We tell the device and install heat pumps, additional equipment and about what problems can be encountered.


Heat pumps work like air conditioners. Sometimes their energy efficiency is almost the same. At the same time, it exceeds this indicator in the heating devices of the traditional design, for example, electrical heaters. The article is telling how to choose a heat pump for a country house.
All about heat pumps for country house
How is the heat pumpThe effectiveness of the thermal pump
Heat pump equipment
Possible problems and errors
How is the heat pump
The heat pump transfers the heat of one environment to another with three interconnected thermal contours. The first medium uses atmospheric air, water or soil. As a second - or coolant, heating radiators, or water warm floor, or air indoor air.
Types of thermal pumps
- air - air (this type and is used in household air conditioners);
- water - air;
- Earth - air;
- air - water;
- water - water;
- Earth - water.
The greatest distribution was the models in which air or land performs the first medium, since the reservoir suitable for use is not everywhere. The second medium is water, due to the popularity of water heating.
In terms of the medium acting as a source of heat, the contour of the pipes is laid, the coolant circulates on it. In the process of passing along it, the coolant acquires the same temperature as the environment. Then he enters the evaporator heat exchanger, where the liquid freon is heated to a boil, located in the secondary system. Freon gas enters the compressor, where it is strongly heated to 55-75 ° C during compression. Further, the freon enters the condenser, where the heated gas gives the heat of the number two, air or fluid-heat carrier from the heating system.
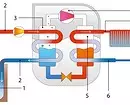

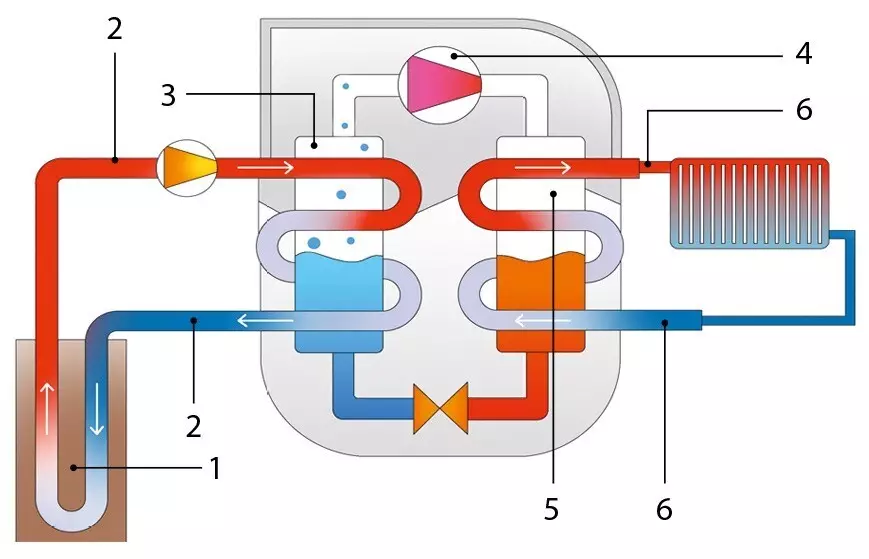
Circuit diagram of the heat pump: 1- heat source; 2 - low-temperature primary contour; 3 - evaporator; 4 - compressor; 5 - condenser; 6 - Third contour (heating).
