What you should know the building foundation: design features, materials, construction methods. Types of soils and their brief description. Special oils and oils with solid wax: the benefits of the material, the technology of applying to the surface, care. Practical advice specialists.
So, the dear reader, the project of the house, its general view, the outer shell and the internal distribution on the premises, the approximate location of the house on the site you are chosen ...
Let's start by S. Basics of the house - His foundations. You can begin to build, but for this it is necessary to transfer the project of the house plan to the natural value to the site, i.e. Make the so-called breakdown of the building in nature. It is necessary to do this especially carefully, because the possible minor deviation of direct corners of the house from 90, imperceptible to the eye, will very much in the device, such as floors and floors, for it is necessary to be customized on the place of beam (coo-concrete plates are even more difficult), and in the floors to install oblique boards .
Geodetic instruments are used for breakdown (theodolite, swelling, measuring tape). Often, a rope rectangular triangle with sides 3, 4 and 5m or other conventional units is used to obtain an angle, but in the same proportions. This "Egyptian triangle" gives fairly accurate results. First, it is installed on Earth, considering the location of neighboring houses, the facade line from the street (no closer to 5 m), noting it with a cord, which is stretched and tied to nails, driven into strong stakes. The stakes are located 1.5-2m outside the home, so that they were not damaged when the trenches of the trenches for foundations or pit. From this cord (facade line) with a plumb, the point of the angle of the house is applied to the vertex of the "Egyptian triangle" and set the perpendicular line of the lateral facade. In this direction also stretch the skins on the seals. From the point A measured the lengths of the street walls (points) and the side (points) of the facades, the last point (the angle of the house) is also found with the help of the "Egyptian triangle" or theodolite and the corresponding lengths of the walls of the house. The correct breakdown should be checked with diagonals: if they are equal, it means that the corners are direct. The cord must be tuned at one level, which is especially important in areas with a significant slope. Using a plumb, you can additionally count and designate cords and on Earth the necessary width of the foundation, trenches and holes under the foundations of the house.
All extensions (terrace, erker, porch) are already tied to the main contour of the house and are neatly transferred with the drawings.
Of course, the breakdown of the building in nature is more expedient, especially with a complex configuration of the plan, in the presence of oblique sites, lead along the center (modular) planning axes of the building, which are indicated in the drawings. Instead of pegs, sometimes suitable (at the corners of the building, in the places of the walls of the walls), the pickup from the strokes driven into the land of 1-1.5m nailed to them. Wet boards and driven nails, noting the cords of the axis and the main dimensions of the building, transverse walls, the width of the foundations, etc. After breaking at home, you can proceed to earthworks on the plot.
The foundation is called the design of the underground part of the building, through which the loads (weight) are transmitted from the overlying structures (walls, overlaps and other weights) and from people, equipment, furniture (so-called payload- for the base, i.e. on ground .
Building bases are two species - natural and artificial. The natural base is the ground, which occurs under the foundation and having a carrying capacity, which ensures the stability of the building and permissible and uniformity of normative precipitation. A soil that does not have sufficient bearing capacity and which is required to artificially strengthen (rubbing, with a decrease in its humidity and swimming, chemical additives) or replace, is called artificial. The design of foundations always depend on the nature of the foundation. Probably cases for suburban one-three-storey residential cottage houses have a sufficient bearing ability of a natural base.
By costs Cottage foundations are up to 15-18% of the total house. The foundations are made under the walls and carrying partitions, under individual supports, as well as under furnaces and heavy equipment, which should be constructed independent of the foundations of walls with a gap 50mm.
According to a constructive scheme Foundations are divided into tapes (under walls or a number of individual supports); columns (under light walls, under columns, with a depth of a suitable base of base below 2m); Complete- under the entire area of the building (with weak inhomogeneous grounds of the base, to create waterproof the protection of basements, in wet soils with a high level of groundwater standing). For example, the famous TsUM building in Moscow, built over the River Neglinnaya, is resting on a solid monolithic reinforced concrete foundation.
