The technology of assembling houses from a glued timber without metallic screeds on the example of the construction of a two-story building with a total area of 300 m2

The glued timber, relatively recently appeared on the domestic construction market, managed to win a great popularity. The new material has brought with you and difficulty in the operation of houses associated with the wide use of metal-element tightening walls. Is it wrong to avoid these problems?
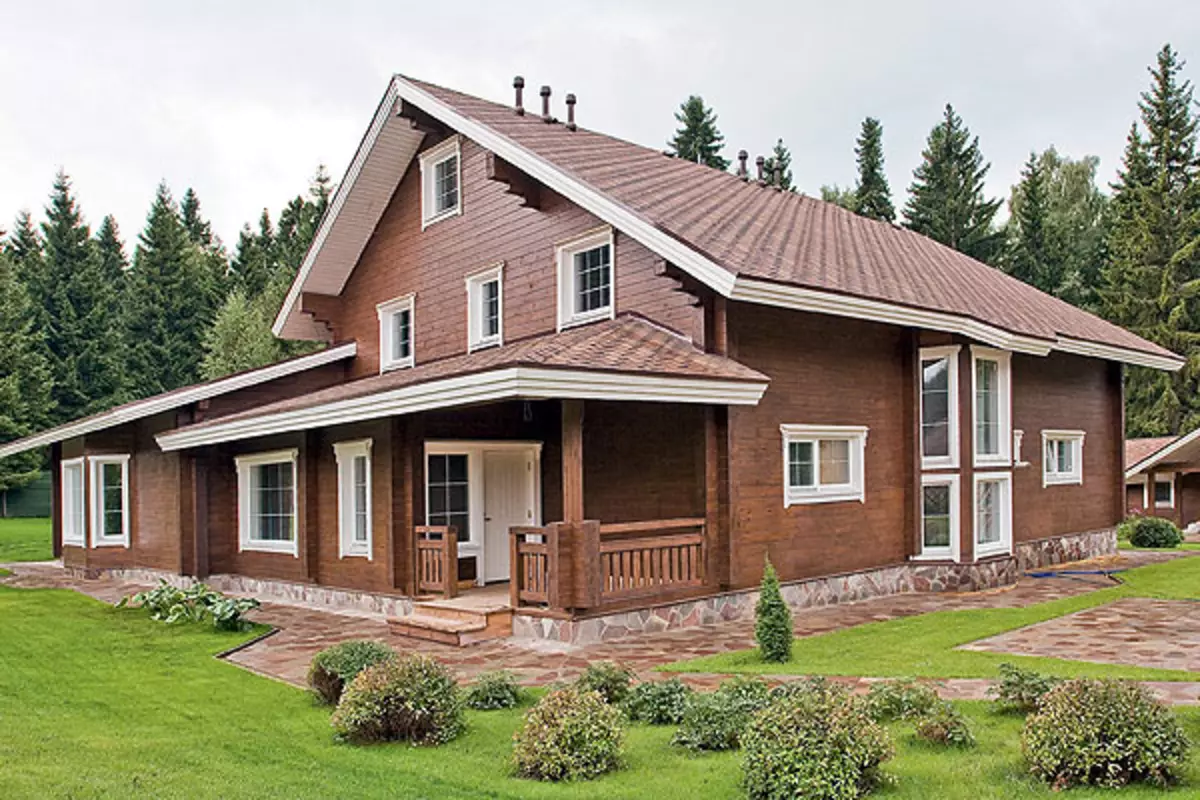

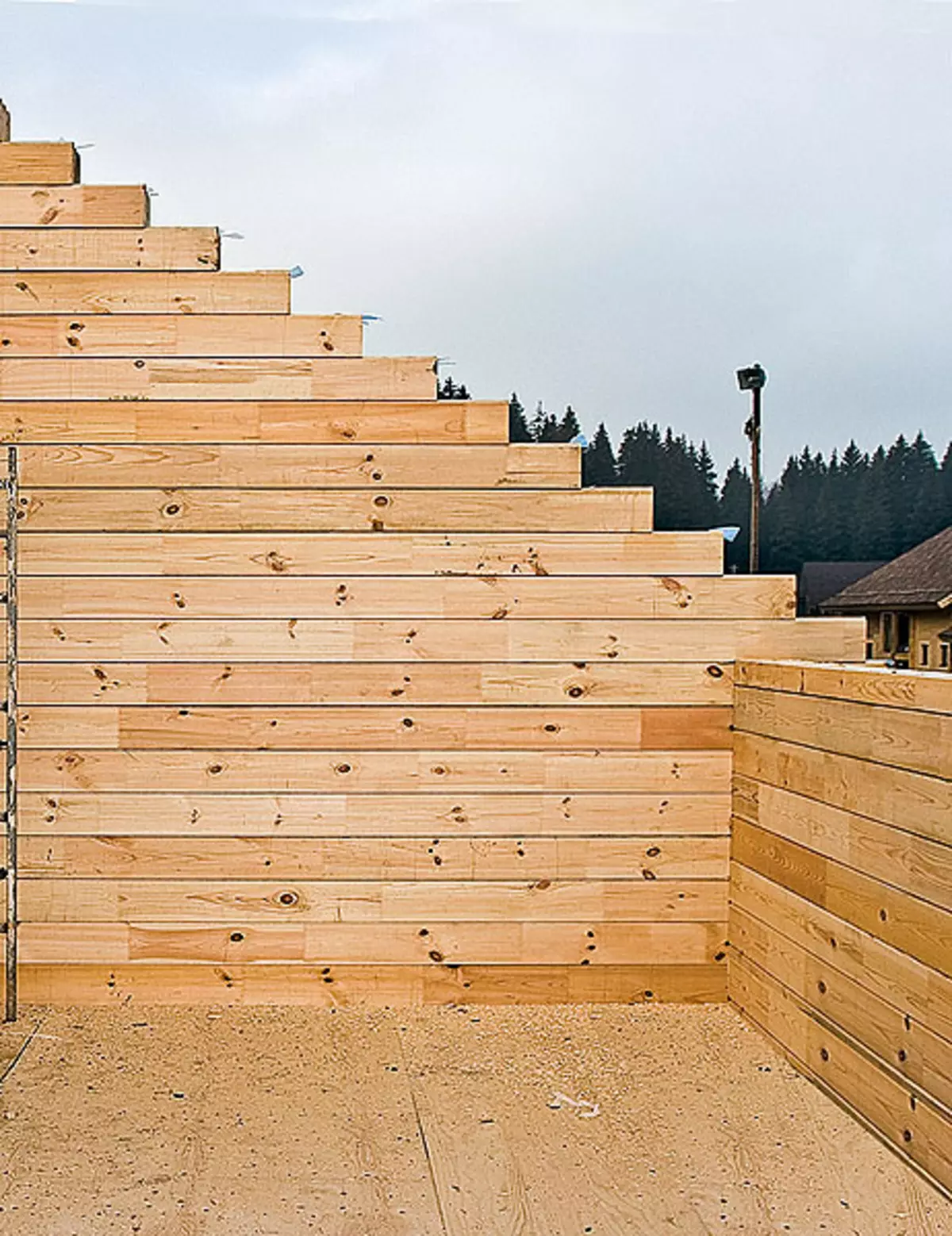
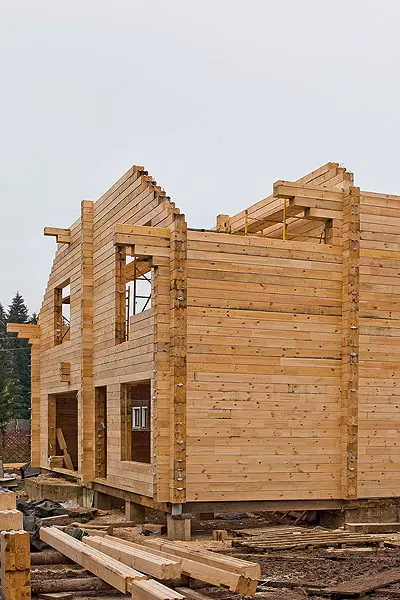
Construction of houses from glued timber is a fairly simple and fast process, because all the details are made on mechanized areas, where they are