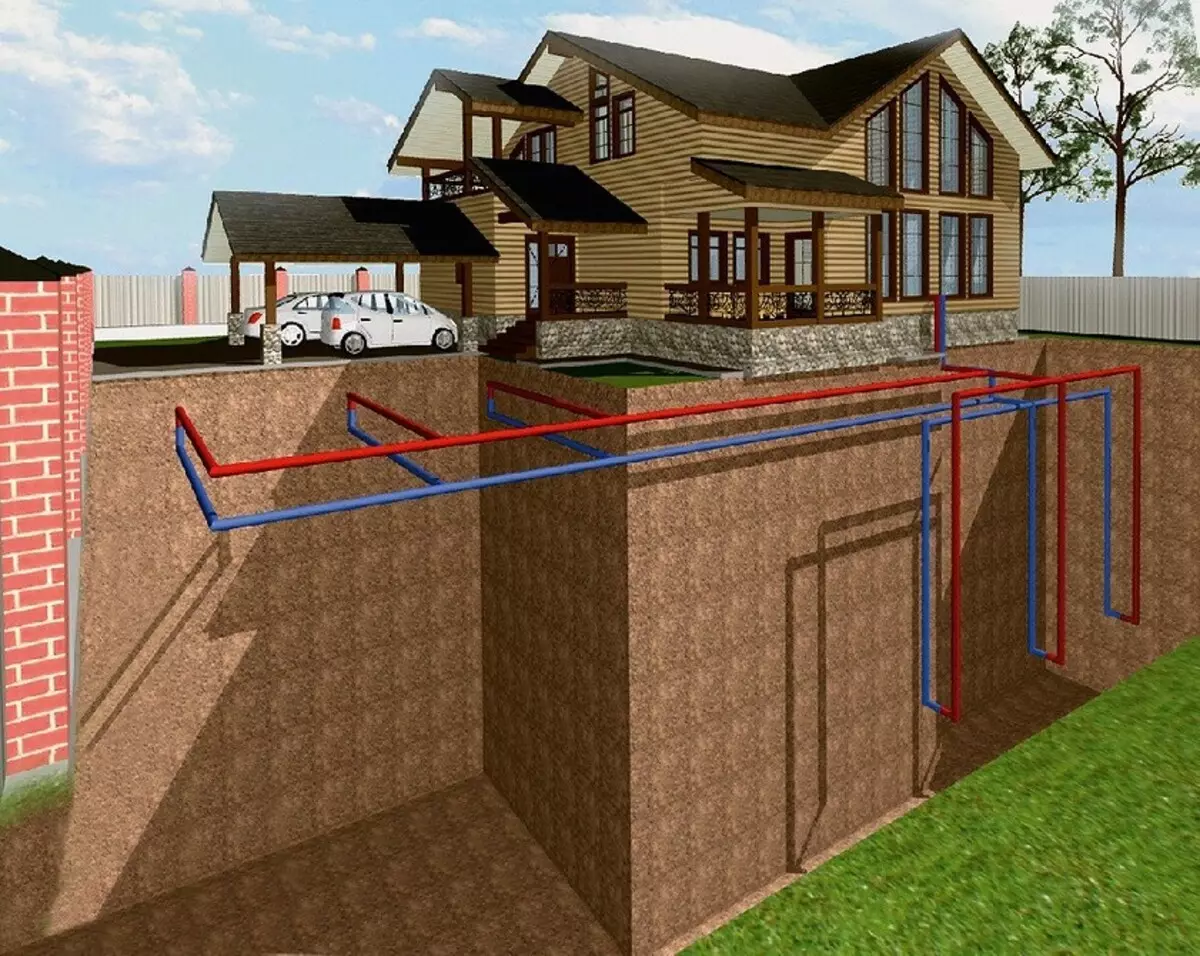
Options for the primary contour device in the ground: vertical (well) occurring, horizontal location.
The effectiveness of the thermal pump
The efficiency ratio is the ratio of heating power to power consumed, roughly speaking - how many kilowatt heat power we get for each electricity consumed by kilowatt. For an electrical heater, this coefficient is approximately equal to one. But in air conditioners and heat pumps, it can be 3.0-5.0 and higher.
In addition to the heat pump, you will need a heat exchange path, which may be more expensive than the device itself, if it is paired in the ground. The air circuit will cost much cheaper, but its use in everyday life is limited, first, due to noticeable noise that produces a fan. And secondly, the low air temperature in a heavy frost dramatically reduces heat exchange efficiency. In a heavy frost, a device of a bivalent heating system will be required, in which two heat sources are used. The bivalent system expands the working range of outdoor temperatures. For example, the device works up to -20 ° C, and with further decrease the additional source is turned on.
