Purpose of abrasive cutting circles, specifications, instructional rules, practical recommendations for work.
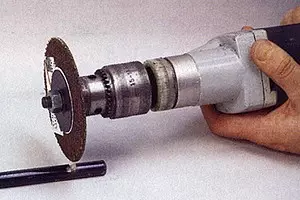

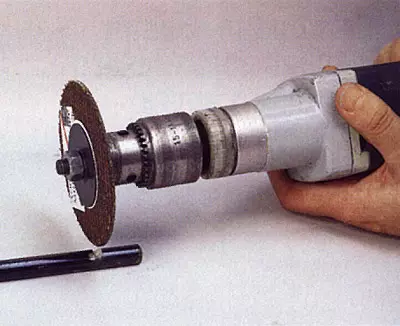



Installation and consolidation of the abrasive cutting circle on the shaft "Bulgarian":
one. Put the metal puck with an outer diameter of no less than 1/3 of the circle diameter on the drive shaft.
2. Take the gasket from cardboard or elastic material, the thickness of which is 0.5-1.0 mm.
3. Secure the circle with the boarding hole, impose a second gasket, then the second metal washer, and each gasket must perform from under the washer by a value equal to its thickness, and tighten this "puff pastry" with a "Bulgarian" nut.


Crack in an abrasive circle (a), chip cutting edge (b) and "sweeping" of the circle (B), under which its use is not recommended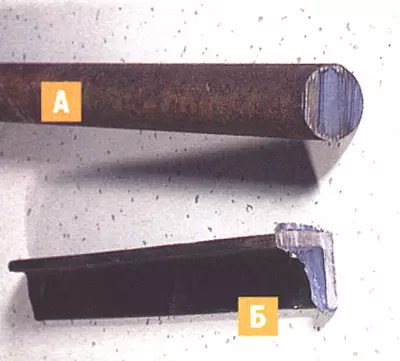
Have you had to cut off the steel corner of 35x35mm for a greenhouse frame or semi-leaf metal pipes for the water pipeline on the household plot? If so, then choosing between the withdrawal metal, a disk saw, a welding electrode, or an abrasive cutting circle, probably preference gave the latter as the most quick and convenient.
Abrasive cutting circles supply such firms such as Austrian Terolit, Czech Carborundum Electrite, German Dronco, Bosch and Carborundum, Italian PG and Sisa, Yugoslav Suma and Uniflex-S, Finnish K'Prof, Hilti from Liechtenstein, as well as domestic enterprises , among which AOOT "Mosshlifinstrument" (Moscow), OJSC "Luzhsky Abrasive Plant", JSC "Isma" (Ivanovo), Plant "Montajabrasivinstrument" (Perm).
Abrasive (delates. Acbrasio-scraping) The cutting wheel is intended for accurate and high-quality cutting of various forms of products like steel, cast iron, non-ferrous metal alloys (bar, pipes, corner, sheet, fittings), and bricks, slate, ceramics, drywall, as well as marble, granite, stone and concrete in small quantities. We need only a portable cutting machine or an angular grinding, called "Bulgarian".
It is necessary to warn that many enterprises that produce cutting machines offer and cutting circles to them under their brand, not being manufacturers.
The speed of rotation of the circle is large, so only the high quality of its manufacture can guarantee safe operation. Circles are made to the list of products and services that undergo mandatory certification. Thus, the quality of products of AOOT "Moskslifinstrument" (they will be discussed) confirmed by the certification institution accredited by the State Standard of the Russian Federation.
Multiple rules for choosing an abrasive cutting circle
Check that the circle is not deformed, and there were no cracks and chips on the surface.It is desirable that the specified maximum value of the rotational speed of the circle would not be less than the rotational speed of the Bulgarian used.
Note that with cutting used only 2/3 of the diameter of the abrasive circle.
The strengthening element is not always provided for by the design of the abrasive circle, and it can be judged by the label. So, in domestic manufacturers, the letter "bu" means "Bakelite bunch with a hardening element". If "y" is absent, there is no such element and put the abrasive circle on the "Bulgarian" is not recommended.