cut according to the required size and form a "cups" system, as well as spikes and grooves, so the bars are easily and quickly connected to each other.

| 
| 
| 
|

| 
| 
| 
|
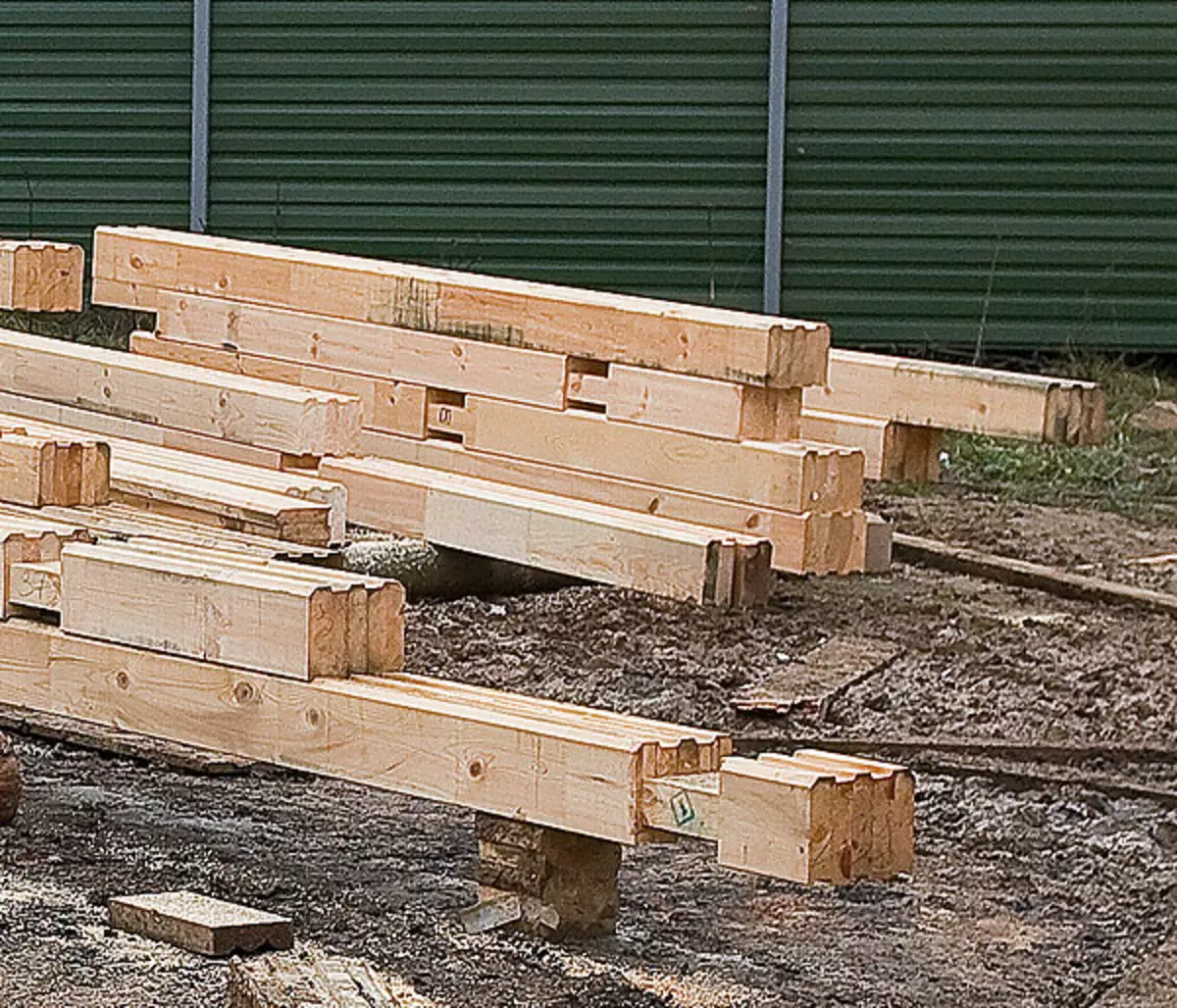
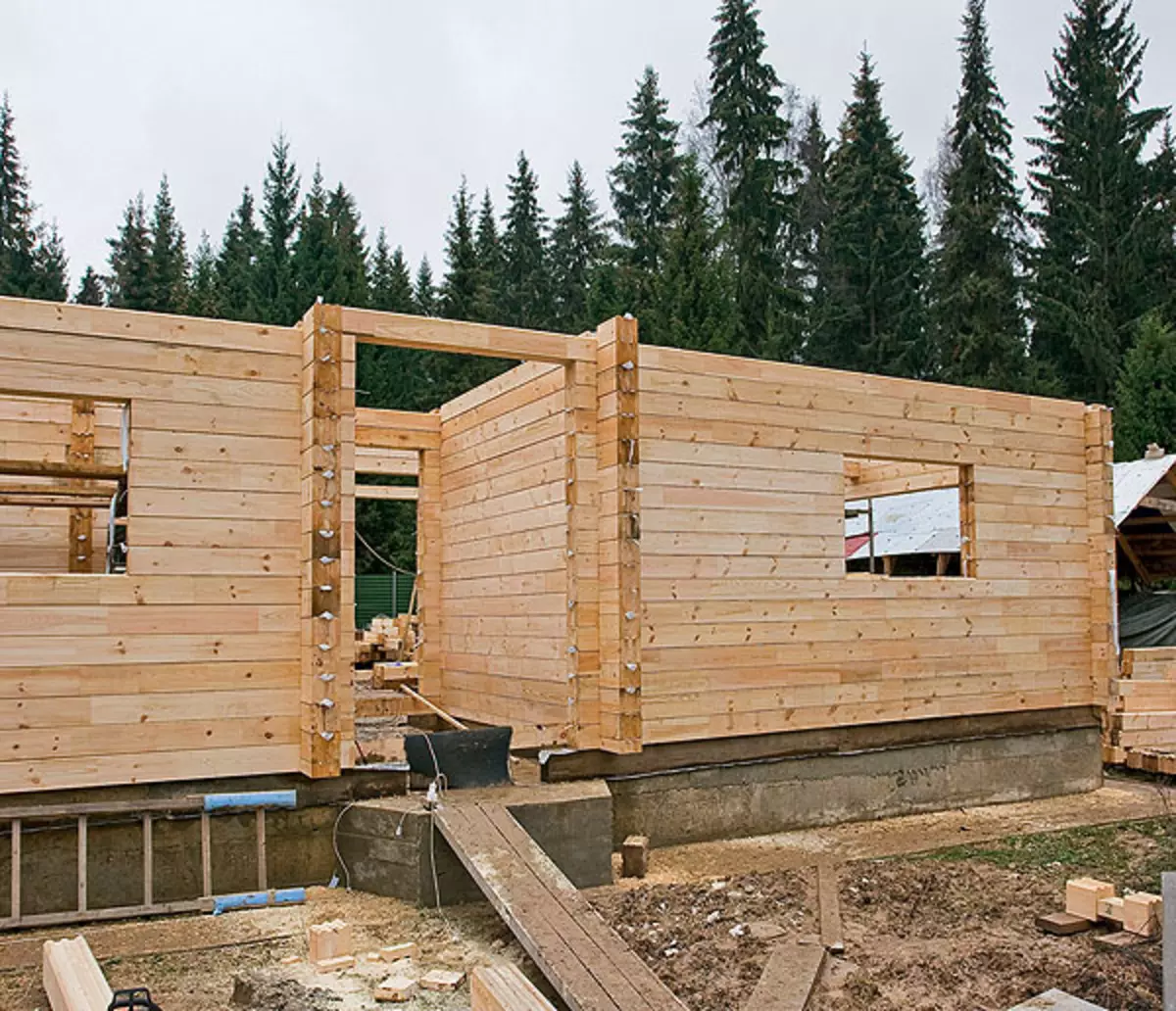
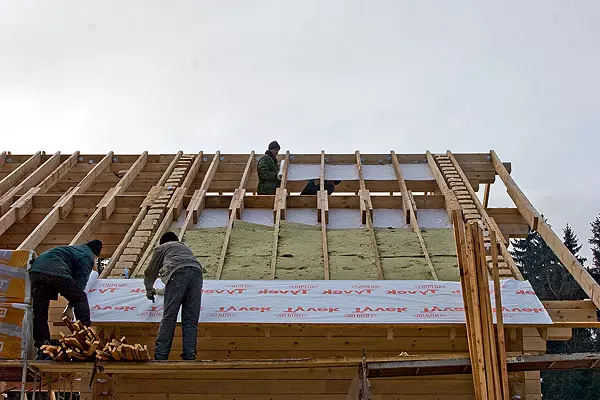
1. The set of fully finished parts came to the construction site, there are even grooves under the cudd bars required for installation of windows.
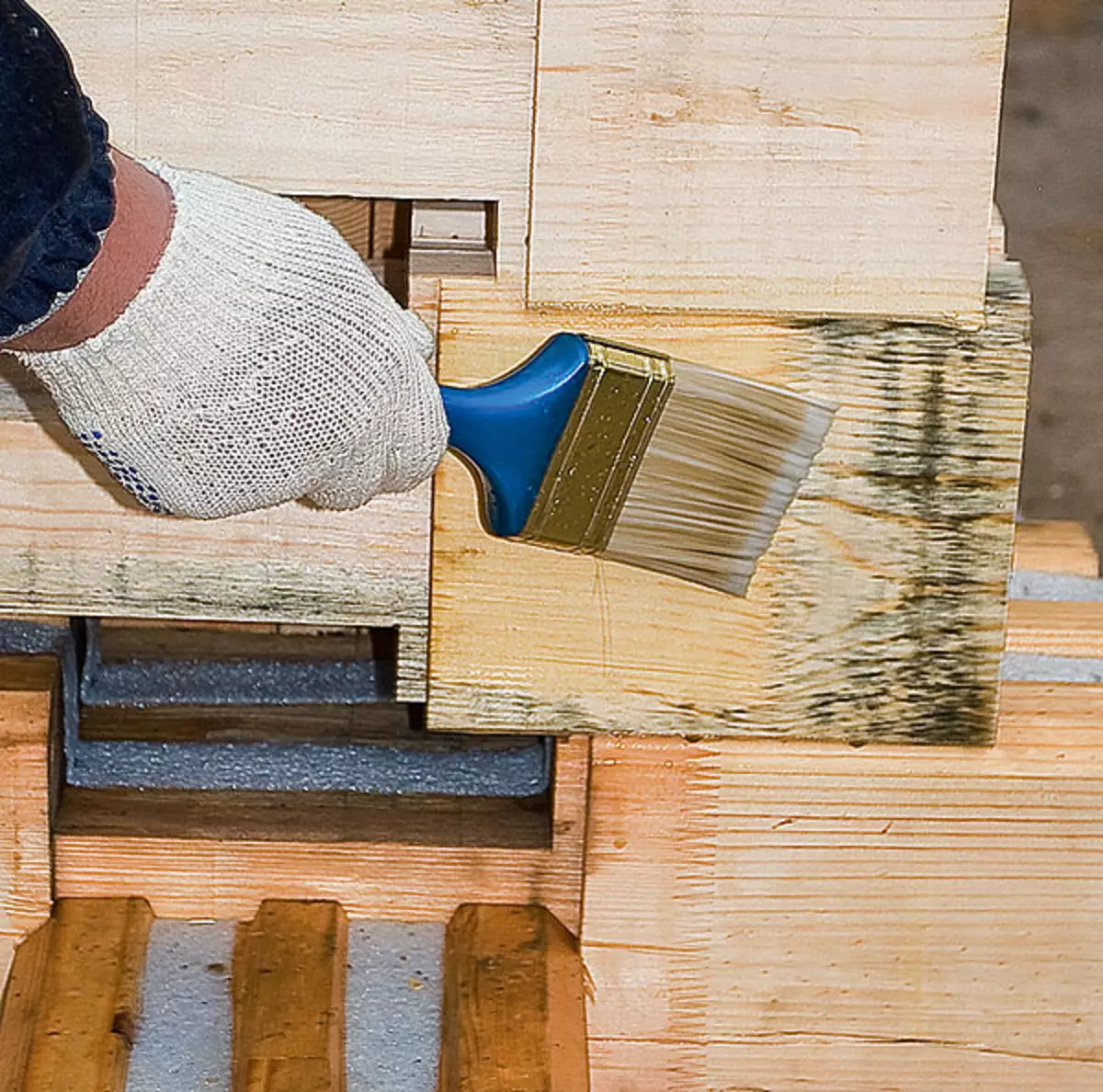
2. When stored under the film, the timber was treated with whitening composition "Mikout".
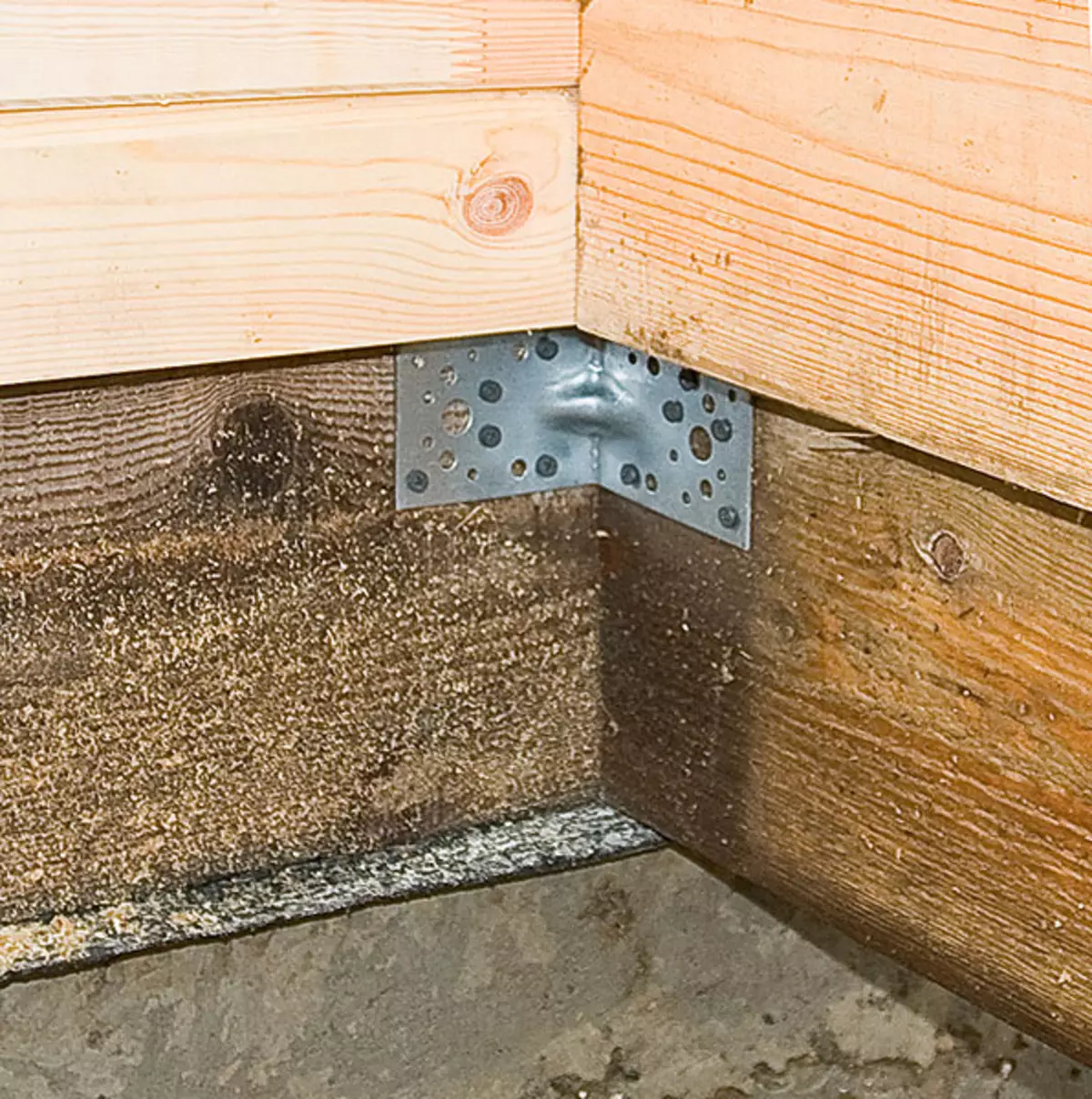
3. Bursts in the corners were combined with steel corners and self-drawing, they were spliced in Polbrus along the length.
