We tell about the advantages and minuses of horizontal and vertical channels for the fireplace and the intricacies of their installation.
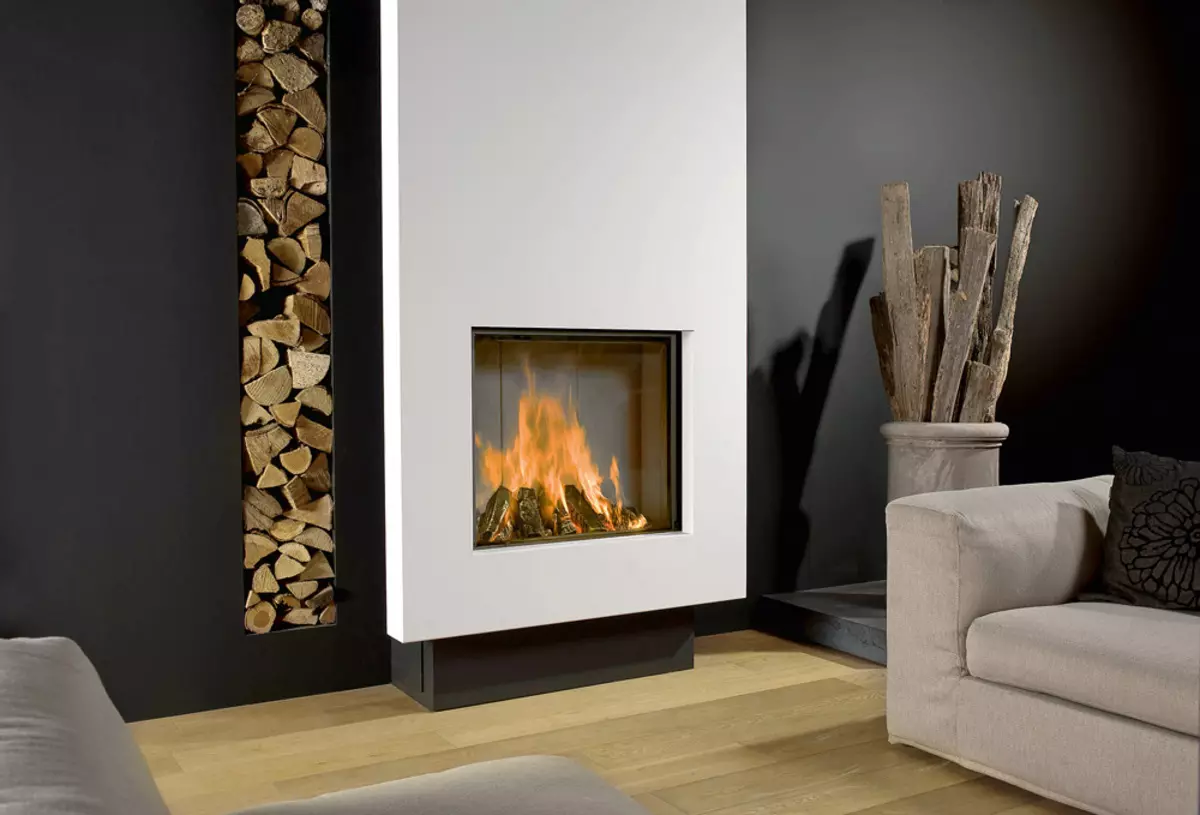


Photo: Blackland Industries
A solid fuel center forms powerful convective air flow and actively affects the composition of the room atmosphere. In a room with a fireplace, a draft, and with tightly closed windows and doors - a stuff. The fact is that the fireplace with a closed heat-winding thermal capacity of 8-14 kW requires at least 40 m3 of air per hour, open - an order of magnitude more. In this regard, the specialists of leading European companies producing heating equipment proposed to serve air for burning from the street.
This solution has opponents that indicate that the fireplace pipe stops working as a hood and does not remove the exhaust air out of the room. This is a fair note, but the current approach to construction involves the installation of the ventilation system in the house, the functioning of which the chimney exhaust is only interferes.
There are two main options for laying an air duct to the furnace, each of which has its own pros and cons.