Recently, pile foundations have become increasingly used for low-rise buildings, especially if necessary to transfer significant loads to weak soil, with a high level of groundwater standing. Of course, when there are piles and simple equipment for the production of work.
Materials used for foundations:
- The stone is natural from heavy natural stones of the brand 200 and above (sandstone, dense shell, limestone, boot or torn);
- Concrete Heavy grade 50 and above and reinforced concrete (monolithic or prefabricated, products from them);
- Metal, asbetic pipes (for pile foundations);
- Brick red, well burned (durable brand 100 or more);
- Wood antiseptic (mainly for wooden buildings).
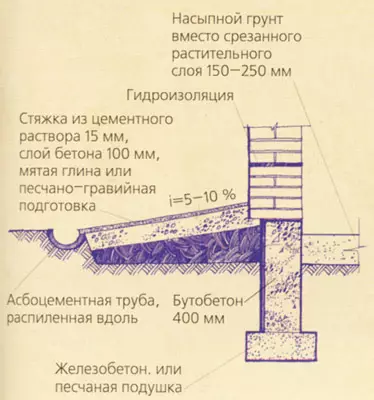
By the construction method Foundations are industrial (prefabricated) and nonindustrial (manufactured directly on the construction site). For a clearer perception of material about foundations, first consider the foundations of cottages without basements. Before the start of the trenches and pits under the foundations, it is necessary to remove the upper vegetable layer of the soil (150-250mm) under the entire area of the house, including the gentle.
If you leave the upper layer, then in the scene it is possible to rotate plants and wooden structures, carbon prepaid. A taped at home is chopped and slightly trambed the soil, revealed later from trenches under the foundations that does not contain vegetable particles and is safe for wooden house designs. This soil is satisfied with a slight increase in soil underground so that the water from the site does not register under the house.
The dimensions and depth of trenches and holes are established depending on the properties of the soil, the level of groundwater standing and the depth of the earth's frozen. For each geographic location, there is a regulatory depth of the primer of the soil (the in the winter the temperature is observed 0С, and for clay and thin soils -1c), as the average value for many years of observations in places purified from snow. So, it is accepted for Moscow and Moscow region 140-160cm, for Minsk - 100, for Samara- 170cm. The depth of freezing in a particular area should be clarified in a local construction or design organization.
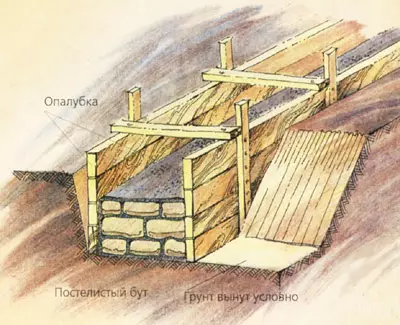
With the depth of trenches up to 1m and width to 0.6 m, its walls are usually made vertical, and a depth of more than 1 m-snowfield extension upwards. In case of bulk, it is necessary to install a temporary formwork from shields, boards that, after the end of work, take out.
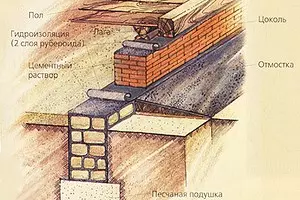
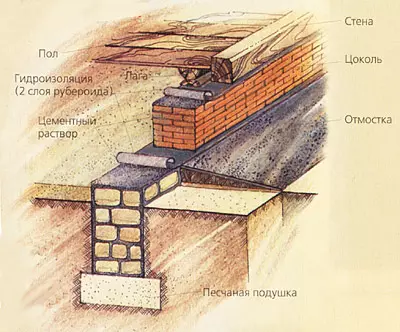
Dimensions for single-three-storey brick cottages of ribbon foundations are usually the same. This is explained by the fact that the loads transmitted from the house on the ground, relatively small, and the area of the foundations (sole of the foundations) exceeds the amount required by the calculation of approximately three times. Thus, the width of the sole for butt foundations is taken at least 600 mm, for boot concrete, concrete and reinforced concrete (monolithic or prefabricated) 400-600 mm, bricks - 510mm. It is necessary for the convenience of work and providing ligation of the vertical seams of stones.
