Once again about the value of protective shutdown devices in the power supply of modern housing. Selected Overview of the Uzo presented in the Russian market.
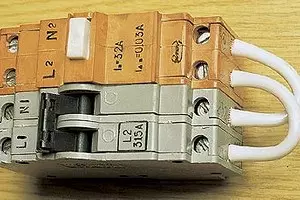





The rapid progress in the field of electrical equipment of modern housing and conservatism of its inhabitants, which is a contradiction between the achievements of engineering thought and those who are addressed!
Since the time of Peter the Great Nights of Technical Progress, whether it is a dutch furnace or urban sewage, they were introduced into the life of the Russians with the highest decrees and coercion. For the past centuries, the inertia of thinking to us, apparently, could not be overcome. This paradox was expressed and applied to the problem of introducing the RCD. Despite all the evidence of the tremendous benefit of this device-guaranteed protection against electroporation, a radical decline in the likelihood of fires, it is not voluntarily established by citizens by no means voluntarily, but at the direction above. By order of the Government of Moscow, since 1995, neither under construction, nor reconstructed housing can be commissioned without the installation of UzO and circuit breakers providing protection against overload and short circuit. NCMOs are often called differential defense devices, differential relays, differential modules, and the like.
So, the use of the UZO in a complex with circuit breakers minimizes the risk of human damage to the current and practically eliminates the possibility of electrical appliances and wiring in cases of overload or short circuit in the network.
Meanwhile, to explain to people the need for equipment of houses and institutions with protective devices of the new generation - the occupation is just as ungrateful as reading lectures on the harm of smoking. Everyone agrees with you, but they do not throw smoking. Similarly, while someone does not hit the current until the iron, a hairdryer, a food processor and the wires leading to them, nobody hurries the RCD. Truly, the wise of the saying, explaining the phenomenon of the mysterious Russian soul: "Thunder does not bother, the man will not cross."
However, the abundance of calls to the editors and written responses to the article on the UZO "do not fit," will kill! " ("The ideas of your home", 1998, N1) indicates that the word of the journalist still falls into the goal. For a more detailed conversation, briefly explain the principle of the Uzo's operation, which, as it turned out when preparing this article, is not clear to each electrician.
Functionally the Uzo can be defined as a high-speed protective switch that reacts to the differential current in the conductors applying electricity to the protected electrical installation.
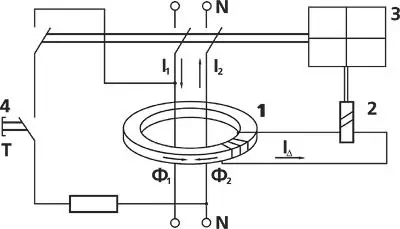
The structure of the UZO is formed from the following basic functional blocks (see. The "Structure of the RCD"):
- In UzO, a differential current transformer is used as a current sensor ( one).
- Threshold element ( 2. ) Performed on a sensitive magnetoelectric relay.
- Actuating mechanism ( 3. ) Consists of a spring drive with a high-current contact group.
- Testing chain, artificially creating differential current, is intended for periodic control of the serviceability of the device by pressing the "Test" button ( four).
When leakage current to Earth or a person's touch to the current-generating parts, the current balance in direct and reverse conductors, and therefore magnetic threads, is broken, a transformed differential current (nobalance current) appears in the secondary winding, which causes the threshold element ( 2. ) influencing the actuator ( 3. ). The actuator acting on the principle of the latch, the actuator actuates the spring drive of the contact group and the protected chain is de-energized.
In the electronic UzO, the functions of the threshold element and partially actuating mechanism performs an electronic circuit.
According to the estimates of energy specialists, the current need of Russians in the Uzo is 100 million. It is not by chance that electric devices are already becoming the most liquid goods in electrical stores. Punta, these are products of foreign production. However, it should not be at all that domestic protective devices are unreliable or uncompetitive in comparison with Western counterparts. The advertising capabilities of our manufacturers are much more modest than those of electrical giants like "Siemens", "ABB", "Schneider", "Legrand". Not always in favor of domestic products and their design. It is clearly not enough for regulatory and guidance materials for the use of UzO .
A serious problem is the absence of landmarks at the potential buyer of the UZO (ATO, as a rule, a person, thoroughly knowledgeable electrical engineering). Non-highly complex precision device. To give a qualified assessment of the conformity of the parameters of a specific device with the requirements of the standard on the Nepod R 50807-95 - only a few specialized laboratories can. The duration of operation of the UZO already installed in Russia is too small to draw conclusions about reliability indicators. Main parameters Device loading current - IN, nominal disconnecting differential current (leakage current) - IDN, nominal non-disconnecting differential current-IDNo, tripping time, operating voltage - un and some other indicators in the most part of the RCO approximately the same. Therefore, when buying has to be guided, first of all, information on reputation in the manufacturer's market. The quality of the product of the defense plant is traditionally higher than what is produced by an enterprise producing consumer goods. Abroad, this is usually large electrical concerns with which in terms of quality and reliability is unable to compete suppliers from Indochina.
Another important criterion when choosing a certificate device. And not "export", issued usually on a small batch of imported devices, and the certificate of the established form with a direct indication of the compliance of the products of the specified GOST. This is important, since recently there is an influx of dubious products: those who have shown in warehouses produced by companies that ceased to exist from GDR, Poland, China, Korea, India, etc.
For overseas products, the cost of the device is proportioned to their quality.
When choosing a UZO, it is necessary to consider the principle of operation of the device. There are two main categories of the UDO:
- dependent on the supply voltage - "electronic",
- independent of the supply voltage - "electromechanical".
