About acoustic issues by simple and affordable language. What is acoustic comfort. What is the nature of sound. How to enjoy music and do not interfere with neighbors.


Photo V.Nepledov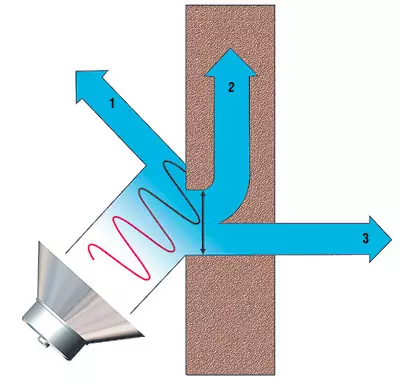
1 - reflected;
2 - absorbed;
3 - past










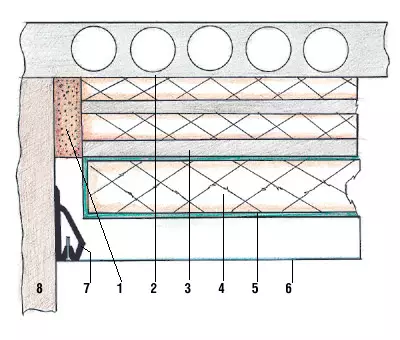
1 - Gasket "Vibrosil-K" 6 mm;
2 - slab overlap;
3 - SIPS-7-4 70 mm panel;
4 - Scoop "Shumanet-BM";
5 - protective layer of the nonwoven Lutracil cloth;
6 - acoustic clipso clipso;
7 - Baged profile for mounting the clipso panels;
8 - Wall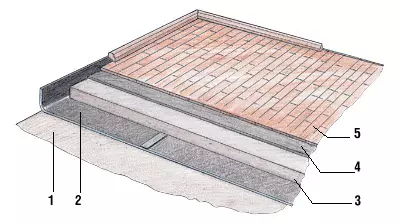
1 - slab overlap;
2 - "Shumannet-100";
3 - concrete screed;
4 - sound-insulating gasket;
5 - Laminate

You purchased a stereo or home theater. Brought, installed and ... How would it be eaten? Did not receive the promised "kayfa". Sound some kind of vague, and a well-known phonogram sounds at all as it should. Plus, different extraneous noises (including coming from neighboring apartments) and mechanical "rattling". And to top it all over the neighbor began to drum into the wall, demanding "to stop this mockery." But why did it happen? Let's try to figure it out.
Part I. Sound. Why did it happen?
Let's start, as they say, "from the stove." More precisely, with the nature of the sound, the laws of its distribution and some features of his perception by human ear.Sound in a wide sense-oscillatory movement of particles of an elastic medium propagating in the form of waves in a gaseous, liquid or solid medium. Av is a narrow sense, subjectively perceived by a special organ of senses of man and animals. Simply put, you slammed your hands, hit the ball about the floor or said the word, that is, only one sound was published, and here in the room where you are, a sound wave is born, which has energy. The wave applies to the room (incident energy), finds the barrier (wall or overlap) and is partially reflected from it (reflected energy). Another part of the wave energy is dissipated in a barrier (scattered or absorbed energy), turning into thermal energy. The anterable part still "breaks through" through the barrier and comes out on the other side (past energy).
Let's notify immediately: this review we were conventionally divided into 3 parts. First of these, we will talk about the perception of the human ear incident and reflected wave, and the scattered and past waves will be left according to the second and third parts.
With the help of hearing organs, a person perceives the oscillatory air movements, distinguishing them in frequency and strength. It is believed that we hear only sound waves with a frequency of 16 to 20000Hz. But in this range, different frequencies are perceived by the human ear unequal. It is best to hear the so-called average frequencies (from 500 to 2000Hz) is a conversation and household noises. Both lower (16-500 Hz) and higher (2000-20000Hz) are perceived somewhat worse. The sound with a frequency of 20000Gz is able to hear mostly infants. Away, the maximum perceived frequency for most people is limited to 17,000-18000 Hz, and to the old age it comes to 15000 Hz. To estimate the sound, an indicator of the level of its intensity L and special units of measurement of the decibel (dB) are adopted. The threshold of human hearing corresponds to the sound pressure of 0 DB (210-5pa). To determine the effects of noise on the human hearing aid, a special technique and a scale A, which makes it possible to estimate the noise of various spectra with one digit into a unit.
