Diamond cutting circle: Selection rules, types of circles, recommended cutting modes, turbo circles efficiency.




(SCHOP for dustproof or without it) makes it possible to use a cutting circle with a diameter of 254mm





Maximum maximum, but dustlessness is ineffective. With the coincidence of these areas, the opposite is
Sometimes there is a need to cut off a piece of asbestos-cement pipe, bricks, tiles, granite or marble slabs, part of the reinforced concrete unit or a stone block - in general, solid building material. And cut off exactly, while maintaining a certain size. It is possible to solve such a problem with the help of a diamond cutting circle, installed on a cutting machine or a portable cutting machine, and most often - on a corner grinding machine, usually called the Bulgarian.
Diamond is a type of pure carbon and the hardest material on Earth, but when heated above 800s it is irreversibly turning into rather soft graphite. By their diamond circle, almost any material can be cut, while still it is necessary to strictly limit the temperature of the circle. It is for this reason that a diamond circle is not used for cutting metals, preferring the abrasive circle.
Diamonds are applied to the steel case of the circle in various ways. The most common is the one in which thousands of technical (artificial or natural) crystals in size from0.2 to0.8 mm are mixed with even smaller particles of metals. In the manufacture of a diamond circle, for example, the type of "crown" around the perimeter of a thin steel disk with a hole in the center of this mixture, a ring of diameterd, height and thicknesses, are pressed. In the manufacture of a diamond cutting circle with an internal cutting edge, the same ring is pressed around the central housing hole. The subsequent sintering of metal particles leads to the formation of a binder frame, which plays the role of rim for durable fixing of diamonds. The cutting circle with the diamondic layer around the perimeter is installed by the central planting hole on the drive shaft of the cutting machine, cutting machine, "Bulgarian".
Basic rules for choosing a diamond cutting circle
The diameter of the circle D is better to take the maximum for the power of the "Bulgarian" used, but not more than 254mm, otherwise it will be difficult to work because of a large torque, especially when starting the instrument.The most high-quality cut without chips will provide a circle of "crown" mounted on a cutting machine when using cooling.
For cutting of natural materials (marble, granite, gabbro, quartzite) circles with an intermittent edge, it is better to choose narrow grooves between segments to exclude a sharp, unpleasant sound, and with a cutting of concrete, wider grooves are appropriate to increase productivity.
When the cutting wheel diameter of the cutting circle is larger than the diameter of the Bulgarian shaft, use the transition ring (it can be purchased, for example, on the company "Splitstone"). Watch that it does not interfere with the reliable fixing of the circle.
The variety of diamond cutting circles is used for cutting without cooling or with forced cooling with water. A bundle of a circle is selected according to the composition very carefully, since it should not only reliably fix the diamonds, but also to withstand a high temperature and a significant mechanical load.
Diamond cutting circles supply several dozen firms to the Russian market, for example, Belgian Diamond-Board, Italian Diamond-D, German Dronco and Bosch, Hilti from Liechtenstein, Bulgarian Sparky, Ukrainian "Ukr-Diamant", numerous Chinese manufacturers, as well as domestic firms Among which is the Moscow "Splitstone" and near Moscow Tomal. It is noteworthy that the company indicated on the label is not necessarily its manufacturer. Just manufacturers of angular grinding machines, cutting machines and cutting machines offer cut-off circles to them under their brand. But in any case, on the housing of the circle or on its packaging, the material must be indicated, for the cutting of which the circle is designed, or the circle body is painted depending on the type of bundle or stick the label of the same color.