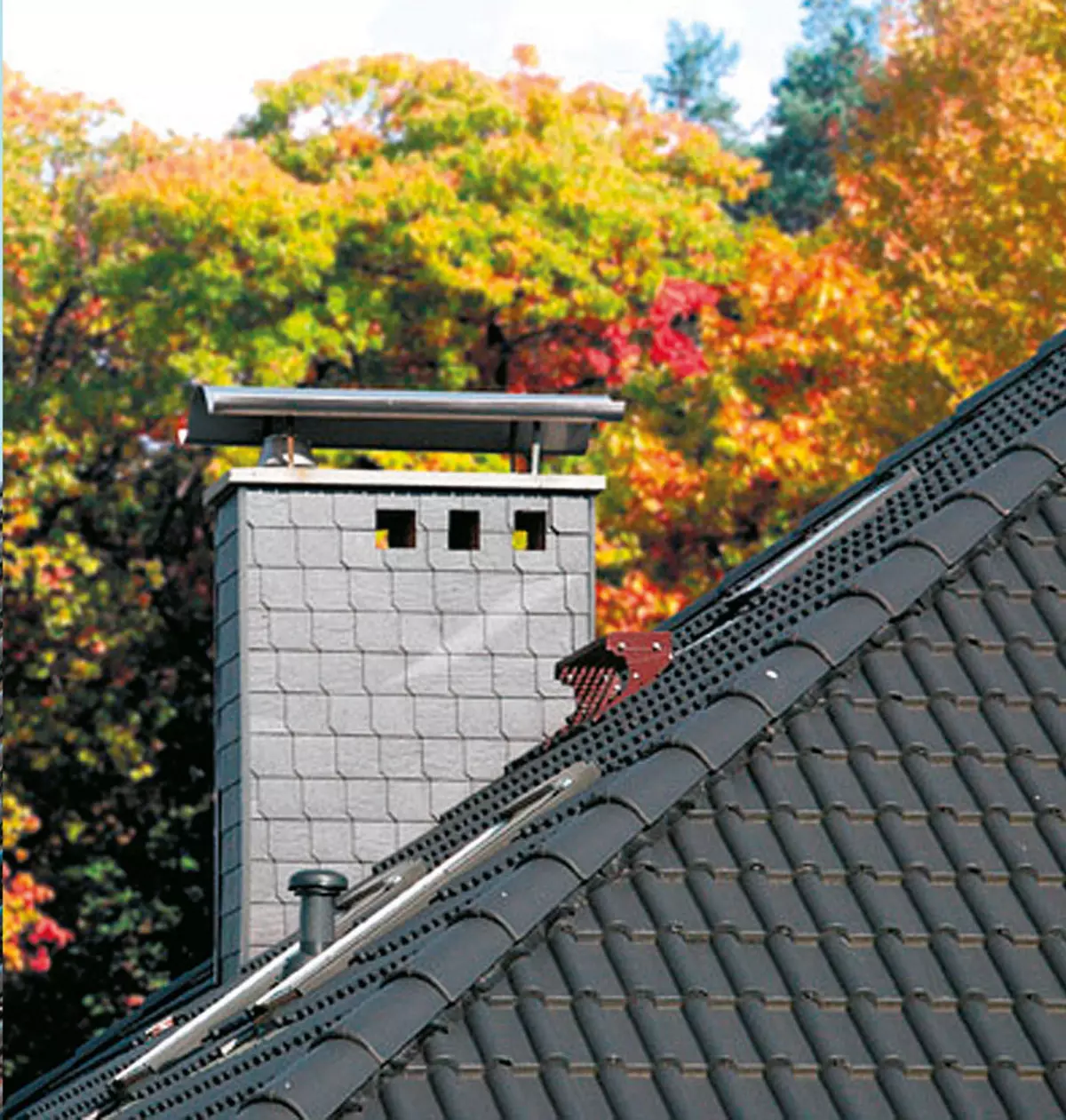

Photo: Schiedel
Horizontal duct for fireplace
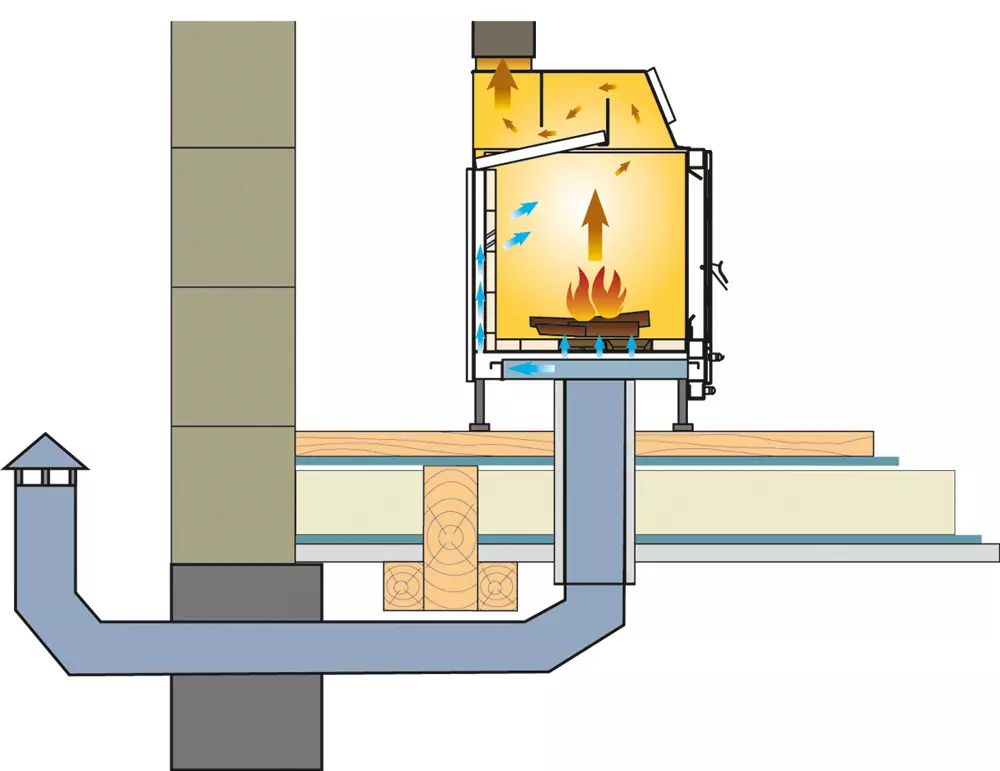
The air canal can be laid out through the underground, while the passage through the overlap must be insulated. Visualization: Vladimir Grigoriev / Burda Media
The horizontal channel makes sense to provide for the design of the building. The air duct is paved along the shortest path to the outer wall in the thickness of the first floor overlapping or in the underground space and output through the base. The channel is best done from a thin-walled stainless steel pipe or an aluminum corrugation with a diameter of 100 mm. When laying inside the design of the draft floor (in the screed, between beams or lags), the pipe must be insulated with basalt cotton and enter into a steel or