With an earthy contour there are no such problems. The soil temperature below the level of the freezing does not fall below 0 ° C. At a depth of 3-4 to 40-50 m, it is approximately equal to the average annual air temperature for a given area, and at a depth, it begins to gradually increase. And the soil heat exchanger works almost silently.
Practice shows that the ground heating complex pays off in about 20 years. And this is at modern prices for electricity. In the future, most likely, electricity will grow in price, and payback period, respectively, decrease. The service life of the thermal pump declared by manufacturers usually exceeds 20 years, and the service life and comes at all up to 70-100 years. So its use, indeed, can be economically justified.
Heat pump equipment
The selection of heating equipment usually begins with the definition of its required power. The thermal calculation of the room is produced, the heat loss counts, the desired amount of hot water for the DHW is taken into account. This calculation is charged better by a specialist to avoid mistakes. Approximate order of numbers issues Calculators on the sites of manufacturing companies.
Next, you can choose the type of device taking into account the site. If at your disposal is quite large water (several hundred cubic meters), then it may be suitable for placement of the system. The latter reminds a serpentine of flexible polymer pipes, it is neatly laid on the bottom and secure there with a cargo.
Air heat exchangers are quite suitable for windy southern regions of our country or for bivalent systems. They can be placed on a distance of up to 30 m from the inner block. In fact, they are striving to arrange as close to home as long as long connecting lines increase losses and reduce the useful power. Ideally, this is a deaf wall of the house, away from the windows of bedrooms.
An important parameter is the minimum outdoor temperature in heating mode. In specially adapted to frost models, it can be -25 ° C.
The ground collector can be arranged in several ways. For example, in the form of a horizontal laying of a long (several hundred meters) of the pipeline on a plane with a gluing above the level of freezing (usually 1.5-2.0 m). The pipeline can be laid around the perimeter of the site or snake, like a warm floor pipeline, but with a much greater step. The total area occupied area of the land is several acres, and the possibility of additional use of this land is significantly limited. It will not be able to dilute the garden or plant trees. Therefore, many homeowners consider the horizontal laying of the collector is irrational and prefer vertical, in the form of several wells separated from each other by 5-10 m. Or in the form of one "bush" of wells (the wells are placed from one point on the surface, but not vertically, and under An angle is usually at least 30 ° in azimuth). Such a "vertical" approach saves on the square, but increases the cost of 30-50%.
By virtue of the technical features, the heat pump is better to apply for a country house in which you live long. They achieve maximum efficiency in combination with "warm floor" systems, which are inertial. The economic effect will be directly proportional to the intensity of use. In domestic conditions (European part of Russia), options for "brine (land) - water" with vertical probes were most common. They provide the possibility of full coating of heating loads and GVS almost independently of climatic conditions.



Heat pump with built-in tank and battery.