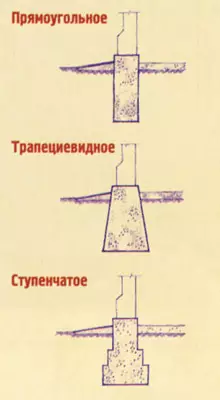
The ribbon foundation under the wall of the cottage in cross section is usually a vertical rectangle. Its upper part (foundation criteris), speaking, taking into account the slope of the site, about 100mm above the marks of the adjacent land, can be wider than the thickness of the wall or already depending on the constructive solution of the house. With weak and inhomogeneous soils (peatman, forest, etc.), when the pressure (weight) of the house on this soil exceeds the normative (local conditions less than 1-1.5 kg / cm2), the foundation sole should be sweded due to the accumulations created by The height of the foundation after 300-600mm or laying in its bottom pillows (concrete or reinforced concrete plate). It is possible to use and sand pillows from large or medium size of pure, sainted sand (particles of 1-2mm particles). This pillow layer 150-300mm is compacted by a rubbing or vibration with moisture.
For strength and durability of the house, it is important to determine which depth, it is important to determine which depth it is necessary to lay on. Contrary to extensive opinions, not always the foundations should be massive and deep, and therefore more laborious and expensive. In many ways it depends on the type of soil.
The greatest danger to the house is the spring of the soil: existing emptiness and pores are filled with water, which freezes in the winter, and the resulting ice, increasing in the volume, when tipping the upper layers of the Earth, squeezes the foundation to the top, which leads to uneven sediments, skews, and destruction of the house.
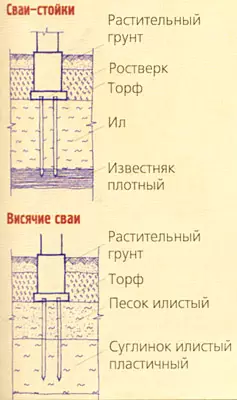
If a Smokes rocks , then they are durable, do not compress, waterproof and frost resistant (if they are without cracks and voids), do not blur and, therefore, are not extended. They can be put on the foundation base - directly on the aligned surface. Such soils under cottages are found very rarely.
Large-grained soils With particles with dimensions of more than 2mm (crushed stone, pebbles, gravel) are a good base if they lie with a dense layer, and are not subject to erosion.
Sandy soils Consist of particles with a size of 0.1 to 2 mm and differ on grave, large, medium size and dusty. The larger and cleaner the sand, the greater the load it can carry and with sufficient power and the uniform density of the layer represents a good base for buildings.
Large-grained and sandy soils (except for dusty particles from 0.05mm) have good, greater water permeability and therefore are not released during freezing.
In this regard, regardless of the level of winter standing of groundwater and the depth of freezing, the foundations for non-empty sandy and large-grass soils should be put on a small depth, but not less than 0.5 m from the surface of the planned land. When determining the level of standing groundwater, it should be borne in mind that in the summer and in the spring it increases significantly, and in the winter it decreases.
Clay soils (a vest mixture of sand and clay) contain very small particles (less than 0.005mm), which have in most scales and subtle numerous capillaries, which are easily absorbed by water. Claiming cases of clay soils are easily moistened and diluted, during the freezing there is an increase in their volume.