Now about direct and reflected sound waves. In the Vuscian language, the phenomenon of reflection sound is called echo, in English reverberation. Reverb (Late. REVERBERATIO-reflection from lat. Reverbero- drop) - the process of gradual attenuation of sound in closed rooms after turning off its source. The duration of such attenuation is characterized by the reverb time during which the intensity of the sound decreases 106 times, and its level is 60 dB. The reverberation time is the greater the greater the size of the room and the less the absorption of the sound on the bounding surfaces. This indicator is hardly an important factor determining the acoustic quality of the room. It is the time of reverberation that has a significant impact on the audibility of speech and music in the room, as the students perceive direct sound against the background of reflected. The reverberation phenomenon in everyday life is noticeable, for example, in a new apartment, not yet filled with furniture. In this case, you hear both straight and reflected from the enclosing design sound coming to you with some delay.
Why are all these scientific details? And to the fact that without them it would be difficult to understand some of the features of the perception of sounds by human ear.
Let's start with the fact that as a result of the evolution of human hearing, it became such that most comfortably perceives the noise atmosphere characteristic of the forest, but not for a fully open (field) or fully closed space (soundproofed room). People are genetically familiar to constantly in the medium where there are various noise of low intensity (there is no absolute silence in the forest), but at the same time there are no loud sounds (such noises acting constantly, in nature there are simply no, and there are only active short-term time Thunder, the noise of the waterfall, the rain, the roar of animals IT.D., and they are thickened by trees). Natural for human hearing is the presence of accompanying all the sounds of reverb (reflected from the trees) with delay in a few tenths of a second. And this reflected signal seems to increase the primary sound and makes it juicy. At the same time, the timbre color of the trees differs in different ways reflects different frequencies. Util the reflected sound is practically no (except from the Earth, and he is quenched by its irregularities and herbal cover). And the person, perceiving only a direct signal, loses the feeling of comfortably the sound becomes "dry".
What time of delay of the reflected signal is felt as the most comfortable? Acoustics specialists believe that it is about 0.02C (the time of delaying the reflected sound from the barrier at a distance of 3.5 m). A signal with a smaller delay time (for example, reflected from the barrier at a distance of 1, the delay in this case is only 0.006c), the human ear is simply not perceived ("dry" sound). Well, and a signal that delays more than 1.5 ° C, leaving for a straight sound, makes it an inseparable - it would seem to hear everything, but you can't understand it (remember the typical vocational situation, when even with a high effort, it is not possible to disassemble everything -Taki announced a speaker).
The noise level of 20-30DB is considered almost harmless to a person, this can be said, a natural noise background. Permanent sound (it is rather considered to be noise) in 35-50DB, the person in principle perceives normally (although it is here all individually, someone's sound in 50 herds greatly interferes). For loud sounds, 80DBA is an allowable boundary. The noises of the level of 80-90DBA cause unpleasant sensations, the level of 120-130dbasses, at 150DB, an irreversible hearing loss comes, at 180 db. Death (for example: atomic bomb is exploded with the sound of 190DB). Any noise of sufficient intensity with long-term exposure to a person can lead to a varying degree of reduction of hearing activity (at high levels of noise, the rumor begins to deteriorate after 1-2 years, it is detected somewhat later, after 10-15 years). In addition, noise has a harmful effect on organs of vision and vestibular apparatus, reduces reflex activity and even causes diseases of the nervous system. But in absolute silence (i.e. without sound signals from the outside), none of us will not be able to. For example, a person placed in a special fully soundproofed camera, a maximum of 10 minutes begins to experience strong anxiety ("Something happened! There is no usual sound information!"), In 15 minutes, he has a ringing in the ears (the body's protective reaction is triggered. Complete silence), he can go into panic and even get strongest stress. The noise background of 25DBe for people is most comfortable, they practically do not hear it, but the "ringing" silence does not oppress them.
In such a way that it is comfortable to perceive speech and music, a person must be in agreed favorable conditions for him- in a room where there are no strong long noise, no complete silence, but there is a small (comfortable for a listener) the time of the sound of sound and, of course , There are no strangers entering out noises. Yes, all that is. That is why there are practically no people who would not like to listen to the organ, piano or symphonic music in the concert hall, but the same music broadcast on TV or the player reproduced, not everyone loves. Not enough of the most reflected and slightly delayed sound. Yes, and extraneous noises of the house can distract. But if you watch a concert or reproduce its stereo recording indoors, where, in addition to sound from speakers, a reflected signal will appear with a delay time corresponding to the concert hall, the music will be perceived in the same way as in this room itself.