aluminum casing. This will avoid the formation of condensate on its outer surfaces, referring and cooling the floor. In order for the inlence of the incoming flow less depended on the direction and strength of the wind, it is necessary to provide a vertical portion with a height of about 0.5-1 m. In addition, the pipe should be equipped with a headband with an umbrella and a metal mesh from rodents.

The air duct is connected to the nozzle located on the bottom of the furnace. Photo: Edilkamin.
Specialists are not recommended to supply air from the underground, because there is always a risk of tipping the thrust, in which the sparks will fall on the draft floor boards and combustible insulating materials. In addition, it is possible to penetrate the house of unpleasant odors from the underground.
Vertical air duct
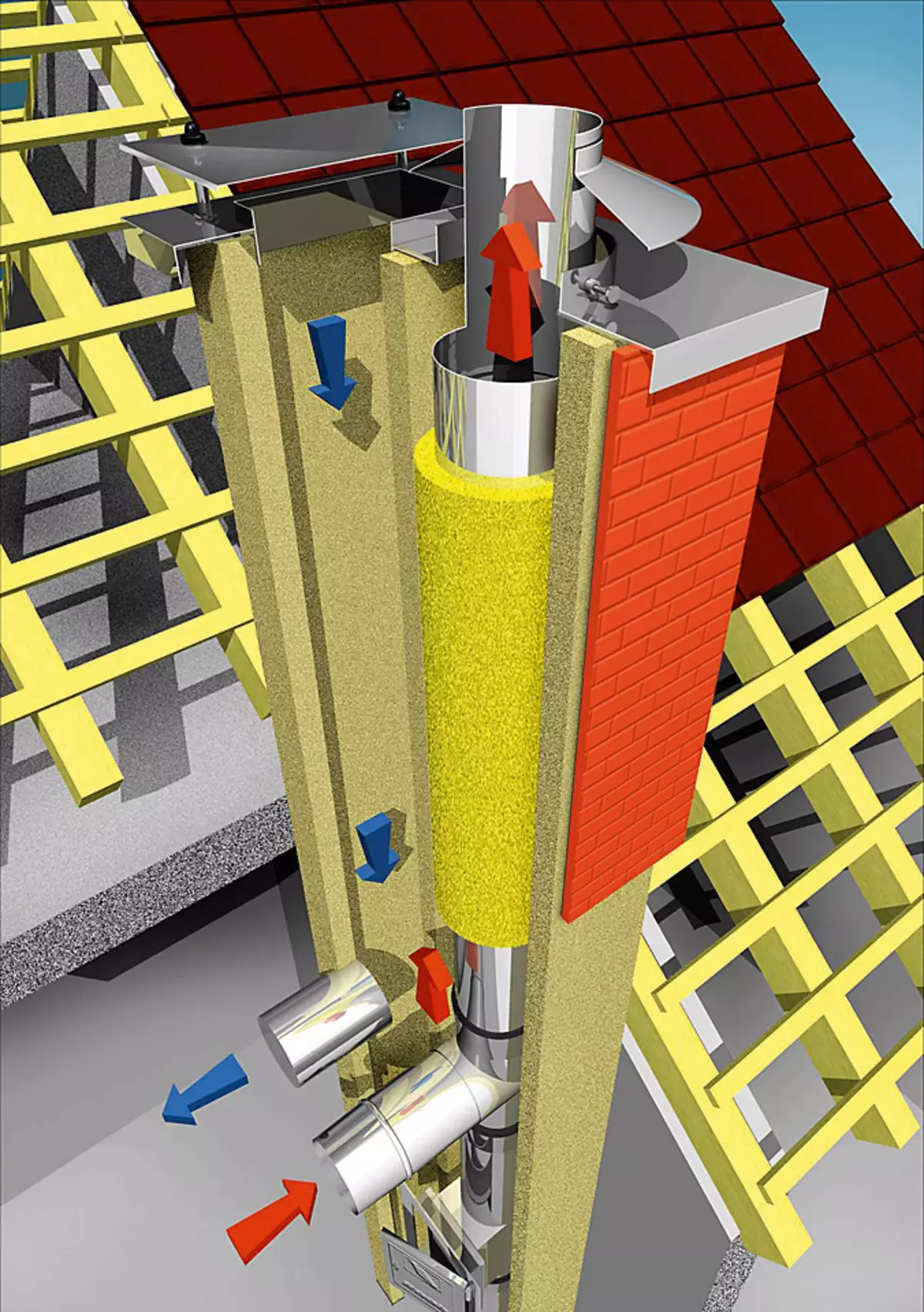
Some chimneys have a second channel, which can be made in suction. However, with a high length of the pipe (more than 5 m) and a significant difference in temperature between room and street air, melt a fireplace and to adjust the craving in the pipes will not be easy. Photo: Raab.
The vertical channel is somewhat easier to install. It is parallel to the smoke tube inside the general box. A double-circuit insulated tube with an internal diameter of 100 mm from galvanized steel is suitable for the channel, which will serve at least 20 years, and then it is easy to replace it. There are also ready-made chimney systems with a supply channel, such as Schiedel Uni (ceramic pipes in a slotted concrete casing) or RAAB LB LAS (stainless steel double-circuit tubes).