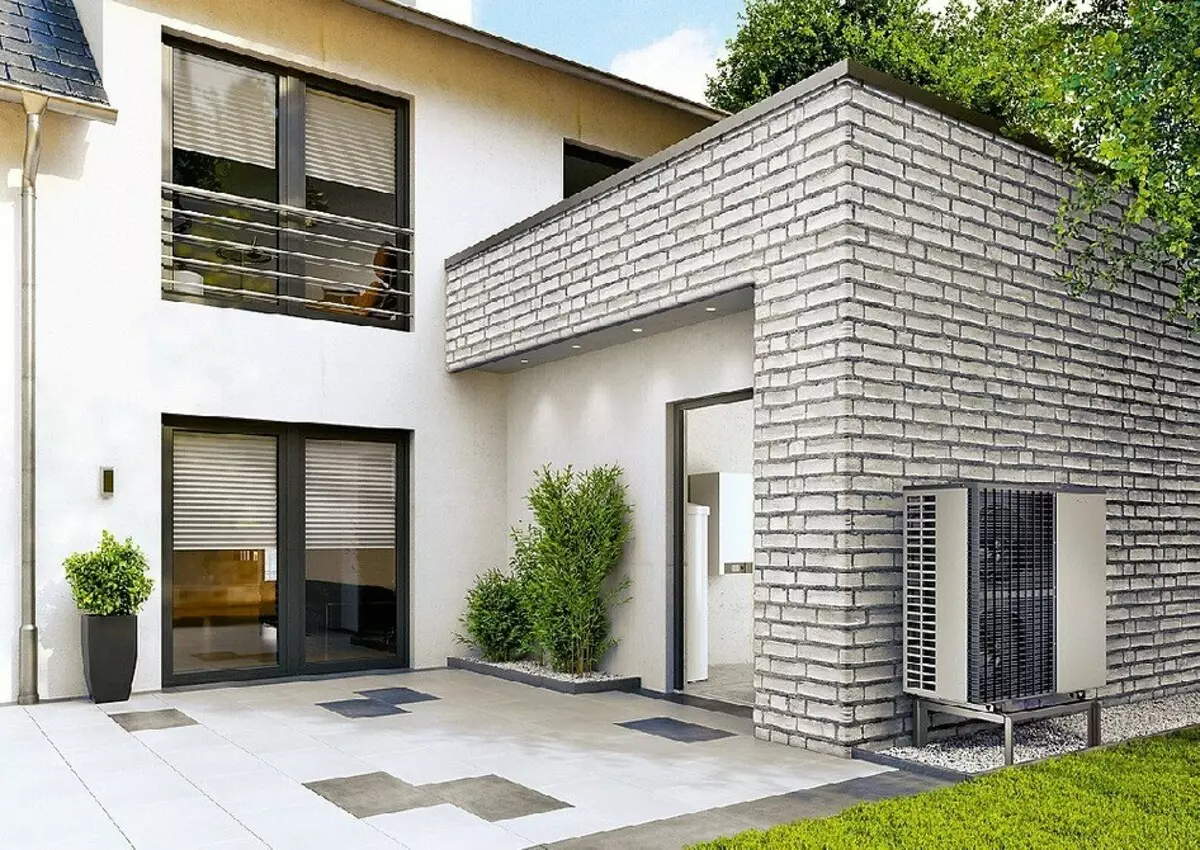

Outer block of air heat exchanger.
Possible problems and errors
In recent years, the number of companies engaged in the design and installation of thermal pumps has increased significantly. Accordingly, a number of problems arise when the heating system ceases to work or function inefficiently. And then, many homeowners find out that the simple replacement of the equipment could not do - they will have to plow the entire area, to re-lay hundreds of pipe meters of the pipe.
All errors can be divided into two large groups:
- Errors performed at the design of the heating system nodes;
- Belt performance of work.
Incorrect heating system will be either not enough powerful or unstable for the power of the main nodes. In the first case, such a heat pump is not suitable for the heating of a country house. In the second case, for example, if the outer contour is unsuccessful, the danger of freezing the pipeline occurs.






Soil heat exchanger
The soil heat exchanger is one of the key elements, with the device whose problems most often arise. It consists of long (several hundred meters) of a pipe threads, folded by rings in trenches or placed in one or more wells.Basic errors in the device:
- Understater pipe diameters.
- Unnecessary savings on materials and technologies. For soil heat exchangers, polyethylene is used everywhere, which moves well negative temperatures. But the use of polypropylene is a gross mistake. For connections of pipeline sections, you must choose only the corresponding elements intended for underground installation, and reliable welding technologies.
- The use of cheap compression fittings, giving flowing after a couple of years of operation. It is important to properly rub the wells so that the probe had a good thermal contact with the soil. For this well, the well-established probe is filled with a mixture, the heat-conducting characteristics of which is not worse than that of the soil. Bentonite in this case is not suitable, as it has insulating heat properties. It is recommended to fill the wells with sand with a small admixture of bentonite and cement. But the use of chip rocks with sharp edges, for example, rubble - should be excluded.