The smaller the height of the circle, the easier it is to cut and less waste, but also wear more. With a minimum height of the circle (5 sizes of particles), a smaller abrasive graininess is used and, therefore, the performance decreases.
The abrasive cutting wheel, usually used in the household, is a thin disk with a diameter of from 100 to 500mm with a height of from 1 to5mm with a seating hole with a diameter of 22 or 32mm, which is most often framed by a metal calibration sleeve. For example, with a cutting "grinder" due to a significant amount of torque, the diameter of the circle does not exceed 230mm. You can meet a cutting circle with a diameter of 100 and even 80mm with a 10mm fitting, mounted on a domestic electric door with a mandrel.
The abrasive circle cuts the metal particles of fine-grained high hardness material (abrasive), resembling in size and form of conventional grains. They are first mixed, and then it is compressed with an elastic synthetic binder mass, the main homes of which is bakelite (plastic) or vulcanite (rubber). The sharp peaks of the abrasive protrude above the surface of the ligament and, hurt for metal, cut into the finest chips. In the manufacture of a mixture of bundles, abrasive and fillers are placed in the form, it is planted and thermally processed. Combs with bakelite bunch are more often used for coarse cutting of metal and building non-metallic materials. Circles with rubber-lesser performance and are designed for cutting iron, titanium alloys and getting smoother edges of the cut (not used in everyday life).
The efficiency of the abrasive circle largely depends on the size and hardness of particles: the larger the particles and the abrasive itself, the faster the metal can be cut. Abrasive graininess, or particle size, can be from0.1 to 2 mm (100-2000 microns). It always indicates marking in conventional units, and in Russia and other countries in different ways.
After testing circles on the mechanical strength and impassableness on the labeling of each of them, the material for cutting is indicated or a color label is pasted, for example, green (for non-metallic materials) or blue (formetals). Additional information is reported there.
In domestic products, the graininess above 50 mkm is denoted as 0.1 sides of the sieve cell through which the abrasive particles are sifted when sorting in size. For example, the graininess 32 indicates the presence of particles of the main size of 320mkm and a small amount of grains of other sizes.
The graininess of from 5 to 63mkm is denoted by the maximum particle size (m). Accuracy, M28 indicates the maximum particle size of 28 μm. According to international standards ISO, the abrasive graininess is given in conventional units that do not reflect the size, while there are two separate standards: on the graininess for abrasive tools, bars, segments (F) and on the graininess for abrasive or grinding skins (P). Thus, F54 suggests that the average particle size of the abrasive particles used in the manufacture of the cutting circle is 300 mkm, and the abrasive skin with the same particle size will be indicated by P50. According to the Russian standard, and for the cutting abrasive circle, and the graininess with the main particle size of 320mkm and a single designation 32 (see Table) most corresponds to the grinding skirt.
These designations of abrasive graining on Russian and international ISO standards (except diamond and boron nitride)
| GOST 3647-80 (ed. 1994), for any abrasive tool | ISO 8486-1.2: 1996 (E) except abrasive skins | ISO 6344-1.2: 1998 (e), only for abrasive skirts | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Designation | Main particle size, μm | Designation | Main particle size, μm | Designation | Main particle size, μm |
| - | - | F 4. | 4750. | - | - |
| - | - | F 5. | 4000. | - | - |
| - | - | F 6. | 3350. | - | - |
| - | - | F 7. | 2800. | - | - |
| - | - | F 8. | 2360. | - | - |
| 200. | 2000. | F 10. | 2000. | - | - |