However, this applies only to the records of an old sample, which specialists for the lack of volume of sound are called "flat". Modern techniques allow you to give the sound the necessary volume. It is recorded in a specially equipped studio, each tool separately. All extra noises and wheezing are removed from the record. Then the tools are superimposed on each other, over the voice of the singer. But this is not limited to this. Next, the sound engineer creates sound special effects and adds what was not when writing in the studio - electronic echo. Yes, we are talking about that reverb. And as a result, the sound is fixed and already "brought to mind" on the record. It remains only to reproduce it exactly as it is recorded, and enjoy.
When are acoustic problems?
After we figured out with the concepts and laws of sound distribution, let us return a little on the entry into this review. Honestly, drawing such a sad picture at the beginning of the material, we, of course, exaggerated somewhat. The deplorable result expects the buyer of the stereo system or home theater far from all cases. For example, many of those who, by purchasing such a system, establishes it in the "ordinary" residential room (most often it is a living room), may well get a completely satisfactory result. It may be satisfactory for two reasons. First, available in the living room carpets, furniture (especially soft) and other household attributes are somewhat "rogulated" the reflected signal. Secondly, in the living room, which is the room for listening to sound recordings, and a home theater, as a rule, not too expensive equipment is installed. So if, due to the shortcomings of the room, some nuances of sound are lost, it will not be especially noticeable.
But this seemingly a positive result still does not mean that there are no problems and they will never arise in your conditions. It may very much that, as soon as you increase the volume, the problems will immediately identify. What can happen? For example, they can start racing glass. Both the window and in the servant (not to mention the dishes located in it). The large-sized windows are capable of working as a membrane and start reflecting and even enhance the sound, at certain frequencies entering the resonance with a falling wave. Therefore, from the point of view of acoustic comfort, it is better if two-chamber windows are installed in the windows. And not with the same quadmillimeters, but with thicker glasses, in this case, than their thickness more, the lower the sound permeability of the structure and the less likelihood that the glass will begin to rattle. For example, it is not bad to use a glass with a formula 6-4-5mm, and even better, with formula 4-6-8 (the thickness of the glass is reduced from the external to the internal). Araz, we spoke about sound permeability, it should be noted that this indicator can be further reduced by applying the so-called "asymmetric" double-glazed glass in which the average glass is approximated to one of the extreme. Such a glass unit does not simply provide reliable protection against outdoor noise, but less resonates. The probability of resonance is reduced and by applying windows separated by imposses (so that the area of individual glass-tubes used in them was as small as possible).
Troubles can come from the windowsill. Stacks of view of acoustics Plastic windowsill are much worse than made of chipboard, because there is cavities inside plastic. About the design of windows and window sills, naturally, it is necessary to think even before their immediate installation. Do you do anything, if anything else already have and all together creates acoustic discomfort? In some (but, unfortunately, not all) cases are able to help heavy velvet curtains. You can still advise to establish massive internal shutters that will be closed at the time of watching the movie or listening to music.
In addition, acoustic troubles can be expected from floors, and especially essential - from laminated and ceramic. These coatings have a rather solid surface and therefore reflect sound much stronger than wooden (parquet, massive board). The rescue means (though, not always) can become a carpet aligned to the floor. And the latest walls and partitions. Especially a lot of trouble can deliver light framework structures, covered with one layer of plasterboard, with the location of the racks every 60 cm. Such a partition can begin to vibrate and even resonate how big glass. You can advise here the following. First, layers of drywall should be at least two, with displacement of seams of one layer relative to the other. Secondly, when assembling, it is necessary to thoroughly tighten the screws that attach plasterboard to the frame (do not forget to control it!). And, of course, the inner space of the frame partition must necessarily be filled with an effective sound-absorbing material. It is better if the designs will rely on the slabs of overlapping, riglels, carrier beams, but in no case are not on the lags or finger floors. Well, how to deal with the vibration of glasses of gray and dishes, we think, it is best to simply remove the servant from the "Cinema".
Much more often with undesirable acoustic phenomena, those "lucky", which price, can be said, the titanic efforts were allocated for a home theater a separate room. And these people are perhaps doubly offensive. Still would! Embedded a special room, acquired expensive equipment- and on you! The sound is such that after a few minutes I don't want anything to listen or look, but it pulls only to leave the room as soon as possible. What creates sound discomfort? For reasons listed above, it is worth adding two more. The first reflections and their duration significantly exceed the recommended values, which creates the so-called "sound porridge". Second, bad form of the room. For example, in rectangular "Penals" often there is a "standing wave" - in some places the sound is enhanced, and in some, on the contrary, weakens. And all because of the same, due to the imposition of the reflected signal to the primary. Other unwanted sound effects may occur. For example, the phenomena of the "fluttering echo" (appears between two parallel walls) and "sound rebound" (sound reflection from two or three converging in the corner of the surfaces).