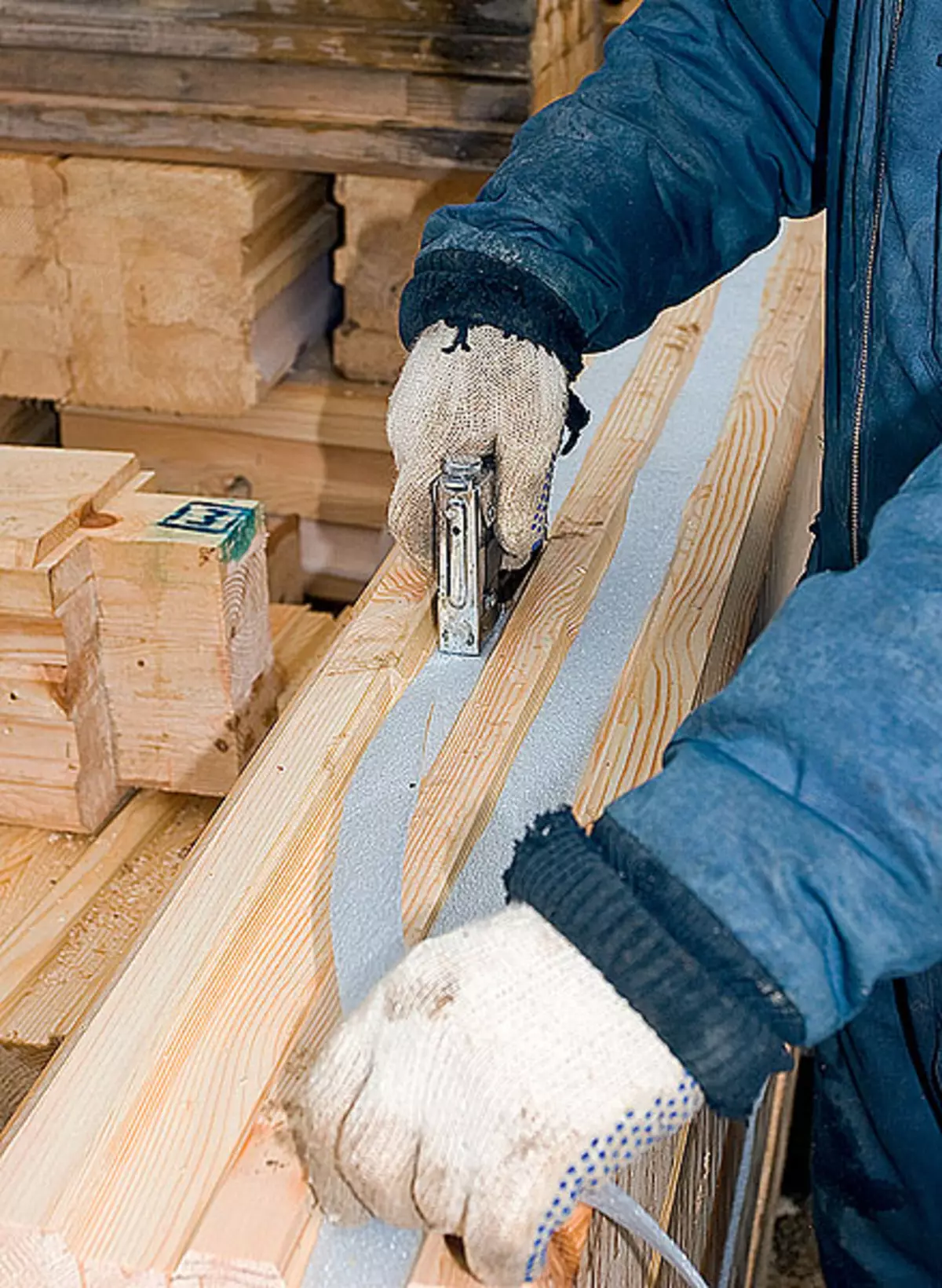
4. To make an unproduced longitudinal connection of the bars, the top grooves were laid with a band-based polypropylene with a thickness of 3mm, fixing them with a stapler.
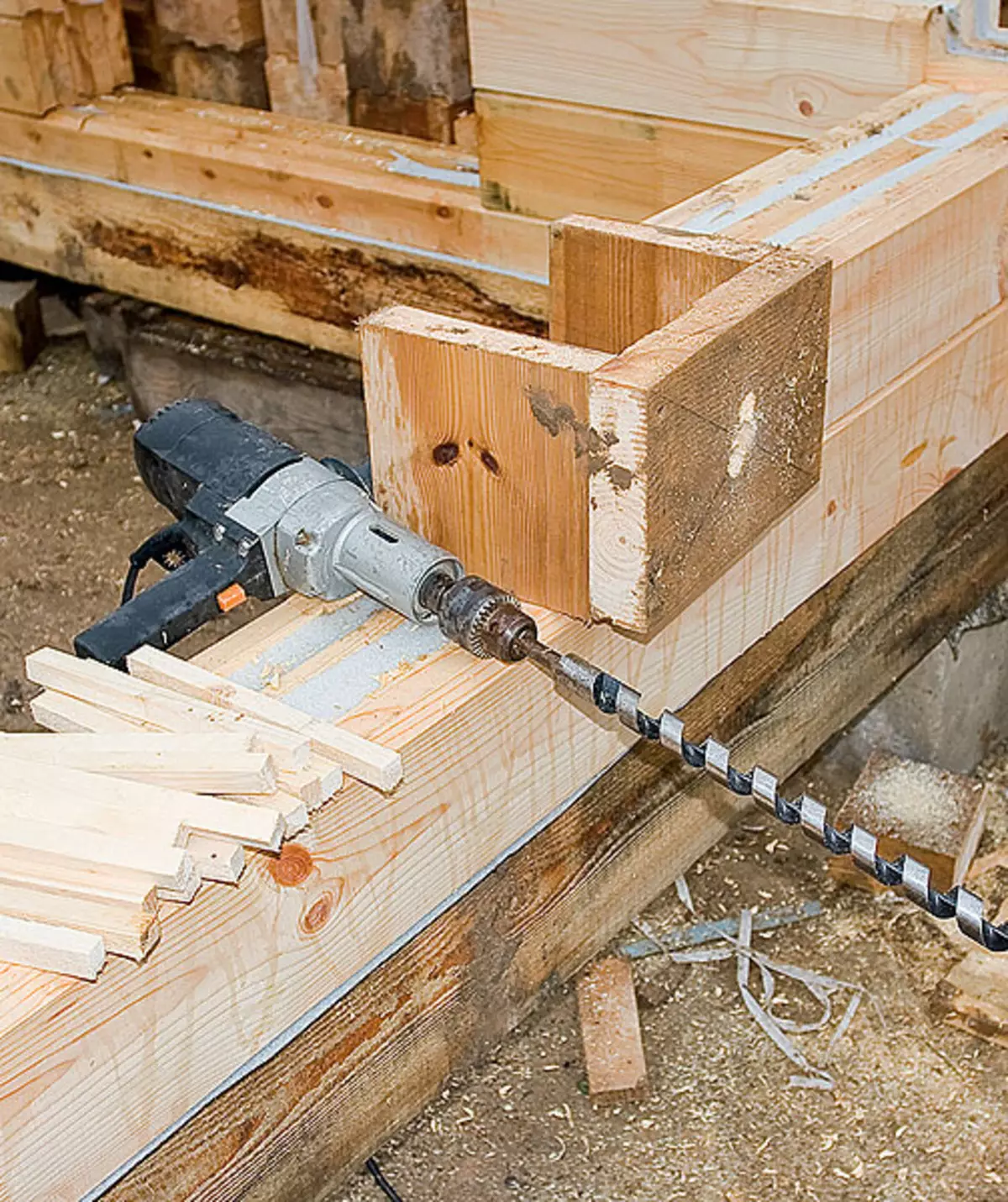
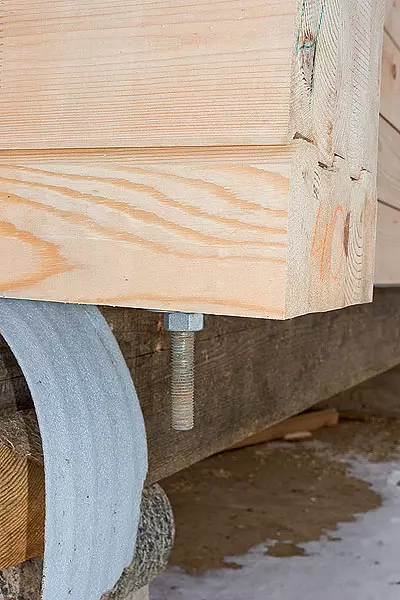
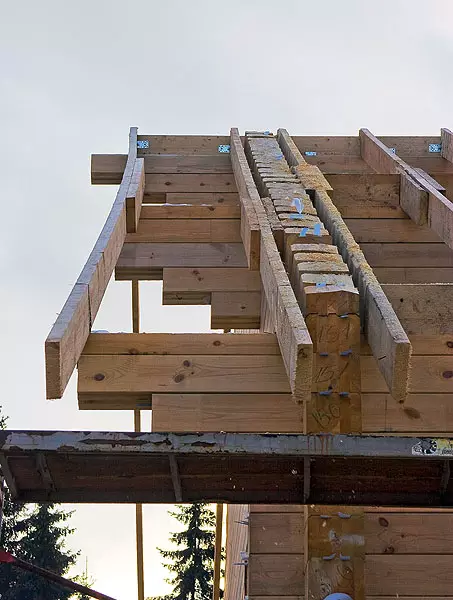
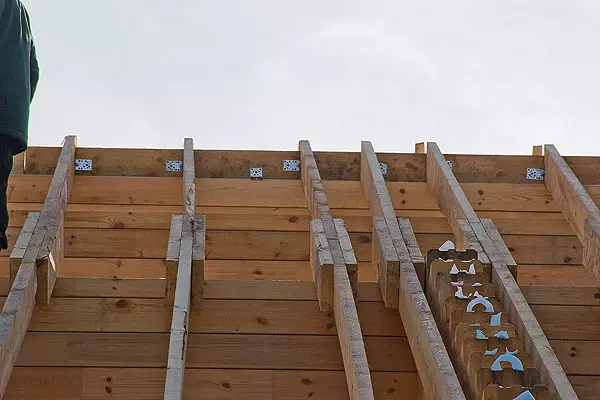
5-6. On the distance of the entire assembly of the house in the releases, using the conductor (5), the holes drilled through which the metallic studs (6) later stretched.