Main types of diamond cutting circles
| Side surface | Cutting edge | |
|---|---|---|
| Solid | Intermittent | |
| Flat | "Crown" | Segment |
| Wave-shaped | "Turbo" | Turbo segmented |
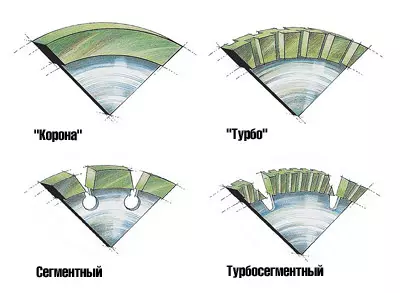
The diamond cutting circle distinguishes the shape of the cutting edge and the shape of the side surface of the diamondic layer. The cutting edge of the diamondic layer determines the performance of the process and is a solid or intermittent, formed by the segments of the circle. The side surface of the diamondic layer affects heat release during cutting and is flat or wave-like. The various combinations of the shape of the cutting edge with the shape of the side surface of the diamondic layer led to the creation of four main types of diamond cutting circles. These four types of circles are referred to as follows: "Crown" (with a solid flat diamondic layer), "turbo" (with a solid wave-like diamondi layer), segment (saber-like flat segments) and turbogene (with diamond-like wave-like segments). Cutting circles with intermittent cutting edge very much resemble disk saws with a peculiar form of teeth. For most circles, the diamond powder of the South African company Debeers is used.
Circles "Crown" provide the smallest consumption of the material and slice with smooth edges, but a large area of contact of the flat solid diamondic layer with the material leads to the allocation of a significant amount of heat. This quantity depends on the rotation cutting modes and the movement of the circle (feed). That is why the forced cooling of circles with water is almost always used, the required consumption of which depends on the diameter D of the circle.
This report uses data on diamond circles and cutting modes accumulated by Splitstone as a result of a large number of experiments.
It should be noted that with a decrease in the values of the cutting modes, compared with the data specified in the tables, the diamond circle is used irrationally, and with an increase in its heating increases.
Circles "crown" They are produced with two types of bundles (based on bronze and cobalt based with the addition of bronze), so they are painted in two colors, yellow and green, respectively. The wheels of yellow are designed for cutting softer materials: marble, plaster, drywall, tiles, ceramic tiles and semi-precious stones, and green-color circles for solid materials: granite, quartzite, labradorite, natural stones, silicon. The diameter D circle "Crown" does not exceed 400mm.
The cutting of almost all circles "crown" must be produced on a cutting machine, providing a constant water supply. But recently there appeared circles of the "crown" diameter of up to 230mm for dry cutting of ceramic tiles. To do this, you can use the usual "Bulgarian".
Practical recommendations
It should be noted that the cutting 1m2 of the material is more expensive than the "turbo" circle, and turbo-segment is more expensive than segment.The new cutting circle is first be sure to twist about 5 minutes, holding the "Bulgarian" with a dressed casing circle from himself. The fact is that when transporting in the Circle case, microscopic cracks are sometimes formed, which can lead to the destruction of the circle.
With intensive sparking and heating of the circle, cutting the cutting, raising the circle above the material for about 10 seconds, and then continue working with a reduced feed.
When a circle "Turbo" on the metal reinforcement in the process of cutting reinforced concrete should be reduced by approximately 30-50%.
After the complete wear of the diamond segments, do not throw away the case of the segment circle. Splitstone firm attacks him new diamondic segments, which will allow you to save about 20% of the cost of a new circle.
Recommended cutting modes with crown circles
| Diameter D, mm | Color Circle | Rotation frequency, rpm | Cut depth, max., Mm | Feed, m / min | Required power, kW | Water consumption, l / min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 110. | Yellow | 7000-10000 | fifteen | 0.4. | 1.2-1.4 | 5-10. |
| Green | 4200-6000 | 0,3. | ||||
| 115. | Yellow | 7000-10000. | 0.4. | 1.4-1.6 | ||
| Green | 4200-6000 | 0,3. | ||||
| 150. | Yellow | 5000-7600. | twenty | 0.4. | 1.8-2.0 | |
| Green | 3200-4500 | 0,3. | ||||
| 180. | Yellow | 4200-6300 | 40. | 0,6 | 2.0-2.2 | |
| Green | 2600-3700 | thirty | 0.4. | |||
| 250. | Yellow | 3000-4600 | 65. | 0,6 | 2.2-2.4 | 10-15 |
| Green | 2000-2700. | fifty | 0.4. | |||
| 300. | Yellow | 2250-3800. | 65. | 0.8-1.0 | 2.4-26 | 12-17 |
| Green | 1600-2200. | fifty | 0.5-0.7 | |||
| 350. | Yellow | 2200-3300 | 80. | 0.8-1.0 | ||
| Green | 1400-2000 | 60. | 0.5-0.7 | |||
| 400. | Yellow | 2000-2900 | 80. | 0.8-1.0 | 2.6-2.8 | 20-25 |
| Green | 1200-1700 | 60. | 0.5-0.7 |
Circles "turbo" Convenient in that you can cut them using the "Bulgarian".