How to deal with it? The first way to struggle is constructive. For example, to eliminate the "fluttering echo", it is possible to make the walls of "cinema" not quite parallel with the help of drywall sheets (with deviation by 3). Or create a set of protrusions and corners in the room using the same plasterboard or furniture. It also helps the installation of the pilaster, the size of which depends on the size of the hall (specialists have special recommendations on this). Both, in the other, and in the third case, the scattering of sound, it will begin to be reflected at an angle that differs from 90. The result of the prompt, as professionals say, the diffusion of the sound field is the likelihood that at every point of the room and in each direction The sound level and its frequency will be the same. That is, all points inside the space will be "sound-valued".
From the point of view of geometry, it is always better if the room corresponds to the formula of the golden section: the ratio of length to width and height is 1 / 0.68 / 0.32. In addition, the room should not be very low (less 220 cm). If it is precisely such (for example, it is a basement), it is not worth trying to create cinema-low frequencies will not still be harmonious.
The second way, speaking by a professional language, is the "acoustic processing" of the room using special acoustic materials. They are divided into sound-absorbing and sound insulation, and each of them makes sense to stop more.
| Material | Firm | Country | Thickness, mm. | Size, mm. | Density, kg / m3 | Coefficient of thermal conductivity, W / (MK) | Sound absorption coefficient | Price, $ / m3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nobasil M. | Izomat. | Slovakia | 40-220 | 500, 6001000 | 30, 35, 50, 75 | 0.034-0.036 | 125Hz- 0.2-0.35; 1000Hz- 0.7-0.75; 4000Hz- 0.35-04 | 40-85 hover. From the dense |
| Paroc Uns. | Paroc. | Finland | 30-200. | 565-870920-1320 | thirty | 0.0335-0.0365 | RW LP - from 40 to 70DB in the frequency range from 50 to 3150 Hz | 52.5 |
| Paroc ssb. | Paroc. | Finland | 30-50 | 12001800. | 100 | 0.034 | RW NP-21-70DB in frequency range from 50 to 3150Hz | 229,4. |
| URSA n 60 * | "Fileer-Chudovo" | Russia | 20-100 | 6001250. | 60. | 0.033 | 125Hz- 0.09; 500Hz- 0.53; 2000Hz- 0.95 | 92.7 |
| URSA p 45 * | "Fileer-Chudovo" | Russia | 20-60 | 6001250. | 45. | 0.034 | 125Hz- 0.1; 500Hz- 0.64; 2000Hz- 0.97 | 74,1 |
| ISOVER KT-11 * | Saint-Gobain Isover | Finland, Poland, Russia | 50 and 100. | 12007000, 14000. | eleven | 0.041 | RW LP - from 40 to 59DB | 26,4. |
| Isover KL-E * | Saint-Gobain Isover | Finland, Russia | 50 and 100. | 1220565. | fourteen | 0.038 | RW LP - from 40 to 59DB | 30.4 |
| Isover KL * | Saint-Gobain Isover | Finland, Russia | 50 and 100. | 910610. | sixteen | 0.036 | RW LP - from 40 to 59DB | 41.9 |
| ISOVER FLO * | Saint-Gobain Isover | Finland | 30, 40, 50 | 1200600. | 85. | 0.033 | RW NP - 35-36DB, RW PD- 54-57DB | 208.6 |
| Light Batts | Rockwool. | Denmark | 50-200. | 1000600. | 35. | 0.036 | 125Hz- 0.32; 1000Hz- 0.93; 4000Hz- 0.35-0.4 | 39.5 |
| * - The surface of fiberglass materials should not remain open. RW-reduced sound insulation index, depending on the design: RW LP- for light partitions; RW np- for bulk seamless floors on monolithic floors; RW PD- in the designs of floors on wooden beams |
Part II. Sound absorption
Now it is time to talk about the absorbed by the obstacle (wall, ceiling, floor) of the sound waves coming from the cinema columns. If you use the definition of a large Soviet encyclopedia, then the sound-absorbing capacity of materials is due primarily to their porous structure and the presence of a large number of open pores communicating among themselves. The total porosity should be at least 75% by volume. " As you know, ordinary building materials have a very insignificant porosity, therefore, they simply do not have to speak about their sound-absorbing ability. For example, concrete, brick, ceramics have a sound absorption coefficient of about 0.05, wood-0.1-0,15. Finishing materials in terms of sound absorption slightly better- even the plug has a sound absorption coefficient of only 0.2, that is, not particularly different from the tree. Finally, the sound absorption coefficient of pile carpets is at the level of 0.2-0.25. Therefore, if we talk about sound-absorbing materials and structures, then only special. They will be devoted to this part of our review.The large specific surface area of sound-absorbing materials created by the walls of the open pores contributes to the active transformation of the energy of sound oscillations into thermal. This happens due to friction losses. Simply put, the sound wave should easily enter the pores of the material, cause the oscillation of air molecules there and due to the friction arising both directly between these molecules and between molecules and the material around the pore, go over, turning to heat.