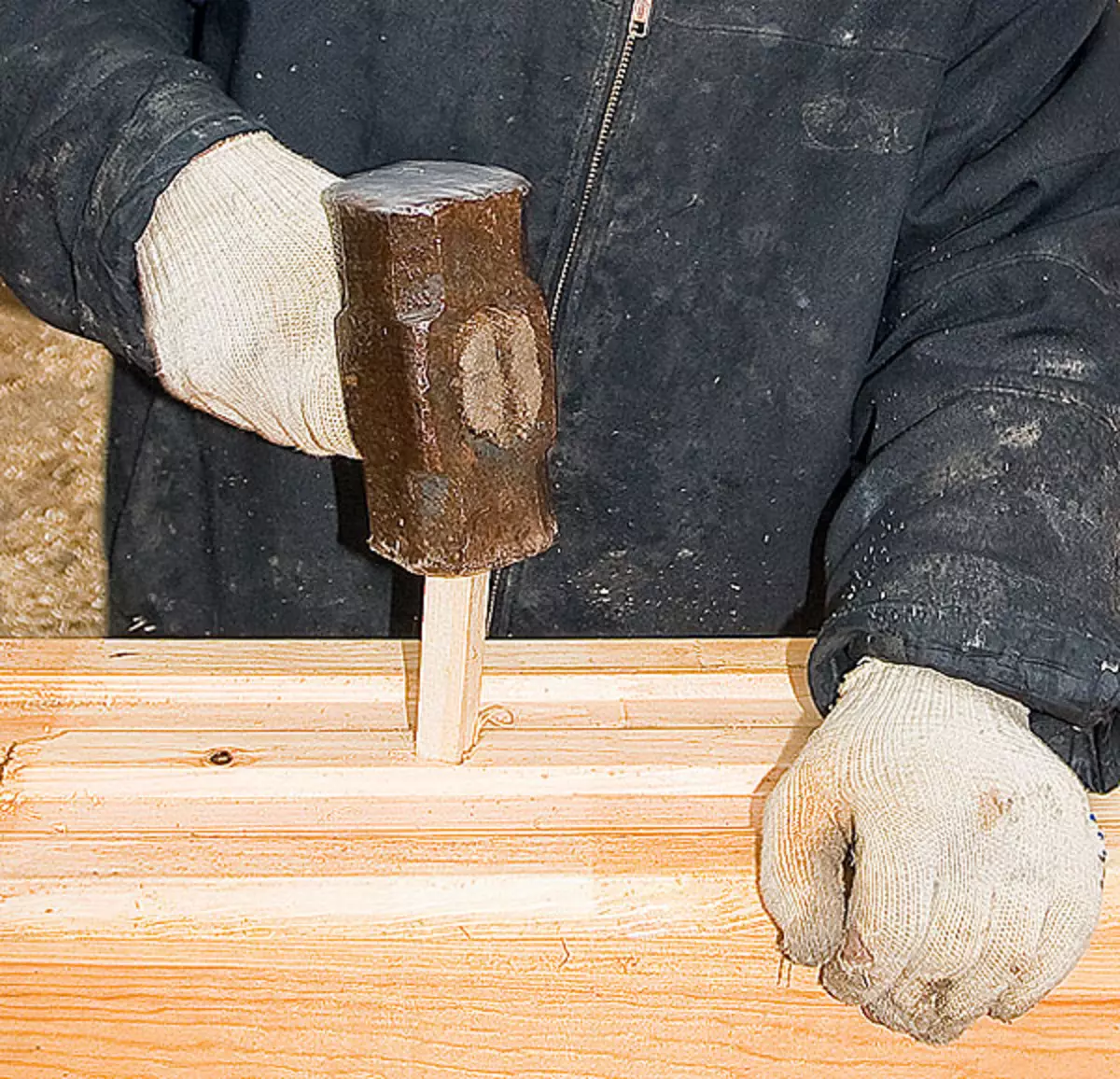
7.The Square wooden brazed (30mmm) was used for the vertical closets (30mm), they were driven (slightly combed) in advance drilled with 1-1,5m opening increments.
8. Sneiseless autumn weather forced the builders to hurry: from the moment of the start of the "Siruba" assembly passed only 5 days, and they have already erected almost completely walls of the first floor.
Pull-dying
The technologies of the construction (more precisely, the assembly) of the walls from the glued bar there is an excellent set. Than just not offered to connect the bars vertically - from "delay" (large screws with turnkey head), twisted in the holes previously flashed in a checked order to steel galvanized pipes. The threaded studs are used to make it use, they are installed in through holes drilled in the wall every 1,5m (by the way, it significantly increases the cost of the construction: the cost of spur - 400-1000 rubles. For 1Pog). But even at the same time there is no consensus: some are offered to push with studs at once the whole wall on top of donomis, others prefer to attract each bar individually with washers and nuts (again cost!). Isv and this motivate the fact that the tightening of the BRUSEV, firstly, makes the house more durable, and secondly, regulates his shrinkage, reducing it to a minimum.
However, this method has both opponents who substantiate their position in that on metal, which is laid in the walls, protecting heated residential premises, under certain conditions there will be condensate capable of bringing the waterproof in the holes. As for shrinkage, you can only reduce its mechanical component. Ana shrinkage as a result of drying the screed does not affect at all.
Scheme of a fine-breeding foundation
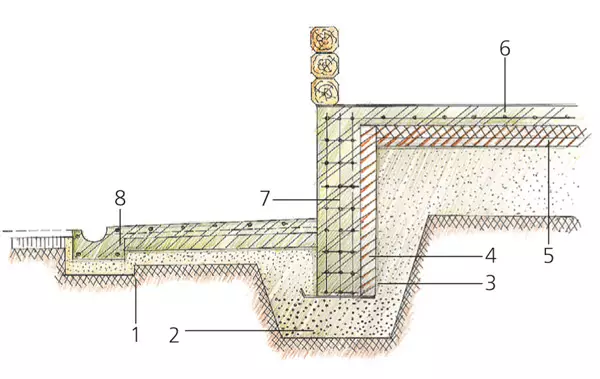
2.Remed by a large sand layers of 150mm
3. Blank PVC
4.Penopolistic 50mm
5.Penopolistic 100mm
6. Monolithic plate
7. Fundament
8.Ontility (bias 5%)
For the sake of fairness, it should be noted that some builders do not use any fasteners at all, and the log house holds only at the expense of "cups", grooves and spikes. This is another extreme.
We conducted a survey of specialists on the topic: "Where did the glued bar with stiletto beeps come from?" As a result, two hypotheses were signed. The first: technology was copied at Finnish house-building. In our opinion, it is unlikely, because the Finns are mostly tightened with studs only issues. The second: invented her domestic specialists at the dawn of development of the production of their own glued timber - special equipment for drying and gluing, nor for the manufacture of grooves, and even more so "cups" were not at their disposal. Well, how else to assemble the twisted bars together? Tighten not only releases, but also the whole wall! Well, quite plausible hypothesis.
It would not be to resort to the proven grades of the cutting technology on wooden impudations, thereby bringing the use of metal rods to a reasonable minimum. On the construction of Lapland House (Russia) at home on such technology and will tell this article.

| 
| 
| 
|

| 
| 
| 
|
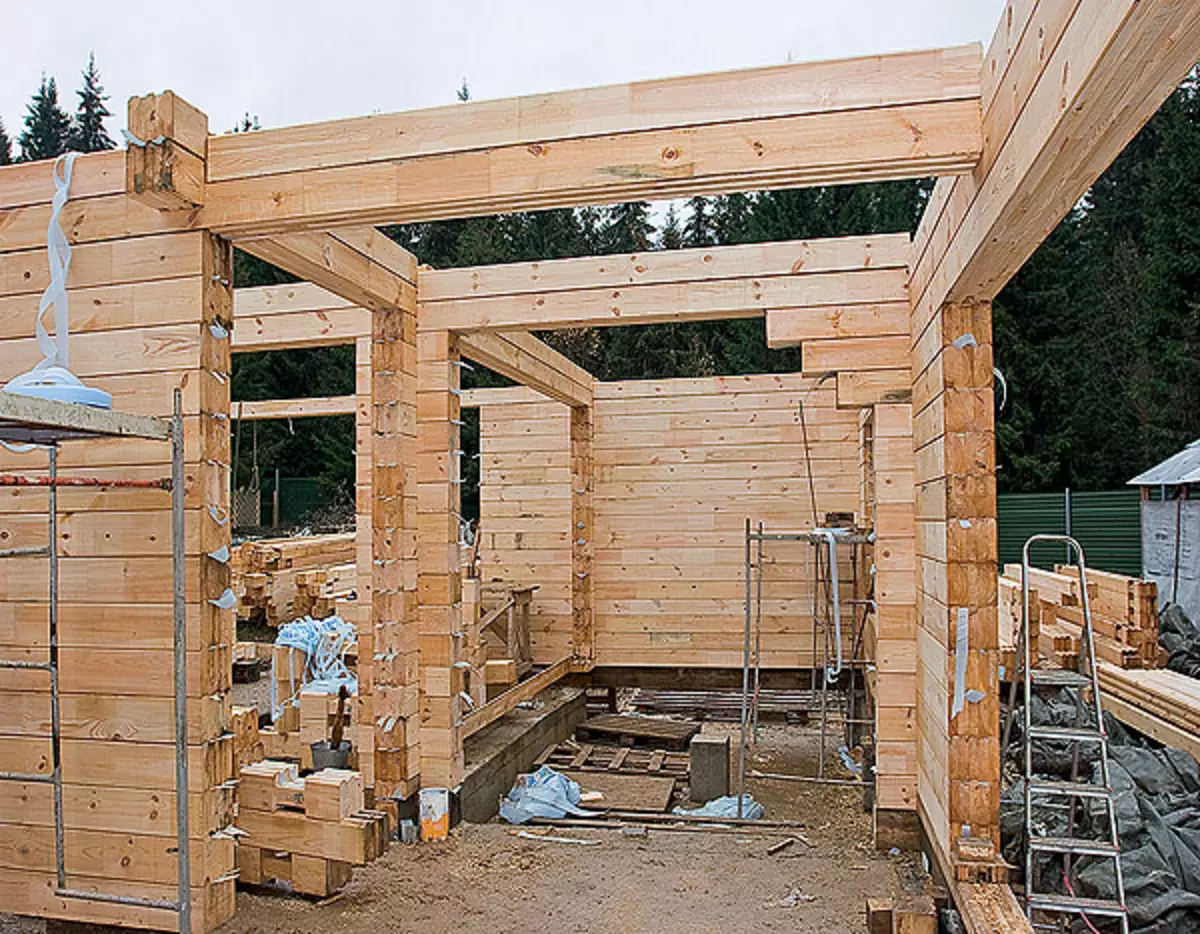
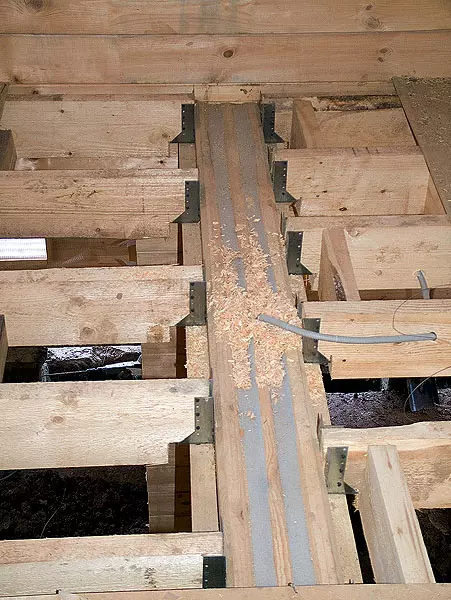
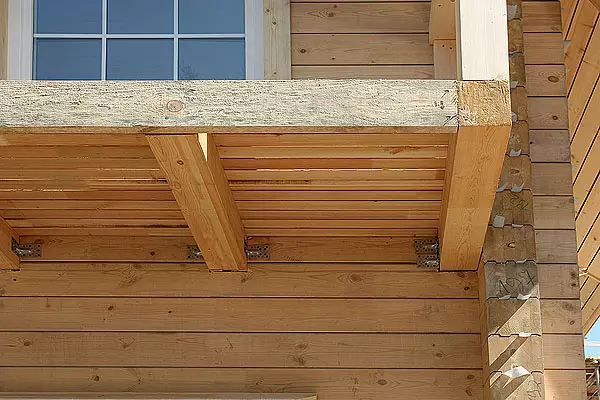
9. The first overlap of the first floor of steel beams made from a dual wall timber. The center of the house is a support for them "pillars", assembled from segments of glued timber without applying metal elements.