To reduce the contact area with the material in the side surface of the diamond-free layer, there are inclined grooves, and it becomes wave-like. Now it is touched only by the vertices of the waves, and the air, captured by the grooves, provides good cooling. Forced cooling with water in this case you do not need to use.
Such circles are produced with three types of bundles (based on bronze, based on bronze with the addition of iron and cobalt or based on cobalt with the addition of bronze), so color, respectively, three colors yellow, blue and green. Yellow circles are designed for dry cutting of marble, ceramic and tile, drywall, roof tiles, limestone, burnt and silicate brick, blue - for medium hardness materials: curb stone, chamotte brick, slate, solid marble, "lung" concrete, circles Green color- for solid materials: granite, "heavy" concrete and concrete with a solid filler.
Their diameter does not exceed 300mm, and the most chassis - 230 mm, which is determined by the size of the standard Bulgarian casing. If it allows its power, sometimes it is set to or without a casing sizing or without it to bring the diameter of the circle to 254mm.
Recommended cutting modes with turbo circles
| Diameter D, mm | Color Circle | Rotation frequency, rpm | Cut depth, max. / Dream circle, mm | Feed, m / min | Required power, kW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 110. | Yellow | 9000-14000 | 15/15 | 0,2 | 0,6 |
| Blue | |||||
| Green | |||||
| 115. | Yellow | 9000-14000 | |||
| Blue | |||||
| Green | |||||
| 125. | Yellow | 8000-1200. | 1.0 | ||
| Blue | |||||
| Green | |||||
| 150. | Yellow | 7000-10000. | 20/20 | 1,2 | |
| Blue | |||||
| Green | |||||
| 180. | Yellow | 6000-8000 | 40/25 | 0,3. | 1,6 |
| Blue | |||||
| Green | |||||
| 230. | Yellow | 5000-7000 | 60/30 | 2.0 | |
| Blue | |||||
| Green | |||||
| 254. | Yellow | 4600-6500 | 65/30 | 0.4. | 2,2 |
| Blue | |||||
| Green | |||||
| 300. | Yellow | 3800-5000 | 80/30 | 2.6 | |
| Blue | |||||
| Green |
Segment circles Allowed to achieve higher performance due to the fact that the cut fragments of the material fall into the grooves between the segments and are removed in the same way as when the disk saw is cutting, without interfering with cutting. The diameter of such a circle can be large, since the segments are made separately, and then soldered to the circle body with silver solder or weld with laser welding. Almost all of them require cooling with water, and a large required power forces the use of special expensive cutting machines, which was mentioned in the report of the "new doorway in the overhaul" (see. Ivdn7 (9) in 1998).
The method of selection of the bundle type and with laser welding, it is possible to make segment circles with a diameter of 254mm for dry cutting concrete and brick, which allows the use of "Bulgarian".