| 160. | 1600. | F 12. | 1700. | P 12. | 1700. |
| - | - | F 14. | 1400. | - | - |
| 125. | 1250. | F 16. | 1180. | P 16. | 1180. |
| 100 | 1000. | F 20. | 1000. | P 20. | 850. |
| - | - | F 22. | 850. | - | - |
| 80. | 800. | F 24. | 710. | P 24. | 710. |
| 63. | 630. | F 30. | 600. | P 30. | 600. |
| fifty | 500. | F 36. | 500. | R 36. | 500. |
| - | - | F 40. | 425. | P 40. | 355. |
| 40. | 400. | F 46. | 355. | - | - |
| 32. | 320. | F 54. | 300. | P 50. | 300. |
| 25. | 250. | F 60. | 250. | P 60. | 250. |
| twenty | 200. | F 70. | 212. | - | - |
| sixteen | 160. | F 80. | 180. | P 80. | 180. |
| - | - | F 90. | 150. | - | - |
| 12 | 120. | F 100. | 125. | P 100 | 150. |
| 10 | 100 | F 120. | 106. | P 120. | 106. |
| eight | 80. | F 150. | 90. | P 150. | 90. |
| 6. | 63. | F 180. | 75. | P 180. | 75. |
| five | fifty | F 220. | 63. | P 220. | 63. |
| M 63. | 63-50 | F 230. | 55.7 | P 240. | 58.5 |
| - | - | F 240. | 47.5 | - | - |
| M 50. | 50-40 | F 280. | 39.9 | R 280. | 52,2 |
| M 40. | 40-28. | F 320 | 32.8. | P 320. | 46,2 |
| - | - | F 360. | 26.7 | P 360. | 40.5 |
| M 28. | 28-20. | F 400. | 21,4. | P 400. | 35.0 |
| M 20. | 20-14. | F 500. | 17,1 | P 500. | 30.2 |
| M 14. | 14-10. | F 600. | 13.7 | P 600. | 25.8. |
| M 10. | 10-7 | F 800. | 11.0 | P 800. | 21.8. |
| M 7. | 7-5 | F 1000. | 9,1 | R 1000 | 18.3 |
| M 5. | 5-3. | F 1200. | 7.6 | R 1200. | 15.3. |
| - | - | - | - | P 1500. | 12.6 |
| - | - | - | - | R 2000. | 10.3. |
| - | - | - | - | P 2500. | 8,4. |
Brands and abrasive grain for cutting circles
| Name and brand Abrasive | Abrasive graininess | |
|---|---|---|
| Bakelite bunch | Bunch of vulcanitic | |
| Normal electrocorundant 13a, 14a | 125, 100, 80, 63, 50, 40, 25, 16 | 46, 25, 16, 12, 10, 8, 6 |
| Chromotytomatic electrocorundant 93a, 94a | 125, 100, 80, 63, 50, 40, 25, 16 | - |
| White electrocorundant 25A. | 50, 40, 25, 16, 12 | 40, 25, 16, 12, 10, 8, 6 |
| Zirconium electrocorundum 38A. | 125, 100, 80, 63 | - |
| Black silicon carbide 53c, 54c | 160, 125, 100, 80, 63, 50, 40, 25, 16 | - |
| Silicon carbide green 63С, 64С | 16, 12, 8, 6 | - |
To reduce the risk of breaking the circle when cutting with a high frequency of rotation, a hardening element is introduced into its body in the form of a round disk from a thin glass mesh. One such mesh element in the middle of the height of the circle (or by the end surfaces) is set in manufacturing. This grid also retains the shape and flexibility of the cutting circle.
Practical recommendations
The new cutting circle is first be sure to scroll around about 5min, holding the "Bulgarian" with a dressed casing circle from himself. The fact is that as a result of possible shots during transportation in the circle case, microscopic cracks may form, leading to the expansion of small fragments.
The gradual wear of the abrasive cutting circle is accompanied by a reduction in the diameter of the circle, so in the case of repeated use, gradually reduce the cutting depth.
In order for cooling with water used extremely rarely (for example, when the cut-off metal is heated), it was effective, slow the circle speed by 30-50%.
Cutting metal consolidate only on one side. In contrast, from strong heating, it is deformed and can jam the abrasive circle.
Circle supply when cutting a thick rod should be reduced by 15-20% during the passage of half of the diameter, after which it can be increased to the initial value again.
Store an abrasive circle with a bakelite bundle follows in a dry place, because the strength of the bundle decreases from the moisture.
Abrasive circle has two advantages compared to diamond. First, when working does not require forced cooling with water, because its temperature usually does not exceed 70-80C. Good natural cooling is provided by a large amount of pores that are formed in a circle in its manufacture. They, as well as a special filler added to the bundle and the sharpening when cutting, contribute to the rapid removal of metal chips.