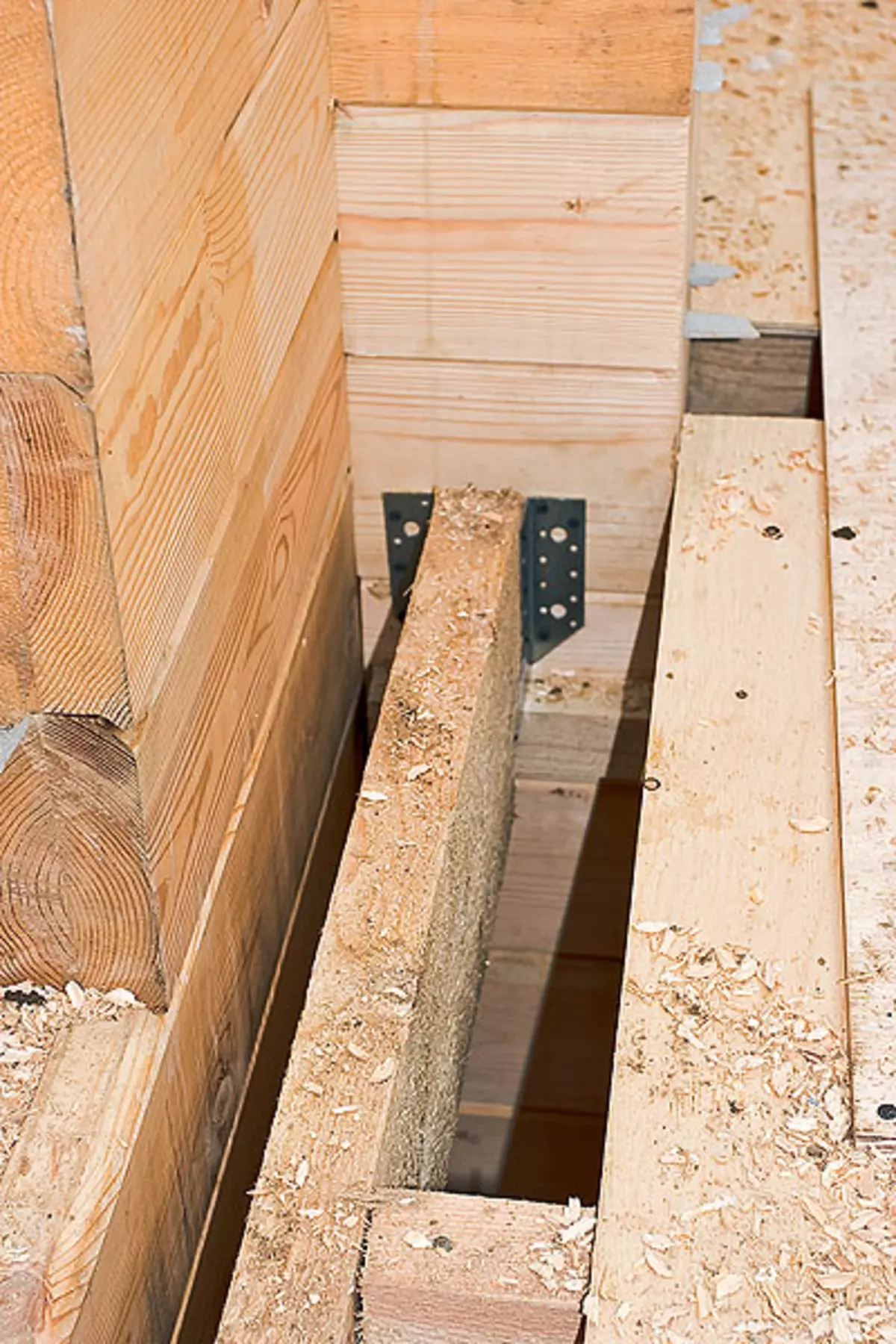
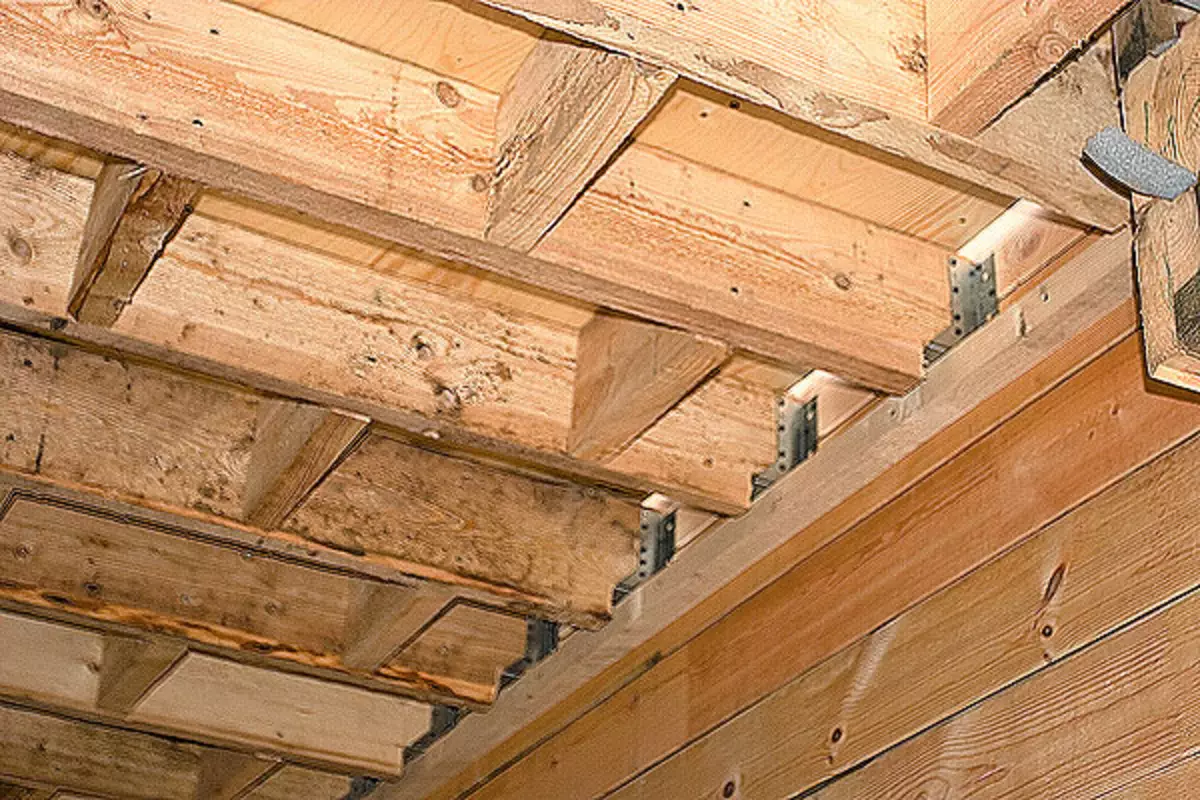
10. When mounting the overlap of the first floor of the beam with a cross section of 20060mm, was laid on the edge on a timing attached to the wall with a cross section of 7050mm, and then for stability were fixed using metalloelements.
11. The ceiling balkes were mounted in 600mm increments. To predict the stiffness design, the spacers made from the bar of the same section as the beams were established between them. Their step ranged within 600-1200mm: what he is less, the tougher construction. Flooring from plywood 24mm thick completed the shield device.
12.Frontons of the attic floor - samstyle (more precisely, self-supporting): they are stacked from the bar as a direct continuation of the end wall of the first floor.
13. The fact of the roof itself created the so-called fowl: in the length of the "log house" increased, gradually increasing the releases of the bar. This technique is used not only in decorative purposes, it allows you to increase the area of the support of the skate runs and the removal of the roof.
14. Summer frontones were combined with three runs from a cohesive timber. Moreover, the auxiliary runs are much more powerful mainly, which is dictated by the calculations for strength.
15. Strengtic design created from a bar of 20060mm. For its installation on the ski run, the bar was laid, to which the rafters attached the corners. The rafting legs soldered over auxiliary run.
16.Things of rafters during the shrinkage of the frontons could be extended to the outside, to the upper veins of the walls, they were attached to moving, using "clamps" made from a steel galvanized strip 2mm thick.
We build the foundation
It all started with the fact that the future house was made by lodging from settlement communications (water supply, sewage, electricity).
The foundation of the building is finely breed. For its device, under the future external and inner walls, the trenches in a depth of 90 cm, at the bottom of which staged a sand-gravel pillow with a thickness of 30cm. Next over the trenches, a wooden formwork was installed, and along the future ribbon from the side facing the house, the plates of extruded polystyrene foam 50mm were laid. Then the framework was then built from the reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm and, using the M300 brand concrete, the foundation tapes of 300mm thick (the height of underground and overhead parts - 500-600mm). At the same time, the reinforcement issues left over the surface of the tapes, which later tied the frame of the monolithic plate.
It was made like this. First, the space between the ribbons was covered with soil, and then the sand layer 300mm (and that and the other thoroughly compressed). On top of the sand placed a layer of waterproofing and two layers of the plate of extruded polystyrene foam. After that, the reinforcement road grid was laid (wire-6mm, the size of the cells - 150150mm) and from the M300 brand concrete cast a monolith plate with a thickness of 120mm. When pouring into a concrete around the perimeter of future walls "deposited" cuts of the steel corner with a 75mm shelf (the horizontal regiment of the corner is in concrete at a depth of 37 mm, the vertical one rises above the surface of the plate), which subsequently attached the strapping bar.
Immediately after that, "insulated" breakfast was poured. The technology of its creation is very similar to the method of manufacturing the plate just described, with the only difference that the thickness of the extruded polystyrene layer was 50mm.

| 
| 
|

| 
| 
|

| 
| 
|
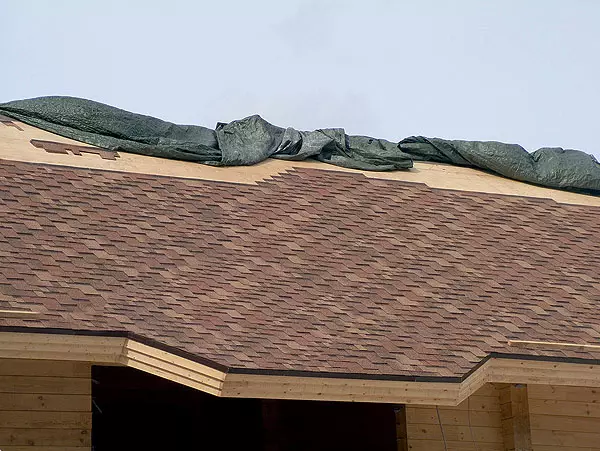
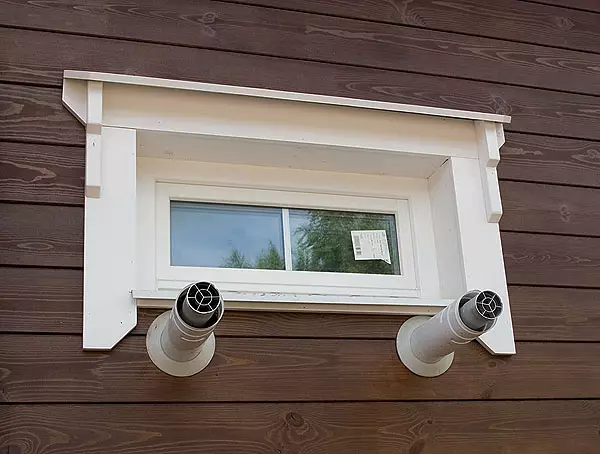
17-18. Projectors and builders gave tribute not only to old traditions, but also modern technologies: the house is crowned with a warmed ventilated roof (17), covered with soft bituminous tiles (18).