The efficiency of absorption of sound is estimated by the sound absorption coefficient A equal to the ratio of the amount of absorbed energy to the total amount of sound waves falling on the energy material. The coefficient A is always greater than 0, but less than 1.
Sound-absorbing materials have a fibrous, grainy or cellular structure and are divided into groups according to the degree of hardness: soft, semi-rigid, solid.
Soft sound-absorbing materials are made on the basis of mineral wool or fiberglass. The books include mats or rolls with a volumetric weight of up to 70 kg / m3 and a sound absorption coefficient from 0.7 to 0.95. We have a group of such a group that has long been used by sound absorbers, like cotton wool, felt, etc.
Semi-rigid materials include mineral wool or fiberglass plates with a bulk mass from 80 to 130kg / m3 and a sound absorption coefficient of about 0.5-0.75. We have a group of sound-absorbing materials that have a cellular structure - polyurethane foam, polystyrene foam IT.P.
Solid materials have a bulk mass of 300-400kg / m3 and the sound absorption coefficient of about 0.5. Produced on the basis of granular or suspended mineral wool. The same group includes materials, which include porous aggregates - strolled perlite, vermiculite, pumice.
Naturally, in domestic rooms in terms of reduction of loss of living space, it is more profitable to apply materials with the maximum sound absorption coefficient, that is, soft. It is they who are widely offered by the modern market as sound absorbers. These are products made of fiberglass companies Saint-Gobain Isover (Finland, Poland, Russia), Flymeder-Chudoovo (ORSA trademark, Russia), as well as mineral wool Rockwool firms (Denmark), Paroc (Finland). Such materials are widely used for the insulation of building structures (you can read more about this in the article "
The warmth of your home. "). The entertaining advantages of these products, except for high sound-absorbing properties, should include ease, hydrophobicity, fire resistance, vapor permeability. Mold and pests simply do not come in them.
Similar to properties, but are no longer intended for universal, but for the specialized use of mineral wool slabs on a basalt basis "Shumanet-BM" (the company "Acoustic materials and technologies"). They can be used as a middle layer in the designs of sound-absorbing cladding with a protective perforated screen, light partitions from GLC and GVL sheets or other sound reflecting materials, as well as "floating" floors.
The lack of listed materials is common: they require additional closure of the surface. This can be done, for example, with a drywall, but then it will reflect the sound and the desired effect of sound absorption simply will not work. So it is better to close the surface with a cloth or perforated screen.
The specified shortage is deprived of special products and designs. In the worse, they only require wage or painting, are ready for use immediately after installation. In addition to the fact that these materials are fire-resistant, eco-friendly and hygienic, they are also beautiful. The number should be attributed:
The sound-absorbing ceilings and the ECOPHON panels manufactured by the Saint Gobain panel at two enterprises: Ecophon in Sweden and Isover in Finland (here the Ecophon brand has changed the Akusto brand earlier). We think, for a long time to talk about the properties of these products there is no need - they are supplied to our market for quite a long time. Let's just say that the Finnish production materials were both and remained "a little simpler". But the prices for them down. The facial surface is covered with glass. The range of Swedish Products is very wide: here you can find both straight ceilings with various types of edges (including allowing you to make the suspended system completely invisible) and curvilinear, plus illuminated caissons. However, let the photos tell about the designer opportunities. The facial surface is equipped with a special coating of Akutex T, absolutely not preventing the penetration of sound waves inside the panel and even with a high reflection and dispersion rate.
Plates perforated gypsum sound-absorbing-PPGS manufactured by Knauf (Russia). The appearance of them, of course, is simpler than the Ecophon brand products, but the price is much more affordable.
Acoustic stretch ceilings CLIPSO manufactured by the company of the same name. Polyester Polyestera cannut with polyurethane coating. Next, it hides the layer of mineral sound-cutter "Shumannet-BM", fixed on concrete overlap. The sound-absorbing capacity of such a ceiling is slightly lower than that of Ecophon's products, but it does not have a single seam on the surface.