- Too close position of wells or pipeline threads to each other. As a result, the heat sink will deteriorate from the pipeline, and the soil can be too frozen - the heat pump will stop working.
- The placement of horizontal pipes in the ground is too deep, below the level of the freezing. The soil may be too frozen and will not have time to warm up for the summer season.
- Placing the collector is too close to the surface. With severe frosts at the end of winter, the efficiency of work will fall sharply.
- Over the collector, there are any buildings or structures that impede heat exchange. In this place, a peculiar "permafrost", an ice lens, which will not have time to warm up for the summer season can be formed.
The soil heat exchange circuit is almost not suitable for repair. If there is a leakage of the coolant due to the mechanical impulse of the pipe or its poor quality, then the thread needs to be jammed or change.
Well
Often, do not take into account the mutual influence of wells. The standard distance is 10 m with a well depth of more than 60 m. If they are located at a distance less than 8-10 m from each other, then it is necessary to increase the depth and number of wells to ensure the necessary level of energy recoil.The contour is placed at a depth of 0.8-1.4 m, so you do not need to use drilling equipment. But at the same time, it occupies a fairly large area, which limits the possibility of a decorative lawn device, bulk tracks, beds, planting shrubs.
Design horizontal contour
To design errors, in addition to inadequate length, there is an insufficient depth of its laying. At a low depth of the environment too much affects the temperature of the coolant. As a result, by the end of the heating season, the temperature of the contour can decrease and fall the equipment efficiency. Due to too much depth of laying, the ground around the system does not have time to warm over the summer. It is worth mentioning one of the erroneous opinions that the collector should be laid below the depth of the ground freezing.
Incorrect operation of the territory
The collector must be located so as to obtain as much heat as possible from the environment, maximize the return from the heating of the soil with warm soil, rainwater. Incorrect operation of the territory under which the horizontal collector is located, also leads to failures in the system. Above the collector cannot be built the buildings, laying asphalt or sidewalk. If a geothermal heat exchanger is under the "roof", then an ice lens formed by a frozen device and a soil around it can occur.Errors in calculations
Very often, when calculated, all values without stock are indicated. For example, if the blood collector is calculated for the ground collector, it is 20-30 W from the routine meter, then when calculating it is taken as 30 W. Accordingly, they choose and "the most convenient" value for the calculation. Similar miscalculations are performed and when choosing a heat pump. For example, instead of a 24 kW model, a device with a power of 17 kW is installed. As a result, the device does not cope in peak loads. A characteristic error is the use of methods of calculation made on European standards. Still, winter is colder and continues longer than, let's say, in Germany. For calculation, regulations apply to the climatic features of the construction region should be applied.
Wrong installation of nodes
Builders may not be incorrect to install the heating system nodes. At the same time, the installation of the heat pump does not represent complexity, especially if we are talking about the latest generation models. Many foreign manufacturers offer fully assembled systems. They are a monoblock that contains all elements, including the Freon-Water Heat Exchanger.
Installation of equipment consists in its installation on a solid base, connecting to electricity and pipe wiring from a cooler floor collector. Although there is sometimes a place for errors. For example, make a fitting from the water supply to the soil heat exchanger, which is strictly prohibited.
Typical errors and methods for their corrections are also specified in the table.
Error | Consequence | Correction method |
|---|---|---|
Insufficient pipeline length of the primary heat exchanger circuit | Freezing of the coolant in the pipeline | Opening a heat exchanger or an additional contour device |
Heat exchanger contour pipe diameter | Insufficient power system | Overall heat exchanger |
Too close location of wells or heat exchanger pipeline thread | Freezing of the coolant in the pipeline | Opening of the heat exchanger or device of an additional circuit or well |
Use of polypropylene pipes, compression fittings | Tepes of coolant | Overall heat exchanger |
Device over horizontally located contour of structures that impede heat access from the ground surface | Freezing of the coolant in the pipeline | Dismantling facilities |