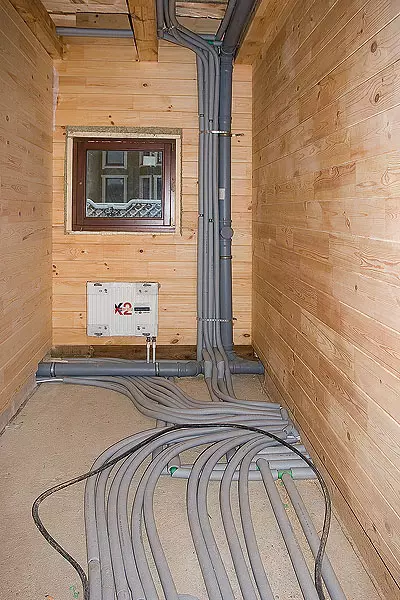
19-20. The electric separation was used the NY cable placed in the corrugated pipe (19). It was laid in frame structures and floors, as well as on concrete overlap (20).
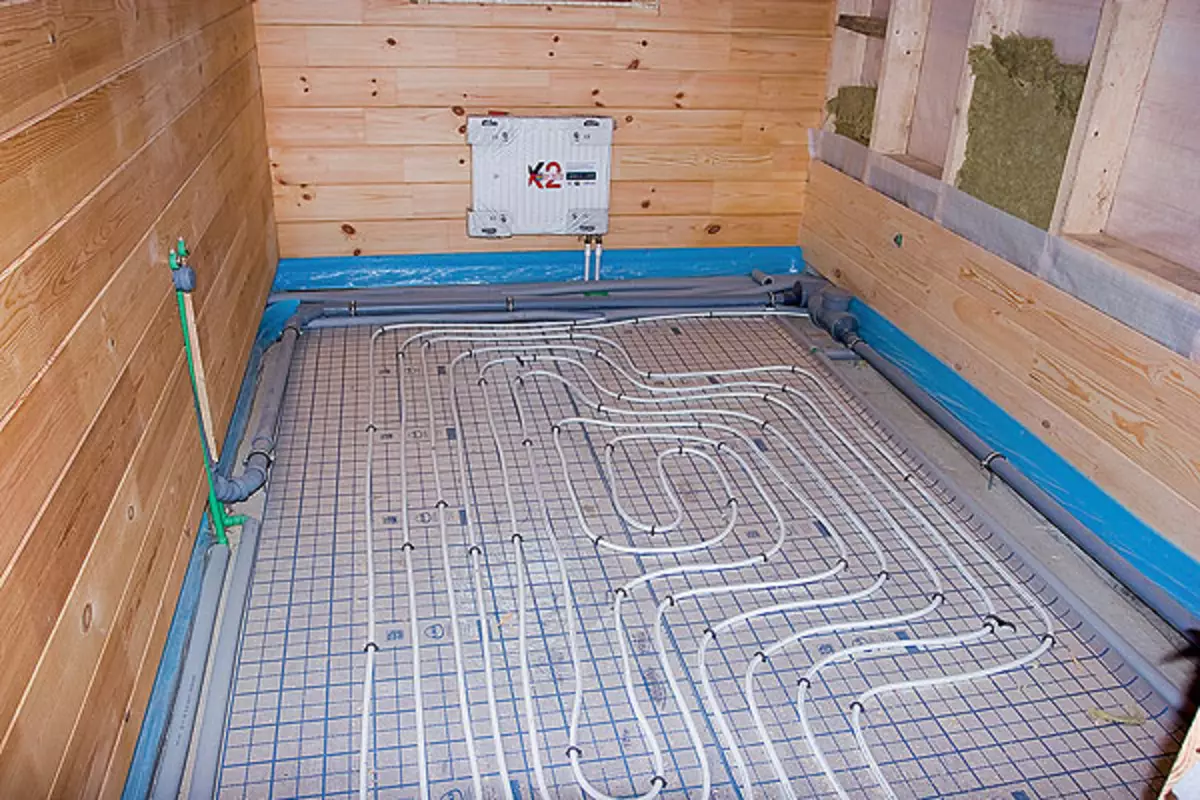
21. By the desire of the owner in most rooms, using metal-and-dimensional pipes, mounted warm floors. Pipes were laid on special plates of foil polystyrene foam 50mm thick and attached plastic brackets to them.
22. The distribution collectors (combs) of warm floors were placed in the special OVENTROP cabinets with a removable lid, made of galvanized steel painted in white.
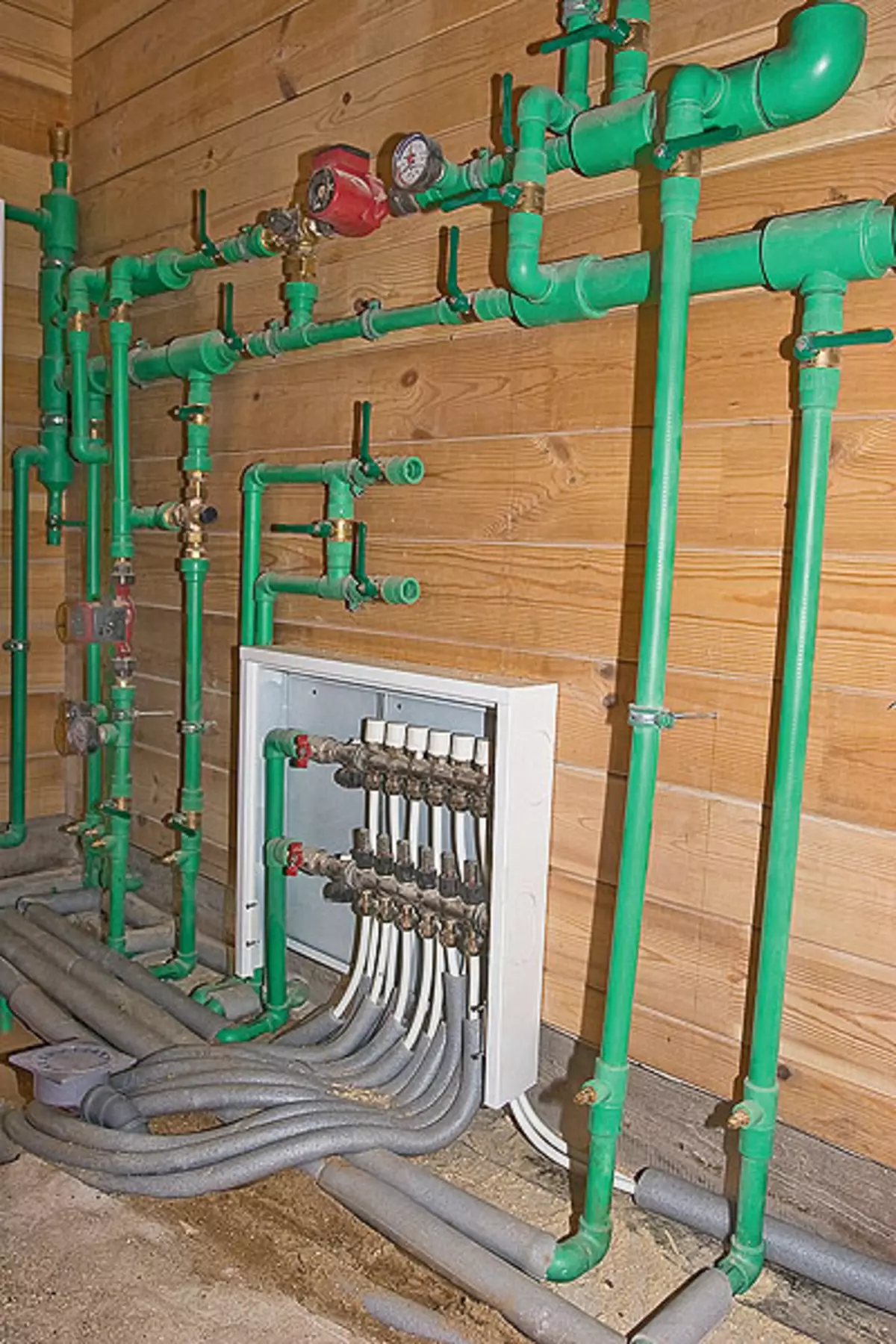
23. In the wiring of the hot water supply system, as well as for supplying the coolant to wall convectors, plastic pipes Fusiotherm (AquaTherm) were used, which were insulated. Later and their, and the electric cabbage hid a cement screed.
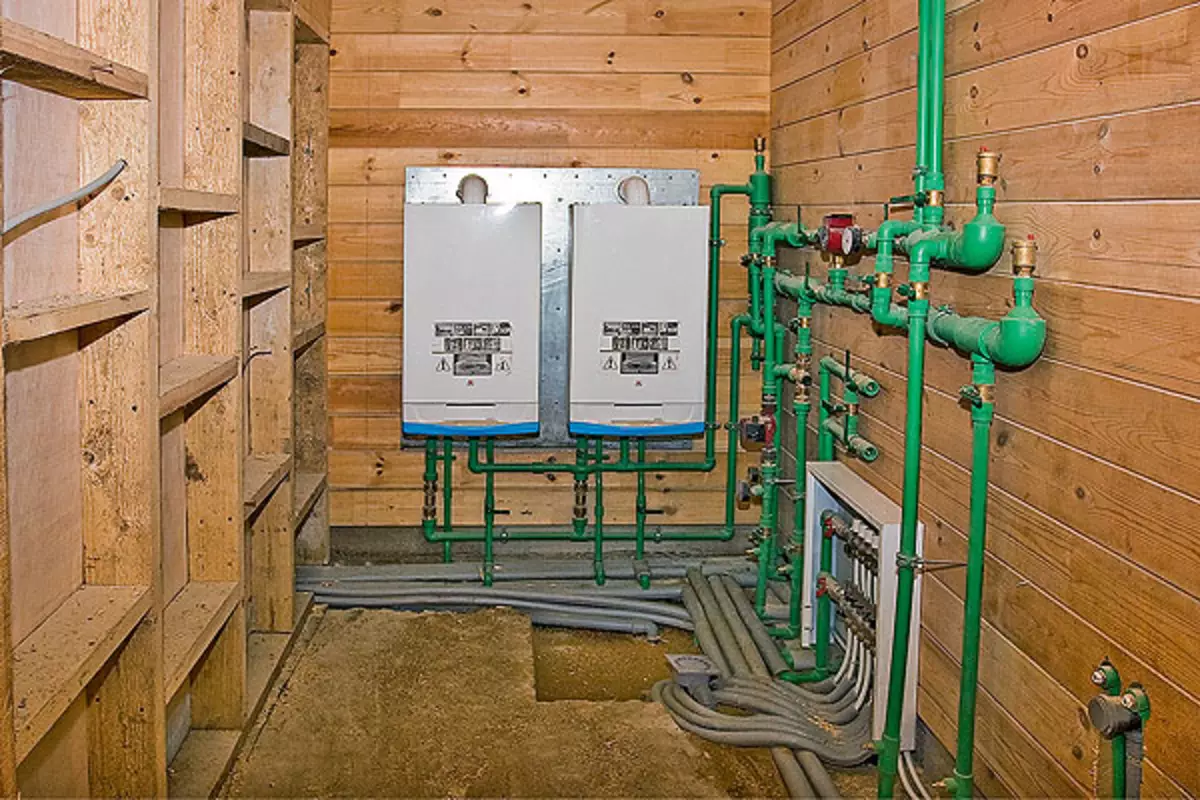
24-25. The "heart" of the heating and hot water supply systems were two wall gas boilersaunier duval (24), "exhaust" from which the wall of the house (25) was removed. Boilers are working alternately: one is constantly in reserve.