Recommended cutting modes segment circles
| Diameter D, mm | Sliced Material | Rotation frequency, rpm | Cut depth, max. / Dream circle, mm | Feed, m / min | Required power, kW | Water consumption, l / min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 230. | Marble | 5200-4800 | 60/30 | 0.1-2.0 | 1.8-2.0 | 8-12. |
| Granite | 2200-3300. | 50/25 | 0.3-1.0 | |||
| Concrete | 3000-4800 | 50/25 | 2.0-10.0 | 5-8 | ||
| W / concrete | 2000-3200 | 50/20 | 1.5-8.0 | |||
| 254. | Marble | 4500-4000 | 80/35 | 0.1-2.0 | 2,0-2.4 | 8-12. |
| Granite | 1900-2800. | 60/30 | 0.3-1.0 | |||
| Concrete | 2500-4200 | 70/30 | 2.0-10.0 | 5-8 | ||
| W / concrete | 1600-2800. | 70/25 | 1.5-8.0 | |||
| 300. | Marble | 3200-3800. | 100/40. | 0.1-2.0 | 2.4-3.5 | 10-15 |
| Granite | 1600-2300. | 80/40. | 0.3-1.0 | |||
| Concrete | 2000-3800. | 90/40 | 2.0-10.0 | 8-10 | ||
| W / concrete | 1200-2400. | 90/30 | 1.5-8.0 | |||
| 350. | Marble | 2700-3300. | 100/40. | 0.1-2.0 | 3.0-4.5 | 10-15 |
| Granite | 1400-2000. | 80/40. | 0.3-1.0 | |||
| Concrete | 1650-3300. | 90/40. | 2.0-10.0 | 8-10 | ||
| W / concrete | 1000-1600 | 90/35 | 1.5-8.0 | |||
| 400. | Marble | 1650-3300. | 140/40 | 0.1-2.0 | 4.5-6.0 | 15-20. |
| Granite | 1200-1700. | 100/40. | 0.3-1.0 | |||
| Concrete | 1400-2900. | 100/40. | 2.0-10.0 | 10-15 | ||
| W / concrete | 800-1200 | 90/35 | 1.5-8.0 |
IN turbo segmented circles Segments with a wave-like side surface of the diamondic layer are welded with laser welding to the circle body. Waich Croach combined the best properties of segment circles and turbo circles: they provide high performance dry cutting.
Firm "Splitstone" It evaluates the effectiveness of diamond circles with the help of a specially developed technique. The use is determined by the cost of cutting 1m2 of the material and the resource of the cutting circle as the total area of the cut cross section of the material in 1m2, and three degrees of the quality of the circles (asparable) can be defined - Standard Silver, Premium Gold and Professional Platinum. The higher the quality of the quality of the circle, the higher its resource and the cost, but the dependence is such that for a large amount of work it is more profitable to acquire the circles of higher quality.
Externally distinguish the circles of the same type and with one bundle, but different quality is possible by the color of the body: a darker tone corresponds to a higher degree of quality, for example, blue (Standard Silver), Blue (Premium Gold) and Dark Blue (Professional Platinum).
Each cutting circle of the new design is tested to determine the real values of the cutting, resource and performance mode, and each cutting wheel, manufactured for sale, is pre-sale control. But in any case, instructions on the use should be made to the diamond cutting circle, which should be carefully learned so as not to cause injury during the work of a high-speed tool.
The effectiveness of turbo diamond circles according to the evaluation of Splitstone
| Diameter CroD layer height Width layers, mm | Resource VM2 / cost 1m2 cut, $ | |||||
| Marble | Granite | Concrete | ||||
| Standard Silver | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1102,26.0 | 10 | $ 2,2 | 2. | $ 3.0 | 3. | $ 4.0 |
| 1152,48.0 | 12 | 3. | 3. | |||
| 1252,28.0 | 17. | 3. | four | |||
| 1502,68.0 | twenty | four | four | |||
| 1802,68,5 | 23. | four | five | |||
| 2302,68,5 | 28. | 6. | 6. | |||
| 2542,68,5 | 35. | 6. | 6. | |||
| Premium Gold quality | ||||||
| 1102,26.0 | fourteen | $ 1,8 | 3. | $ 2,4. | four | $ 3.5 |
| 1152,48.0 | eighteen | four | five | |||
| 1252,28.0 | twenty | four | five | |||
| 1502,68.0 | 23. | five | 7. | |||
| 1802,68,5 | 27. | five | eight | |||
| 2302,68,5 | 35. | 7. | 10 | |||
| 2542,68,5 | 42. | eight | eleven | |||
| Quality Professional Platinum | ||||||
| 1102,26.0 | twenty | $ 1.0 | four | $ 2,1 | 6.5 | $ 2.9 |
| 1152,48.0 | 23. | five | 7. | |||
| 1252,28.0 | 24. | 5.5 | eight | |||
| 1502,68.0 | 29. | 6. | nine | |||
| 1802,68,5 | 35. | eight | 10 | |||
| 2302,68,5 | 45. | 10 | 13 | |||
| 2542,68,5 | fifty | 11.5. | fifteen |
The report uses the terms from GOST 9206-80 (Ed.1987), GOST 10110-87 (Red.1998) and GOST 16115-88 (Ed.1998)
The editors are grateful to the company "Splitstone" for help in the preparation of the report