The advantage of electromechanical circuits of their complete independence from oscillations and even the presence of voltage in the network. This is especially important, since the electrical networks often happen to break the zero wire, as a result of which the danger of electric shock increases: because a person suggests that there is no voltage in the network, and calmly touches the current parts. The use of electronic RCOs is advisable when a safety net is needed for security purposes, for example, in particularly dangerous, wet rooms. Has you can not buy a hairdryer, which in the fork is not built in the UZO, there it is determined by law. In fairness, we note that the letter of the Glavgosenergonadzor in the Russian Federation is recommended for use and electronic, and electromechanical RCDs that meet the requirements of current standards and having a certificate of conformity.
When choosing the Uzo, the following factors have the most important:
- Installation site UDO;
- RCD parameters: Rated load current, nominal differential disconnecting current, thermal resistance;
- scheme solutions for various grounding systems for feeding networks;
- Selecting a UDO type.
Due to the introduction of the power supply system with the third zero protective wire and the use of the RCD, in the old (two-wire) systems, when installing these devices, a clear separation of zero working and zero protective wires in the zone of the Uzo, i.e. The zero working wire should not connect to grounded installation elements.
Before entering the electrical installation with the UZO, it is recommended to measure the background leakage currents to the ground while simultaneously or sequentially turning on all electrical receivers. Of course, for this it is necessary to contact a specialized organization. Insulation damage is possible in phase, and in zero wires (at the same time, the RCO responds to leakage in both cases), however, when using single and three-phase circuit breakers in electrical installation without dismantling the circuit, it is impossible to find a leak from the zero wire by a sequential shutdown. Therefore, in the schemes of networks with a zero protective conductor, it is advisable to use two- and four-pole circuit breakers, swing both phase and zero wires.
For readers of our magazine, we make a selective overview of the UDOs presented in the Russian market that meet the requirements of the State Standard and the Glavgoseregonadzor.
Stavropol Plant "Signal" produces electronic "UZO-20". According to the MNIITEP at the beginning of 1997. It was installed about 45000 devices of this model. It should be borne in mind that they received numerous complaints of specialists and users due to numerous failures. The cost of UZO-20 is one of the lowest products for the electric facilities of this type.
Tekhopark-Center OJSC manufactures an ASTRO * UDO electromechanical device in the Austrian license. It is allowed for use in residential, public and industrial buildings, has a certificate of conformity. Astro * UZO retains performance with any oscillations and even in the absence of voltage on the network, for example, when the zero or phase conductors are broken.
The astro * RCO family has 9Modifications that differ from each other by the number of poles (two- and four-pole), parameters of the rated current (16, 25, 40 and 63a) and the nominal disconnecting current (30 and 100m). The service life of astro * UZO is at least 10 years, resource- 4000electric and 10000-dimeric cycles.
The cost of bipolar astro * Uzo modifications F11111- 372rub., F2211, F3211- 306rub., F3311-3212., F3311112, F3312, F4212 and F4312- from 450 to 560 rubles.
In OJSC "Research Institute of ProjectElectromontazh", based on a summary of more than 25 years of experience of the Institute in the field of electrical safety, an electronic UZO-2000 is developed and produced. Available in combination with a circuit breaker.
The peculiarity of this is the high ability to maintain performance with short-term (up to5set) voltage failures up to 50% of the nominal. This mode is possible with short circuits at the time of operation of the system ABR (automatic reserve input device). Switching wear resistance of the UDO-2000 - 20000 Cyclov. Cost - 210 rub.
As for the imported UZO, in this review, we note only the products of firms, long ago and seriously cooperating with Russian energy. They are intended to ensure the electrical safety of people and protection against fires of residential and office premises.
Well-proven firm "ABB" offers devices F360, F370, DS640 / DS650, DS652 and DS654. The average value of these products in the stores of the Group of companies "TFS" - 90u.E.
The French company "MERLIN-GERIN", which is part of the industrial group "Schneider", produces UzodpnnVigi, Vigic60, Viginc100, C60, NC100 or NC125. Their average price according to TFS Price List - 85U.E.
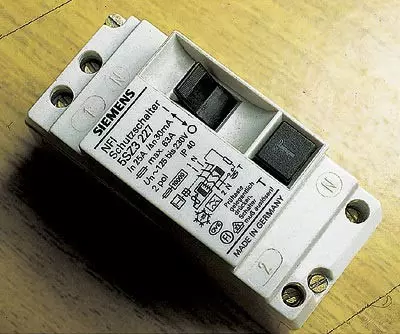
A wide selection of the UZO offers the "Siemens" concern. Dozens of dozens of devices whose variety can satisfy any customer requirements. The most popular model is a bipolar RCNFI5SZ3227. The cost of products "Siemens" is almost no different from the analogues of the above-mentioned firms.
The French firm "LEGRAND" supplies UDO type DX / D40, two- and four-pole. Their value in the stores of the TFS company - up to90u.
It is time to recall once again that it is also impossible to give a comparative characteristic of protective shutdown devices supplied to the Russian market as it is also impossible to make a "tabel about rank" manufacturers and suppliers of these devices in Russia. Want to see the compliance of the purchased Uzo or differential automaton required parameters? Calculate the characteristics of your device with similar to the UDO-2000 and for astro * UZO. If imported analogues are inferior to them, buy domestic products. If possible, advise with experts. As for the quality and reliability of devices, it is possible to rely on the reputation of their manufacturers and sellers. Preference should be given to specialized stores and electrical trading homes.
The editorial office of the journal thanks the staff of the Technical Department of Technopark-Center, General Director of JSC "Research Institute of ProjectElectromontazh" E.M.Feskovkova and the leading manager of the Electrotechnical Trading House "TFS Electrical Equipment" S.A. Ptashkin for help in the preparation of the article.