We collect the walls
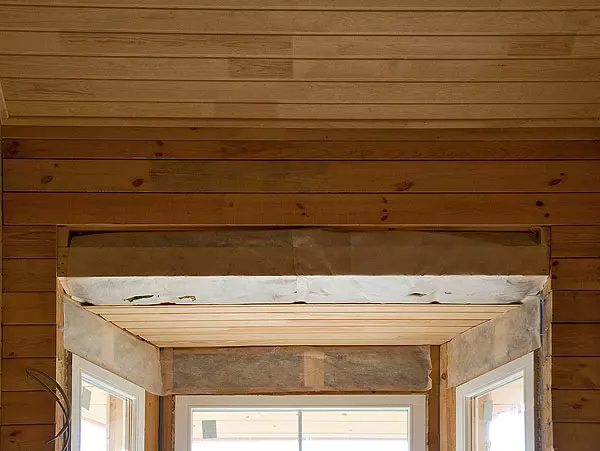
On top of concrete on the perimeter of future walls, waterproofing tapes were laid on the perimeter (rubberoid in two layers), and on their strapping with a cross section of 200150mm (made of larch and pre-treated with flame care), attaching it to the corners.
A set of details for the house made from the Angarsk pine (about the process of manufacturing the glued bar.
"IVD", 2007, No. 5) on the Irkutsk Plant of ZBBC "(Russia) according to the project project sent there. On the decision of the host, the timing of this plant was influenced by two factors. First, Irkutsk pine is more dense and durable than pine from the middle strip, it is better processed, and water absorbs less. Secondly, the selected factory is absolutely new, and therefore the likelihood that the sawing technology recommended by the foreign supplier equipment, drying and gluing is fully respected, very high. The calculation is precisely for this, according to the owner, fully justified.Avot on the construction site did not cost without wasting. The bar, brought before the construction of the foundation, was folded on the pads in the stack and covered with rain with a plastic film. Ito was a mistake. Summer heat caused an intense evaporation of soil moisture, and a Bar-ventilated Bar became black (according to experts, for the beginning of this process, under certain weather conditions, there are sometimes enough only 1 day, and after 3-4 days, wood can turn in full). Therefore, naturally, it was necessary to treat the whitening composition affected by the "black" part.
Now about the configuration and technology of bars laying. It has a section of 210165mm. The side chamfer was removed on the upper plane and two longitudinal trapezoidal grooves of a depth of 15mm, which formed three wedge-shaped protrusions were removed. On the lower plane, the sharp side edges are left and three grooves are profired: when laying one bar to another two protrusions on the bottom surface are included in the grooves on the top. At the same time, the side edges are based on the skeleton areas of the underlying bar, sealing the gap.
From the use of threaded screeds refused; The exception was the end-to-end studs in the outer releases of the bar wall-data elements are quite far away for the "warm" perimeter of the house, so there will be no condensate.
For the cohesive of the vertical bars, the square was used to be made up with a cross section of 2222mm and a length of 250mm- they better slide in a hole drilled in a bar during a shruck shrink. The location of the heated is traditional for log cabins: in the wedges - in a checker, step in one vents - 1-1,5m.
The incomplete polypropylene foam polypropylene was used.
Particular attention to the builders paid the processing of leaving the ends of the bar. Why? It is through the ends in the wood that the atmospheric moisture penetrates, and if they are not processed, they certainly crack. Many builders for such treatment apply PVA glue. But the owners decided not to save and use the acrylic sealant Sikkens (Netherlands).

| 
| 
| 
|

| 
| 
| 
|
26. Made from drywall, the backlight layer diversifies a solid "wooden space".
27-28.Erker performed on frame technology. After installing its windows, applying the products of the company Rockwool, insulated (27), and then weathered on both sides by imitating the timber board (28).
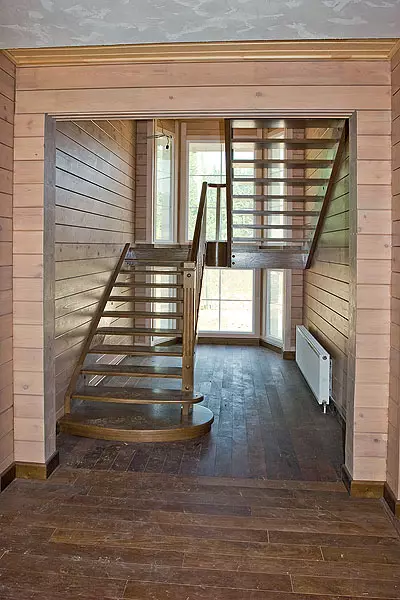
29.Tube ladder made to order.
30. Roofs were powered by a wide clapboard made from Angarsk pine.
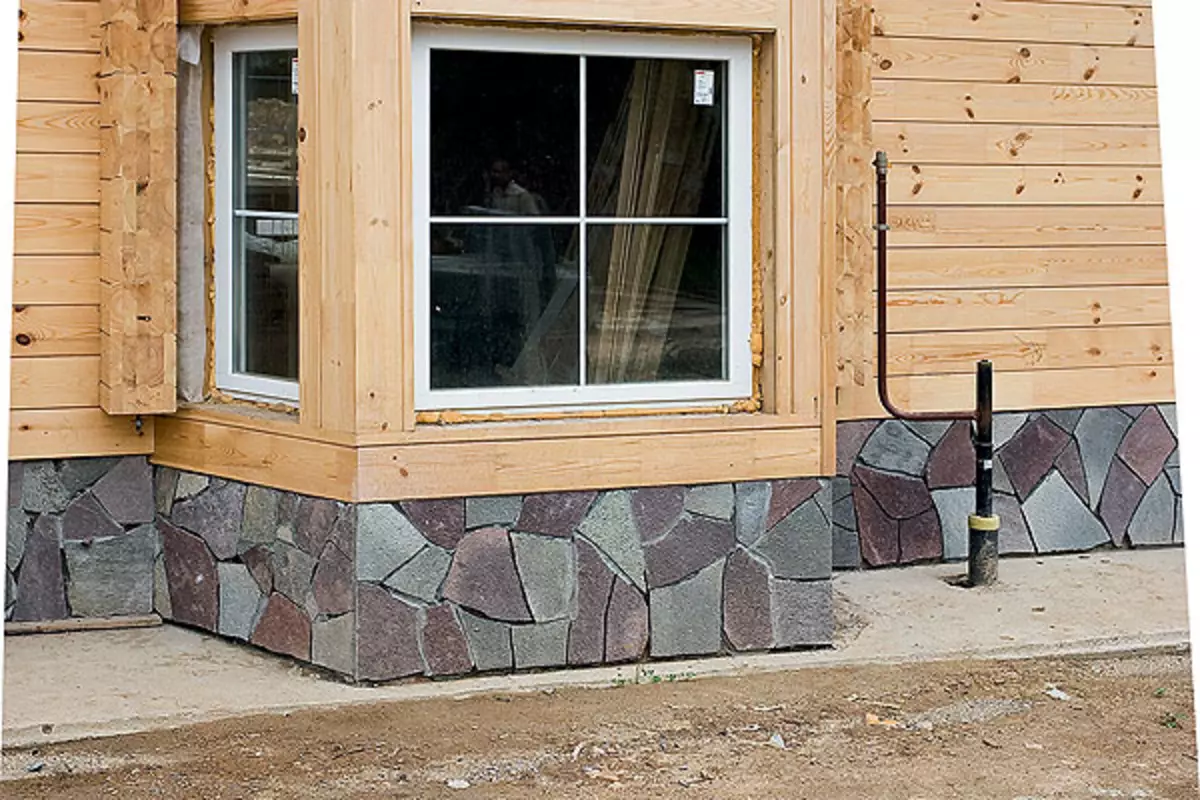
31-32. The present on the balcony is not delayed, its flooring was performed from a larch board laid with gaps (31). The base of the house, the scene, as well as the gardens of the garden tracks were covered in the Ural region of Russia with natural stones (32).
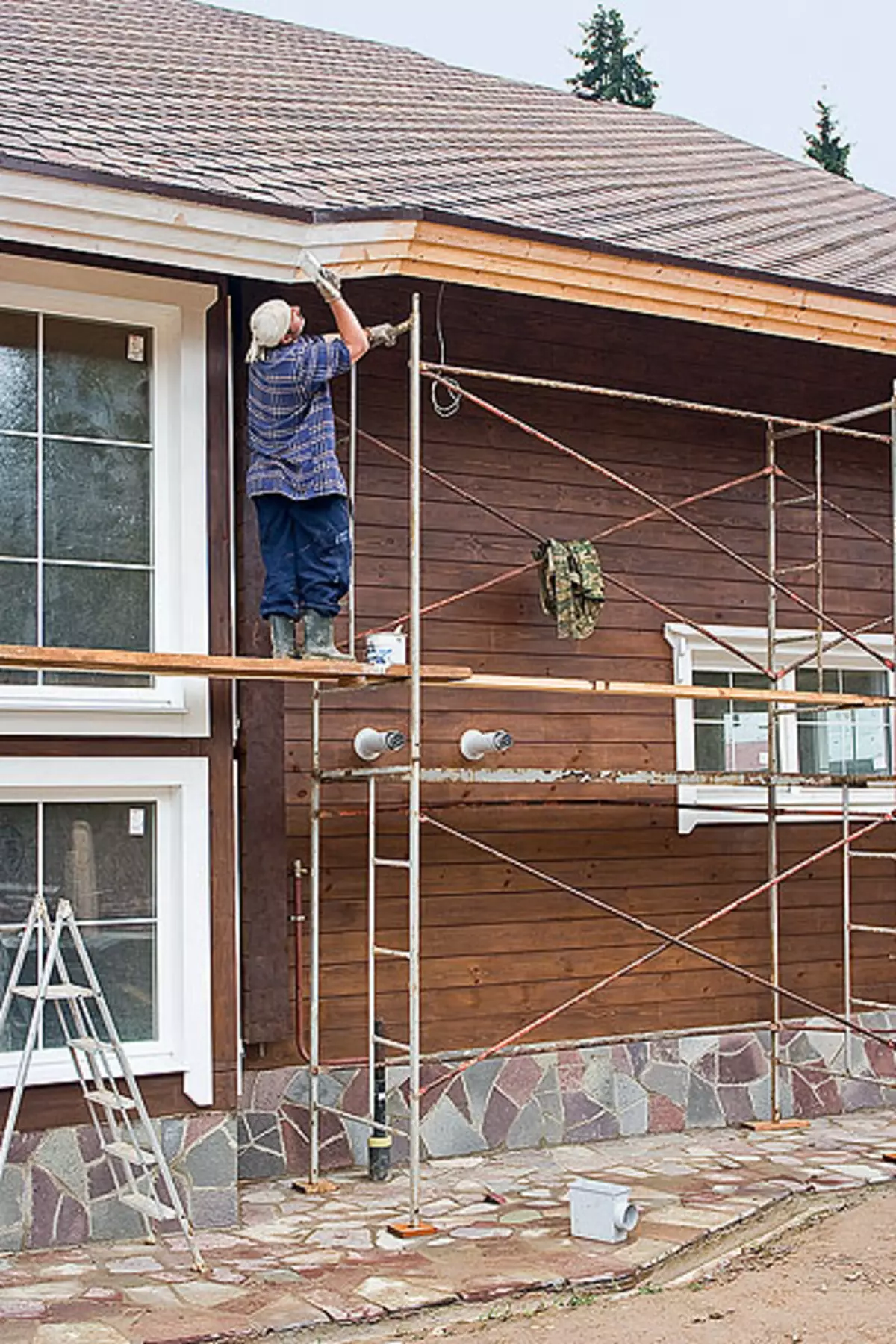
33. The internal finish of the house is located in Spartan. The wooden surfaces were thoroughly ground, and then coated with biolated composition: outside (it is better protecting the wood from the action of ultraviolet), and practically colorless.
Epilogue ... or the beginning of a new story?