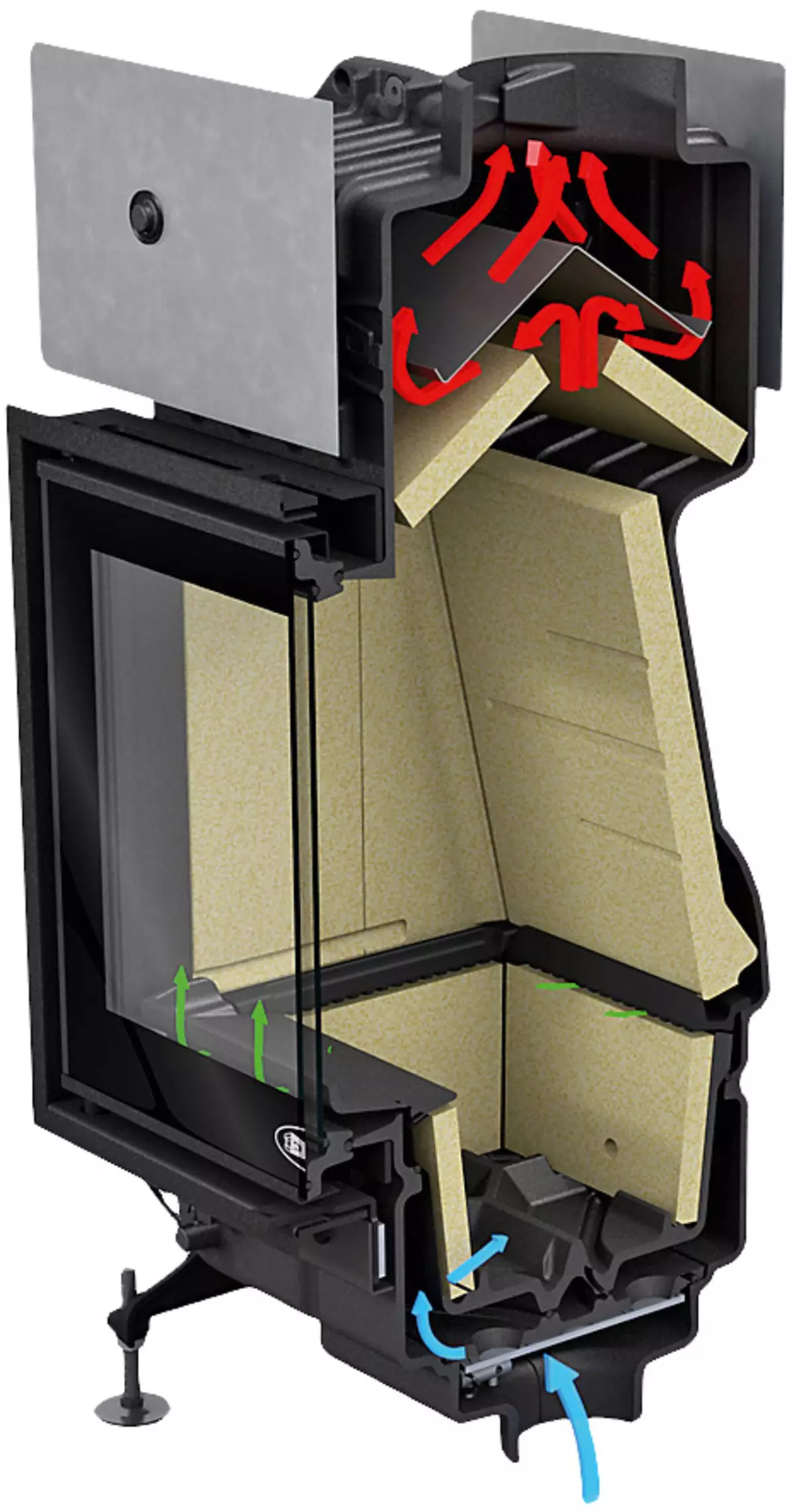

Air flows inside the furnace should be directed in such a way as to ensure the most complete combustion of fuel (it increases the fireplace of the fireplace) and prevent the air pollution to Soap. Photo: DovRe.
Note that the vertical channel is suitable only for sealed furnaces with an inlet nozzle equipped with a damper (if you simply output the air duct into the room next to the focus, it will work as an exhaust). Melt the fireplace with a fully closed flap, and open it (at the same time closing the furnace door), only when the stable thrust in the chimney occurs. In general, vertical systems are more capricious and in them quite high the likelihood of traction violation, as well as an increase in the amount of condensate in a nearby chimney due to the cooling of the last street air.
Cold air from the street lowers the temperature in the furnace. As a result, the firewood burns not completely, the fireplace gives less heat, and the chimney and the glass are faster than polluted. Solving this problem helps the survival chamber with a catalyst.
Knot docking
Many modern fireplace furnaces (and steel, and cast-iron) are optionally or regularly equipped with a connector for connecting the supply channel. Such, for example, the models of Romotop Heat, Kratki Basia, La Nordica Focolare.
The nozzle is necessarily equipped with a throttle valve, which allows you to adjust the combustion intensity. The method of supplying air depends on the design of the furnace - the flow can be directed to the grate zone, to the central part of the furnace or at the same time to the cooler and in the injectors of the shoes (the last option provides the most complete combustion of the fuel).
If the furnace is not equipped with an inlet nozzle, the horizontal trim channel is equipped with a module with a damper and remove into a room under a fireplace or in front of its facade, as close as possible to the air intake holes. At the same time, the system provides air supply not only for burning, but also for a submersion in ascending warm streams from the walls of the unit.