Secondly, such a circle is not blinking, as they say, "self-causing", while the initial diameter is gradually reduced by the destruction of particles of abrasive and burnout bond. Valid dreams from a diamond circle, cutting with an abrasive circle is always accompanied by intensive snaps of sparks, the particles of the ligaments and the smallest metal chips are burning, which fly by tangential in the direction of rotation. They are too small and cannot cause injury in the form of scratches or burns.
Cutting modes with abrasive cutting circle grain 63
| Diameter votadiametrum., Mm | Cutting speed, m / s | Cutting depth, mm | Feed * Circle, m / min | Required power, kW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1153,022. | 60 or 80. | No more than 0.15d | 0.2-0.8 | 1.0 |
| 1503,022. | « | « | « | 1,4. |
| 1803,022 (32) | « | « | « | 1,6 |
| 2003.022 (32) | « | « | « | « |
| 2303,022 (32) | « | « | « | 1.9 |
| 3003,032. | « | « | « | 2,2 |
| 4004,032. | « | « | « | 2.6 |
| 5005,032 | « | « | « | 3,2 |
The operation of the circle is determined by its speed and feed (movement). The maximum speed must necessarily be indicated on the circle marking or on the label. On domestic products, the speed value is additionally highlighted by the color of the diametral band: yellow (60m / s), red (80m / s) or green (100m / s). So, due to a limited number of turnover of "Bulgarian" with a half value of the speed, its resource decreases by 30-50%.
Moving should be strictly in the range from 0.2 to 0.8m / min. When applying less than 0.2 m / min, heat dissipation during cutting is significantly increasing, which contributes to the "squeezes" of metal and burning off the ligament and forces the use of cooling with water. When applying more than 0.8 m / min, even if the process goes without a significant physical force, the abrasive particles begin to sharpen too quickly from the bundle ("crumble") and due to the intensive heating of the metal being cut, it is possible to join a circle that can lead to the output from Building the engine "Bulgarian". The thickness of the metal cutch should not exceed 15% the diameter value of the circle. Failure to comply with this restriction leads to the "fourth" metal, a reduction in the resource of the circle and productivity.
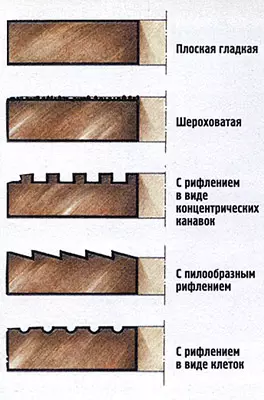
To reduce the heating of the abrasive circle, its end surface is either flat, but very coarse, with a bunch of abrasive grains, either make a rifle due to shallow grooves, for example, in the form of concentric circles. This reduces heat dissipation and power consumption by 60-80% compared with a smooth surface. When cutting the groove, especially in the metal, the circle is used by 0.1-0.2 mm thinner to the center than along the outer perimeter. Abrasive circles are more elastic than diamonds, allow for short-term, albeit unwanted sneaks in the groove and economically less effective. This is especially noticeable when cutting a solid building material, such as concrete. The abrasive circle has a shorter resource measured by the total cross-section area in 1m2 of the material being cut. This is confirmed by a decrease in the diameter of the circle.
The effectiveness of the cutting of concrete by the abrasive circle of AOOT "Moskslifinstrument" and the diamond cutting circle of the company "Splitstone"
| Type of circle (diameter 230mm) | Circle price, $ | Resource, m2. | Cost 1m2, $ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasive circle | 0,6 | 0.05 | 12.0. |
| Diamond circle "Turbo" | 38. | 13 | 2.9 |
| Diamond circle segment | 95. | 25. | 3.8. |
As can be seen from the table, the cost of the abrasive circle is many times less. Therefore, if you need to cut a little, then it is more profitable to purchase an abrasive cutting wheel, and if you need to constantly have a circle at hand, a diamond cutting. We emphasize that such a statement does not concern the cutting of metals, where the abrasive cutting circle is out of competition.
Before working, read again by the instruction of using the Bulgarian, which should be observed in the most thorough way to avoid injury during the cutting process by this high-speed instrument.