You can tell about the construction of this house for a very long time, because the owners received from the builders at their disposal fully prepared and housing, and the part of the selection. Interesting moments during the work there were quite a lot. For example, the process of creating a warmed ventilated roof was so simple and rapid that we decided to describe it in a separate article, which we will offer readers in one of the following log numbers. In this case, for a lack of space, we, perhaps, we will finish this article, providing the reader the opportunity to familiarize yourself with the photographic materials, in detail (it is possible to say - chronologically) illustrating almost all stages of construction and finishing works.
But, as often happens in life, our construction history has not ended. At first, the owners asked the builders to build a canopy for two cars with a small workshop adjacent to him and the Hozblock. Then, when the "complex" was already almost ready for delivery, they decided to attach a small pool to the house. As you understand, we just could not go past this process and we suggest read about it in the next room.
Explanation of the first floor
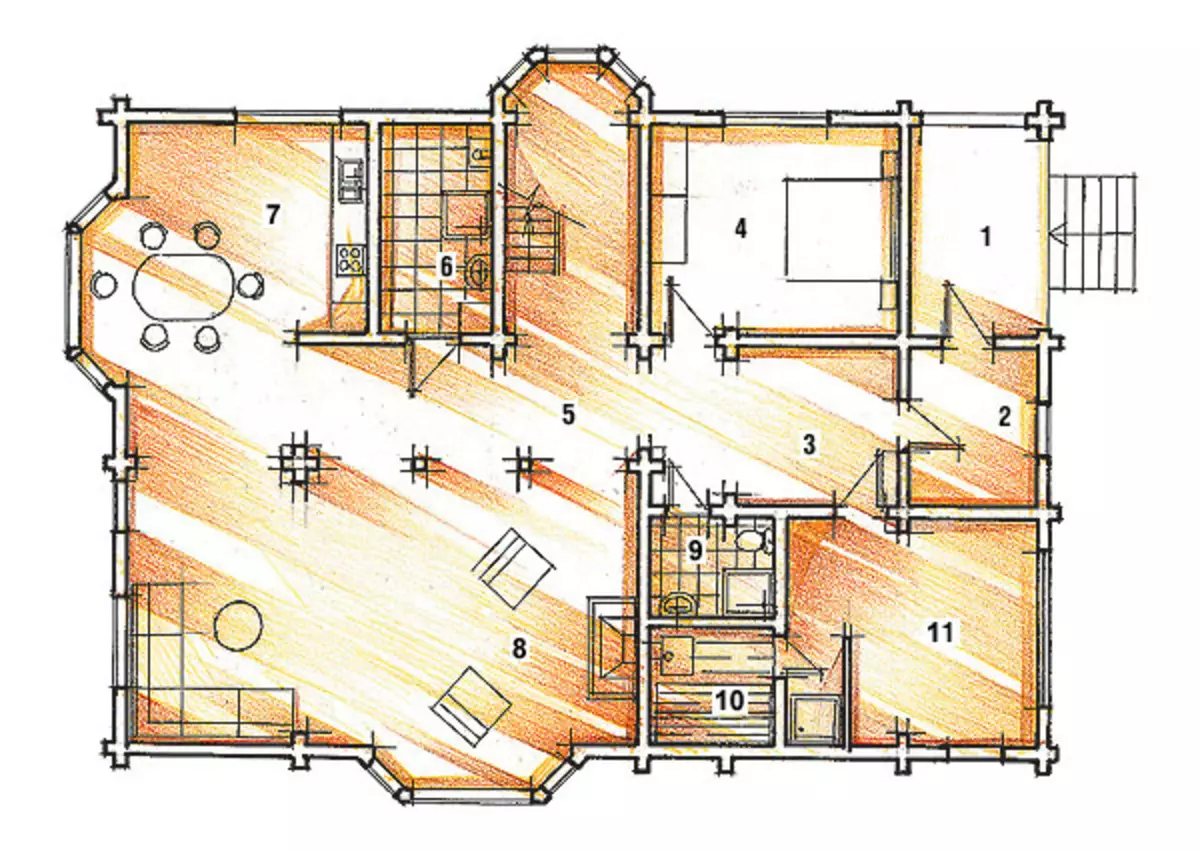
2. Tambour ........................................ 8,3m2
3. Hall ........................................... 12,4m2
4. Bedroom ....................................... 16m2
5. Hall ........................................... 24.7m2
6. Shopping room ................. 7,3m2
7. Kitchen-dining room ............................................ 24.7M2
8. Living room ...................................... 47.3m2
9. Bathroom ........................................ 2.9m2
10. Sauna ......................................... 4,6m2
11. Restroom ............................ 16m2
Explanation of the second floor
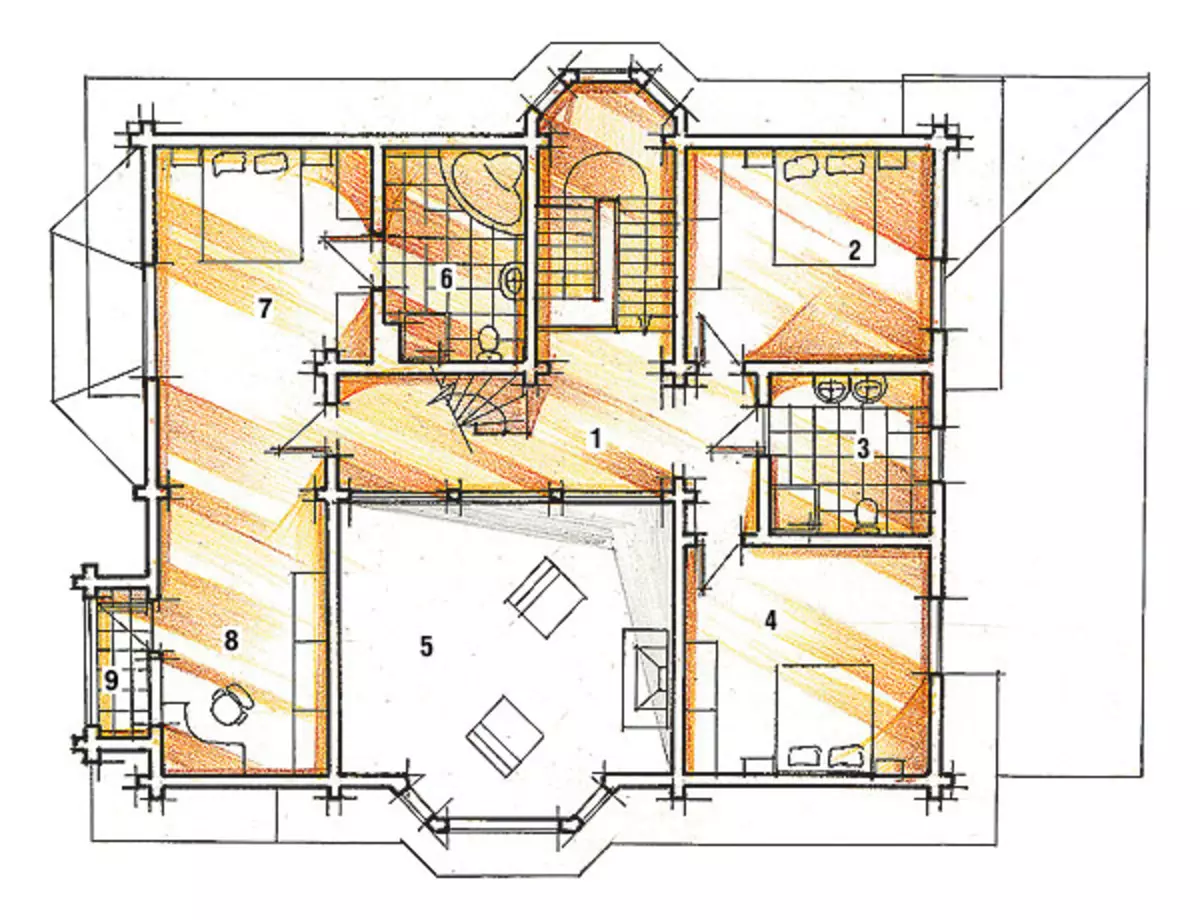
2. Bedroom ..................................... 16,1m2
3. Bathroom ...................................... 8m2
4. Bedroom ..................................... 17,9m2
5. "The second light" living room
6. Bathroom .......................... 9,2m2
7. Bedroom ..................................... 20,5m2
8. Cabinet ..................................... 15,2m2
9. Balcony ....................................... 2.4m2
The enlarged calculation of the cost * construction of the house with a total area of 300m2, similar to the submitted
| Name of works | Number of | price, rub. | Cost, rub. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fundamental works | |||
| Takes up axes, layout, development and recess | 86m3 | 670. | 57 620. |
| Device base under the foundation from sand, rubble | 30m3. | 420. | 12 600. |
| Device of the foundations of tapes, plates of monolithic reinforced concrete | 59m3 | 4200. | 247 800. |
| Insulation of the monolithic slab insulation | set | - | 12,000 |
| Waterproofing horizontal and lateral | 220m2. | - | 79 200. |
| TOTAL | 409 220. | ||
| Applied materials on the section | |||
| Gravel crushed stone, sand | 30m3. | - | 39 000 |
| Concrete heavy | 59m3 | 4500. | 265 500. |
| Hydrosteclozol, Bituminous Mastic | 220m2. | - | 63 800. |
| Armature, Formwork Shields, Heater and Other Materials | set | - | 89 300. |
| TOTAL | 457 600. | ||
| Walls, partitions, overlap, roofing | |||
| Build the walls and partitions from a bar | 48m3. | 4300. | 206 400. |
| Overlapping device | set | - | 62,000 |
| Device of the rafter system | 210m2. | - | 157 500. |
| Insulation of coatings and overlaps insulation | 320m2. | 90. | 28 800. |
| Hydro and vaporizoation device | 320m2. | 40. | 12 800. |
| Bitumen Tiles Coating Device | 210m2. | 420. | 88 200. |
| Swinging sinks | set | - | 27 300. |
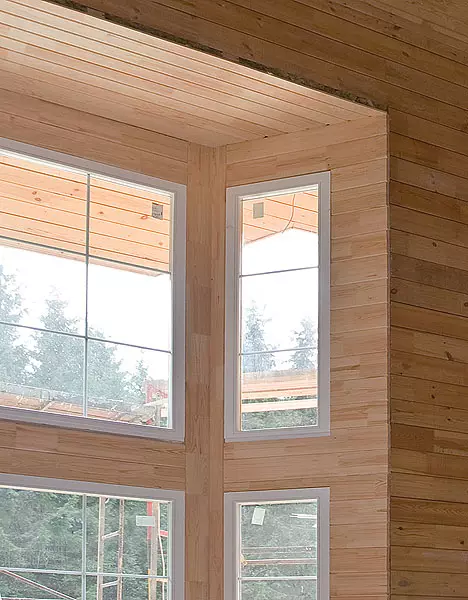
| Installing window and door blocks | set | - | 73 400. |
| TOTAL | 656 400. | ||
| Applied materials on the section | |||
| Mounting kit (glued, sawn timber, other materials) | set | - | 5 140 000 |
| Interwidden insulation (polypropylene foamed), braided, fasteners | set | - | 25 800. |
| Steam, wind and waterproof films | 320m2. | - | 11 500. |
| Insulation | 320m2. | - | 34 800. |
| Bituminous tile, Dobornye elements | 210m2. | - | 109 500. |
| Window and Door Blocks | set | - | 443,000 |
| TOTAL | 5 764 600. | ||
| Engineering systems, finishing works | |||
| Electrical and plumbing work | set | - | 657,000 |
| Finishing work | set | - | 825,000 |
| TOTAL | 1 482,000 | ||
| Applied materials on the section | |||
| Plumbing and electrical equipment | set | - | 1 823,000 |
| Gulf board boards, porcelain stoneware, staircase, plasterboard, door blocks, varnishes, paints, protective compounds, dry mixtures IT.P. | set | - | 1 750 600. |
| TOTAL | 3 573 600. | ||
| * The calculation is made without accounting of overhead, transport and other expenses, as well as profit firms. |
The editors thanks Lapland House for help in the preparation of material.