Panels Saundlux ("Acoustic Materials and Technologies") with a metal perforated housing, inside which plates "Shumane". The main advantages are the wonderful appearance, the "anti-vandality" of the front surface and the ability to paint into any color according to the RAL catalog without deteriorating acoustic properties.
Mappysil panels (MAPPY, Italy). Move from foamed polyamide (foam rubber). The back side is smooth, the outer has a pyramidal, wave or trapezoid profile, which increases the sound-absorbing properties of the panels.
Sonasprey sprayed acoustic coatings (US technology and equipment). This is a whole complex consisting of secondary cellulose fibers, binders, chemical impregnations and special additives. The coating is removed using a special installation. The thickness of the layer of texture plaster "under a fur coat" - from 2 to 4 cm. Very economical material. It is especially advantageous its use on complex geometric surfaces, that is, where other sound absorbers are simply not applicable.
Where to place a sound bag?
When installing modern stereo systems, in which the columns are located ahead, on the sides and rear (for example, six-channel, 5 + 1, Dolby Surround systems), the entire room must be evenly processed by sound-absorbing materials (alternate sound-absorbing and sound transcending surfaces). But it is not necessary to strive for the expression of specialists, "fully drowning the room" (that is, completely closed the walls with sound-absorbing panels) - in such a room it will not be possible to achieve acoustic comfort. For example, in the absence of an inclusive phonogram, silence will be simply "ringing" here, and such silence, as we have already found out, the person is simply not used to.
Part III. NOISE
Surely an attentive reader has already noticed that the same sound phenomenon we call differently: that sound, then noise. AVSE The fact is that the line between these two concepts is very conditional. For each of us, the sound is something that the useful information is at the moment (unless, of course, the power of this sound does not exceed the permissible limit). Ashum is the fact that at the moment useful information is not. Unclear? Explain easier. You are watching the movie in the home cinema with the sound level of 70DBA and enjoy. What you listen to is the sound. AB is the time in the next room. Your mother-in-law is trying to read the book (well, I do not like the film that you are watching). So, for her, what comes through the wall is noise. Aesley in another room is your child with angina and high temperatures? It is clear that you need to regret (our neighbors do not even mention). And, it means that we are with you the time to talk about the sound waves, after all, those who have passed through the barrier (wall, ceiling, floor) from the home theater's room, and at the same time the sounds that penetrate it from the outside. That is, about noise and noise insulation, more precisely, sound insulation.Soundproofing
The noises of the air, generated directly into the air in any source (conversation, reproducing devices), and the shock, occurring during mechanical exposure to building structures (first of all, on overlapping), for which they run, run or (do not give God!) Jump . If the noise of repair, which goes on the twelfth floor, is heard on the second, this is the so-called "structural" noise, which extends to the elements of the building design. Why do you need to talk about all three types of noise and corresponding to them noise insulation? If you watch a movie with a "decent" volume level, maybe you will not hear how in the next room my wife turned on TV or radio, - the sound of the cinema just muffled this noise (but not the fact that the wife turning on the TV, the sound of The cinema will hear stop). Well, and the loud top of the neighbors or the sounds of a drill from the top floor you will hear necessarily.
It is worth starting with the fact that the soundproofing ability is no longer a characteristic of a single material (concrete, brick, glass IT.), and the design of the structure made of this material. Why? First of all, because it stands in any design to appear a small hole or cracks, as all efforts for soundproofing the premises will go scamper - the outer noise literally fill the room. That is, the soundproof properties of the design to a great extent depends on the quality of its manufacture. But also from the material from which it is made, also depend. For example, from concrete, a soundproofing design is easier to create than, let's say, from the wool, despite its excellent sound-absorbing properties. Breaking Walls just Mala Mass. What is the mass? Let's figure it out.
Let's start with terminology. The terms "sound absorption" and "sound insulation" at first glance are very similar. But only for the first. The problem of sound absorption is the elimination of noise in the room in which it appears. Simply put, this is the task of absorbing noise, do not let it reflect from the obstacle back into the room to enhance the already available. The task of sound insulation is not to allow noise to pass through the wall of the room. And it makes it mainly by reflection. Consequently, the materials for solving these such various tasks are also needed different. AB created by the protective design so that both those and others should be attended.
