety of architectural elements and details of country houses was always characteristic of the buildings built at the beginning of the XXVEK.
So, the dear reader, some of the main provisions on constructive wall decisions have now become more familiar.
Now you can professionally talk to builders, choosing certain variants of wall structures, watching construction progress.