Dust-sandy soils with an admixture of very small clay particles, discharged with water, are called floating. They are not suitable for use as a natural base, as they have greater mobility and very low carrying ability. If there are from 10 to 30% of clay particles in a mixture, the soil is called a loam, and if there are from 3 to 10% soup. Plush soils The depth of the foundation is determined on the basis of the depth of the soil and the level of groundwater during the freezing period. With a low level of groundwater standing (below the depth of 2M and more freezing, the soil has a small humidity and the depth of the foundations can be arranged close to the surface of the Earth, but not less than 0.5 m.
If the distance from the planned surface of the Earth to the groundwater level is less than the depth of the frozen, then the base of the foundation should be put on the depth of the frozen or even 0.1 m deeper. The depth of the attachment of the foundations of the inner walls, columns and partitions in regularly heated buildings (the steepness of the premises is not lower than + 10c) can be taken equal to 0.5 m, regardless of the depth of the primer of the soil.
The calculated depth of the freezing under the foundations of external walls of regularly heated buildings is reduced compared to its regulatory value: by 30% - with floors on the ground; A20% - with floors on lags on brick columns and at 10% - with floors on the beams.
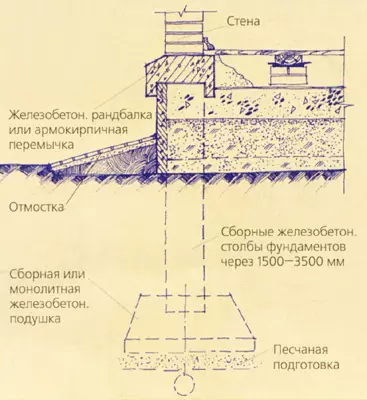
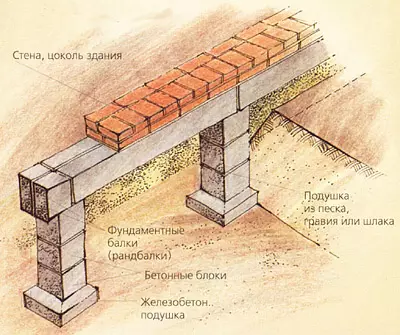
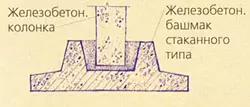
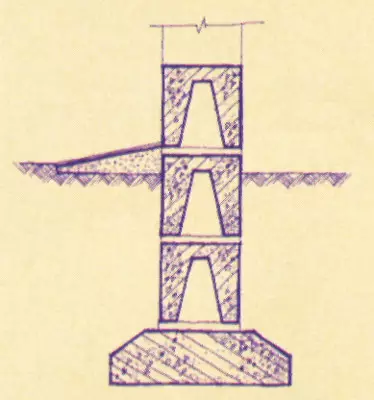
In cottages with dense soils, with light walls, with a great depth of the foundations, it is advisable to construct them non-tape, but by column, which is less laborious and more economical two to four times. They can be brick, boot concrete, etc. More industrial and accelerating construction are concrete or reinforced concrete poles (columns) of factory manufacture. The pillars put in 1.5-3.5 m and necessarily in the locations of the load: the corners of the house, the places of the intersection of walls, etc. Minimum pillars size: boot concrete- 400400mm, butt- 600600mm, bricks - 510510mm (under the walls of single-storey buildings and partition 380380mm), precast concrete components - 300300mm and 200400mm. Under the columnar foundations make some batch of foundations, laying a concrete, reinforced concrete or sandy pillow with a thickness of 100-300mm.
On top of the poles are connected by reinforced concrete base beams (randbalkas) or other jumpers (for example, iron-bricks with small loads and spans), on which the base, walls are erected.
The foundation pillars made of small-piece elements (brick, boot) should be reinforced by height every 250-400mm sixmillimeter wire or reinforcement grid. It is advisable to arrange and vertical reinforcement.
Due to the possible brightness of the soil, located under the jumpers, and the pillows are satisfied with the pillows under the jumpers (submissions from sand and slag layer 500mm with a gap of 40-50mm).