If you build a small "house" from the Ecophon panels, get up in the middle of it and shout loudly, then your own scream you almost do not hear the sound absorb panels. Avota man standing next to the "house", cry hear, let the panels weakened, but the sound will be left out. But if you build the same house of concrete, then the picture will be straightforward - a man standing outside, your voice will not hear, and you may well lay ears due to the enhancement of sound due to its reflection from the walls. The reason is that the soundproofing ability of the building structure is determined primarily by its massive wall, the more difficult to scour it. And old buildings with heavy walls and overlaps are an excellent confirmation of the sound insulation in such houses is simply exceptional.
It would seem that everything is clear: it is necessary to make the walls as thick as possible. But it is impossible to fulfill it, and it is impractical. It is impossible because there will be a catastrophically, the weight of the structure, the load on the foundation and the cost of construction. It is inappropriate, because the dependence of the sound insulation capacity of the wall from its thickness is subject to logarithmic law: an increase in thickness by 2 times causes a real increase in sound insulation properties by only 5-6dB. This, of course, a rather noticeable value, but ... as they say, it is not worth the heater. And you will not stop the neighbors to hear (if they interfere with you, it means that you hear the noise greater than the background, at least 10-15DB). The output is to create or acquire ready-made soundproofing designs.
On the creation of soundproofing structures and materials necessary for this, our magazine has already written in detail and repeatedly (for example, in the articles "
Gypsum + cardboard = repair spent ","
Secrets of a quiet house ","
Roman with plasterboard "). It can be falsewheres made of drywall both with a pure air gap between the capital construction and the rawpanel, and with a gap, partially filled with a fibrous sound absorber. Such walls reduce the noise level and go beyond the limits of your apartment, and falling into it From the neighbors - by 4-6DB and, therefore, not very effective, but the area "eat" is quite a lot. Much more efficient is the use of multilayer panels, in which "hard" (drywall, gypsumber) and "soft" (sound absorber) Layers. The mechanism of action is simple: the sound is reflected from the "solid" layers and sinks into "soft". Such a panel with smaller losses of the area allows you to play no more than 6, and 10-13DB. Included in the example, we give the puzzle Materials and technologies "), the amount of solid and soft layers in which can be equal to both two and four. In addition, the panel is mounted to the wall (without an additional frame!) H Yerez so-called vibration-insulating mounting nodes (8 nodes on each panel), which enhances its soundproofing ability.
Now about impact noise. The cheapest (but not the most efficient) way to avoid shock noise, which will be born in your apartment, but to hear in the next, - put on the floor the carpet. If we talk about constructive measures, then to ensure the absence of a drum noise problem, the thickness of the reinforced concrete overlap should be about 1m. It is clear that creating the overlap of such thickness is simply unrealistic. And there will be a multi-layered design, consisting of the overlapping, sound-absorbing gasket and a concrete screed weighing 80-120kg / m2. It was such a puff construction that was implemented in the arrivals of five-storey houses-Khrushchov. True, the screed there was "eager", and a thick plate Fiberboard was used as a gasket.
Now on sale there are special "laying" materials. For example, the "glass cholester" "Shumannet-100" with one-sided bitumen coating or a "noisy-c2" plate from staple fiberglass. Thus, the "shumanet-100" thickness of only 3mm, laid under the speed of 60mm thick, reduces the level of impact noise by 23DB, and with a thickness of 5 mm ("Shumnet-100C") - by 27dB. "SHOYSTOCK-C2" thickness of 20mm will reduce the shock noise for the whole 42DB. Such a floor needs to make a "floating" - a layer of screed should not touch the walls in order to avoid the formation of "bridges", according to which the sound from the wall can pass the floor. For this, the "gasket" must be started on the walls around the perimeter of the room (be sure to follow this when installing!). In addition, under the purity floor, it is possible to put cork sheets (the plug applies precisely for insulation of shock noise, but not air) or any other elastic gasket material, which will even more increase protection against impact noise.
But remember that such a "floating" floor design protects only from shock noise, but from air noise, which will penetrate you from the bottom floor, saves badly. And it means that it may still be necessary to lay a layer of sound-absorbing material with a thickness of at least 50mm and a device of a concrete screed over it. Then the air noise will be able to play Decibel 8, but the floor level will rise significantly.
In my apartment, you, of course, such a multi-layered design can well create, but what about the neighbor above? He is not obliged to reconstruct his home and arrange a "floating" floor, and as a result you will hear every step in the apartment. Any suspension suspended ceiling is capable of a soundproofing ceiling, the same Ecophon, only between it and the reinforced concrete slab will have to lay a layer of an efficient sound absorber. Extreme cases are permissible to apply the same ZIPS panels. True, the level of shock noise will decrease the entire decibel on the 10- sound insulation design on your part in this plan less effective than the "floating" floor from the neighbor's side. But from air noise it protects perfectly.
Fight structural noise generated by elevators, pumps, electric motors, fans and other similar devices, even more complicated. You can, of course, try the same techniques as to combat air shock noise, but there is no guarantee of the success of these measures. Effective means of combating structural noise, competent installation of the most noisy equipment, the use of elastic gaskets and competent layouts. For example, the bedroom should be located as far as possible from the elevator shaft. Or collect all the equipment in a separate soundproofed room, located as far as possible from the residential zone (naturally, if it comes to your own home).
Doors
Perhaps the last thing you need to discuss are the sound insulation properties of the doors. Let's start with the fact that modern glass, plastic and hollow doors collected from two laminated panels, the sound is practically delayed. Even cellular panels from a fibrodone laid inside them as a sound absorber do not help hollow doors. A decent soundproofing and sound-absorbing properties have only massive doors (here as with the walls: the more a massive door, the better it reflects the sound). Even better, special noise insulating models.Soundproofing and seals on the perimeter of the door can significantly improve the sound insulation. Asset is to a greater extent it will improve the installation of two doors with each other. And the more the distance between them, the better. Very good to cover the walls in the interval between the doors of sound-absorbing materials.
Well, what should I do if you change anything to install an existing door? In this case, it is necessary to sound the wall opposite the door. And then in the room located behind this wall, it will become much quieter.
Epilogue
This is perhaps everything that we were going to talk about sound, noise and sound insulation problems. We sincerely hope that this article will be useful not only for those who decided to organize a home theater, but also for those who have not even thought about it, but who has unresolved sound insulation problems. We fear only one. We tried to tell about acoustic problems with a simple and affordable language. But this does not mean that you can solve them as easy and simple. Yes, on its own, using, for example, practical advice that sounded in this review. Everything can be much more complicated than you think, and the actions that you do can be absolutely useless. Therefore, let yourself give you the last advice. Call an acoustical specialist (firms that provide such services are already quite a lot). There is such a challenge, of course, not particularly cheaply 1000 rubles. But you immediately get a competent consultation, how and what needs to be done and in what means it can pour. Illiterate independent actions are able to require significantly high costs.
Technical and acoustic characteristics of sound-absorbing materials
| Mark. | The foundation | Coating | Number of standard colors | Size, mm. | Weight | Sound absorption coefficient | Price, / m2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plates "Shuminet-BM" | Mineral wool | - | one | 100060050. | 35 kg / m3 | 0.9 | 3.5 |
| Playing needle-free mats "Vibrosil-E" | Fiberglass | - | White | Roll width 920. | Surface density 780 kg / m2 | Reducing shock noise at least 27dB | From 3. |
| ISOVER-ECOPHON Ceilings | Fiberglass | Poklovoyalka | four | 600600 and 6001200, thickness 15, 20 and 30 | 1.3-1.9 kg / m2 | 0.85-0.9 | 7-11 |
| Ecophon ceilings | Fiberglass | Fiberglass | 7. | 600600/1200/1600/1800/2000/2400, 12001200, thickness 15, 20 and 40 | 1.3-2.5 kg / m2 | 0.9-0.95 | 11-39 |
| Ecoophon panels | Fiberglass | Special Akutex T, Fiberglass Mesh, Shockproof Mesh | 7. | 2700600/1200, thickness 40 | 5 kg / m2 | 0.9-0.95 | 27.7-66.7 |
| Plates of PPGZ | Gypsum | - | White | 59559510 | 7-8 kg / m2 | 0,62-0.87 | 6. |
| Acoustic stretch ceilings Clipso | Polyester | Polyurethane | White | Width 5100. | 240 g / m2 | 0.68 (with "Shumnet-BM) | 50 (turnkey) |
| Panels Saundlux | Fiberglass | Perforated steel | Any ral catalog | 250036040. | 10 kg / m2 | 0.9 | 40 (without fastening system) |
| Mappysil panels | Foamed polyamide | - | Graphite | 10001000/2000 | 30 kg / m3 | 0.55 | From 7. |
| Sonasprey sprayed coating | Cellulosic fiber | - | 6. | Thickness 15-40. | - | Up to 1. | From 12 (turnkey) |
The editorial board thanks the company "Acoustic materials and technologies", "Scandinavian building materials", Rockwool, Saint-Gobain Isover, Paroc, Flyderer-Chudovo, Izomat for help in the preparation of material.