Prefabricated foundations from reinforced concrete pillars (columns 300300mm and more) are installed in glass-type reinforced concrete pillows, which are placed on the sand layer (100-150mm).
Pile foundations have their advantages. Their structure significantly reduces the volume of earthworks (by 80% compared to tape), reduces the consumption of materials (concrete - by 40%), eliminates the need to prepare the foundation and water supply on the site.
Depending on the pile material there are wooden (tens of thousands of oak piles of St. Isaac's Cathedral in St. Petersburg still serve so far, in the foundation of the famous Church of Santa Maria della Salute in Venice, 110 thousand piles clogged), reinforced concrete (residential buildings of Northern Norilsk are built on reinforced concrete piles, Driven in the perplexed soil), steel and combined.
Depending on the nature of the work in the ground, the piles of the racks are distinguished, which are based on the durable soil with their ends, and (if the durable primer is deeply hanging piles, which have pressure resistance from the building due to the occurrence of friction forces between the side surfaces of the piles and the soil surrounding them.
According to the manufacturing and immersion method into the pile soil, they are divided into clogging, immersed (clogged) into the ground in finished form and printed, manufactured directly in the ground (edged channels).
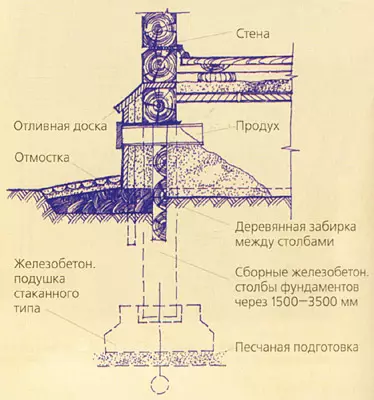
In low-rise pile houses, up to 5m under the walls are located in one or two rows at a distance from 3 ddiameters of piles of tubular cross section (300-400mm and more) reinforced concrete or asbette, filled with reinforced concrete or after 1-1,2m with reinforced concrete piles of square section from 250250 up to 400400mm.
The pile on the aligned head towers is associated with each other with reinforced concrete monolithic or national painter width equal to the thickness of the walls (but not less than 300 mm), a height of at least 150m. Pile foundations are one of the most progressive types of zero-to-to-floor floors. Given that not all cottage builders have mastered this type of foundations, it is advisable to enlist the calculation and method of producing these works. A similar solution and the project should be adopted when equipped with a solid monolithic foundation under the whole house.
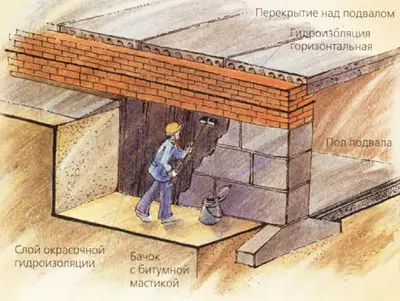
The designs of basement foundations (ficole floors) in principle does not differ from the designations discussed above the structures of the foundations of unchanged buildings; The books are imposed similar requirements, and they are executed from the same materials. The floor of these premises in most cases is lower than the depth of the soils, therefore, under the walls of basements, as a rule, a ribbon foundation is placed, the sole of which is only structurally located slightly below the floor mark. The largest distribution was the device of the walls and foundation of the basement from the prefabricated, industrial concrete blocks. Of course, the use of other traditional materials (brick, concrete, etc.) is possible. With weak soil, the blocks put on a reinforced concrete pillow stacked on sandy preparation with a thickness of 150mm.
Blocks of foundations and walls of the basement are molded from concrete brand 100 or 200. The usual thickness and height of blocks 400, 500 and 600 mm, length (nominal dimensions) from 900 to 2400mm. For precast walls of heated basements, it is advisable to apply lightweight blocks with emptiness, wide width, not more than 40mm or wide, closed on the upper side, voids. However, the hollow blocks in saturated water of soils may need additional waterproofing and heat.
When construction on weak strongest soils on reinforced concrete pillows and on the edge of the basement in the corners and the intersections of the walls, the reinforced distribution horizontal belts (seams of 30-50mm thick) should be laid on the cement solution of the brand 100.
The savings of the material with dense soils can also be obtained in the device of intermittent foundations, in which reinforced concrete blocks-pillows are stacked with the intervals of 200-900mm, falling asleep with the soil.
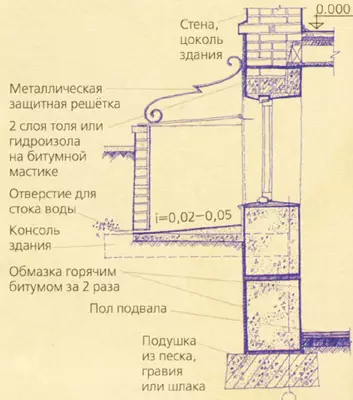
To illuminate and ventilating basements in their outer walls, windows are arranged, located its significant part below the level of the Earth, and in front of the windows - the wells called the pit. The veil walls are performed from red brick or reinforced concrete. Outside, the walls are deceived by hot bitumen twice, from the inside is placed with an alkaline solution; The bottom is performed from concrete with a bias from the window and draining stock. From above, the veil and the window is closed with a protective metal grille.
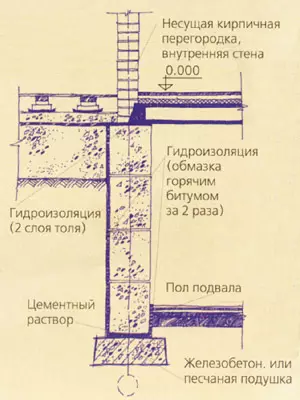
Protection of buildings from the soil (capillary water lift) and surface (rain, snow) are arranged in all cases from horizontal and vertical structural layers called waterproofing. To protect the foundations and walls from rain and melt waters along the outer walls, the breakfast is arranged with a width of 600-800mm (N200mm more of the roof s) with a bias from a building of 5-10%. According to the outer edge of the scene, it is advisable to break through the groove or lay the camp along the asbetic tube. If the pavement is adjacent to the building, then the gentle is not done.
In order to block the rise of the capillary moisture throughout the horizontal section of the outer and inland walls, lay the waterproofing layer, consisting, for example, of two layers of rubberoid on mastic or from a layer of 20-30 mm of a fatty cement mortar of 1: 2. This waterproofing is placed in the outer walls by 100-150mm above the level of the breakfast or sidewalk; In the domestic level of training under the floor.
If there is a basement, horizontal waterproofing is arranged at two levels: the first layer in the floor level of the basement, the second one is slightly higher than the level of the scene. In addition, the outer walls of the basement are protected by both vertical waterproofing, having it on the surface in contact with the soil. With dry soils (groundwater level below the floor of the basement or above it, but not more than 0.2 m) can be limited to the coating of hot bitumen twice. When the groundwater level is located from 0.2 to 0.8m above the floor of the water, from the outer side of the walls, an inlet insulation is used, consisting of three layers of rubberoid on bitumen mastic. This isolation from possible damage is protected by masonry from iron-iron (120 mm) on cement mortar and in the presence of aggressive groundwater layer 120-250mm mint of oily clay.
The insulation of the outer walls of the basement should be positioned by 0.5 m above the level of groundwater, as it is possible to vibration. The upper part of the wall above the inlet insulation is covered with two bitumen layers. The basement floor design must withstand quite large water pressure from below, therefore, on top of the horizontal insulation of the floor laid on concrete preparation, the load layer of the concrete or cement (asphalt) tie a thickness of at least 50mm is placed.
In the following meetings, who hope you do not miss, we will continue the conversation about other house designs. Good luck to you!
